answers to solutions day on
advertisement

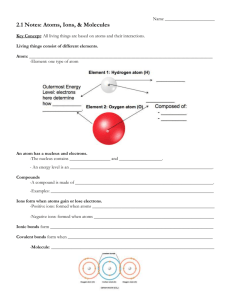
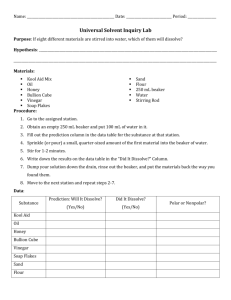
Section Review Answers – Solutions and Solubility Student Textbook page 289 1. solute and solvent 2. a) steel, bronze, brass b) methanol in water, vinegar c) air 6. Soluble indicates that a certain amount of a solute will dissolve in a given amount of solvent. Miscible refers to two liquids that will mix together in any amount. Immiscible refers to liquids that will not dissolve in each other. 7. An alloy is a mixture of two or more metals that have been melted and mixed together in some proportion and then allowed to solidify. Bronze, brass, and white gold are examples. An amalgam is an alloy of a lesser amount of liquid mercury in a greater amount of silver solvent. Dentists have used this combination to fill cavities. Today plastic solutes are dissolved in silver to perform the same function. 8. Ionic solids dissolve best in polar solvents such as water. Examples are KBr and NaCl. 10. Liquid A was the pure substance as it left no residue showing that it is composed of only one substance; liquid B was a solution containing solutes that did not evaporate but were left behind as a residue. 11. If you boil the pure substance, nothing will remain. If you boil the miscible liquids, one liquid will evaporate, while the other will remain. If you boil the solution, only a solid will remain. 12. a) Oil is a nonpolar substance that does not dissolve in seawater, a polar solvent. c) Wave action dispersed the oil. Prince William Sound has less wave action than the open sea, and the lesser wave action slowed the progress of the oil. 13. Food colouring would be a nonpolar molecule since it is added to foods like candies, ice cream and icing which will all have high fat content. Fat molecules are nonpolar and will be able to dissolve the food colouring as a result. Pg. 325 3. Liquids that dissolve in each other are said to be miscible. The solvent is the one found in the larger proportion. In this case, the solvent is turpentine. Pg. 301. 2. When water vaporizes it is the intermolecular attractions that are broken. Intramolecular bonds still hold the water molecules together. 3. a) More solid dissolves at higher temperatures. b) Less gas dissolves at higher temperatures. Pg. 325-327 4. Water is a polar molecule. The negative and positive regions of the water molecule can surround and solvate any molecule that also has negative and positive regions. 5. Electrolytes contain ions. Electric conduction requires the movement of electrons, and this is facilitated by aqueous ions. Nonelectrolytes contain no ions and cannot conduct electrons, even if they do dissolve in solution. 7. “Like dissolves like” means that substances having a similar type of bonding will dissolve in each other. Polar solvents dissolve polar solutes, and nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes. 8. Factors that affect rate of dissolving are temperature, agitation, and size of the particles. 9. a) soluble ionic solid (polar) b) insoluble covalent molecule (nonpolar) c) soluble ionic solid (polar) d) insoluble hydrocarbon (nonpolar) 10. Napthalene is soluble in benzene, while sodium fluoride is not these two molecules have similar nonpolar structures. Ethanol will be slightly soluble in benzene. Its polar functional group will not mix with the benzene, but the hydrocarbon end of the molecule will. 34. Since vitamin A is a fat soluble vitamin, it would require fat reserves in the body of the children in order to accumulate. As these children do not have much fat in their diet, they probably would not have any fat reserves to store this vitamin. As a result, even if they obtain the vitamin in their food they are not able to keep it in their bodies.