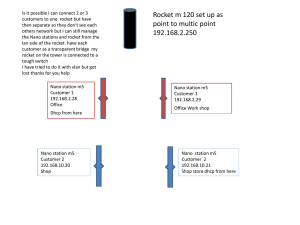
Subject Code/ Name: CY6151 / Engineering Chemistry
advertisement

Subject Code/ Name: CY6151 / Engineering Chemistry - I DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY UNIT – V Nano Chemistry PART – A 1. What is meant by Nanochemistry? (A.U. Dec 2014)-(2 times) It is defined as the study of phenomena and manipulation of materials at atomic, molecular and macromolecular scales. 2. What are nanoparticles? Nanoparticles (NPs) are solid particles or particulate dispersions with a size in the range between 1 and 100 nm. Example: ZnO,CdS,SiO2 3. What are nanomaterials? Nanomaterials are the materials having components with size less than 100 nm at least in one dimension. Nanomaterials, in zero dimensions are quantum dots. 4. Distinguish between bulk particles and nanoparticles. (A.U. June 2013)-(3 times) Nano-particles Bulk particles Size is less than 100nm Size is larger in micron size Collection of few molecules Collection of thousands of molecules Surface area is more Surface area is less Strength, hardness are more Strength, hardness are less 5. What is CVD? CVD is Chemical Vapour Deposition. It is a process of chemically reacting a volatile compound of a material with other gases, to produce a non-volatile solid that deposits automatically. 6. Define nano-wires. Nano wire is a material having an aspect ratio ie., length to width ratio greater than 20. Nano-wires are also referred to as “quantum wires”. 7. What are nano rods? (A.U. Dec 2014) - (2 times) Nano-rod is a material having an aspect ratio in the range 1 to 20 with short dimension of the material being 10-100 nm. 8. What are nano clusters? (A.U. Dec 2012) Nano clusters constitute an intermediate state of matter between molecules and bulk materials. These are fine aggregates of atoms (or) molecules. 9. What is magic number? It is the number of atoms in the clusters of critical sizes with higher stability. Different types of clusters can be distinguished by the nature of the force between the atoms. Clusters containing transition metal atoms have unique chemical, electronic and magnetic properties, which vary with the number of constituent atoms, the type of element and the charge on the cluster. 10. How are nanoparticles prepared by precipitation techniques? (A.U. June 2013) Nanoparticles are synthesized by the precipitation reaction between the reactants in presence of water soluble inorganic stabilizing agent. 11. What are carbon nanotubes. (A.U. Jan 2014) Subject Code/ Name: CY6151 / Engineering Chemistry - I Carbon nanotubes are allotropes of carbon with a nanostructure having a length-todiameter ratio greater than 1,000,000. 12. What is laser ablation? (A.U. Jan 2014) In laser ablation, high-power laser pulse is used to evaporate the matter from the target. The stoichiometry of the material is preserved in the interaction. The total mass ablated from the target per laser pulse is referred to as the ablation rate. 13. Mention some characteristic properties of nano materials. (A.U. Jan 2014) 1. Nano materials are very strong and withstand extreme strain and tension. 2. It possesses very good electrical properties and thermal conductivity. 14. Name some physical methods of synthesizing nano-materials. Laser ablation Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) Electro-deposition 15. Mention some important applications of nano-wires. Enhancing mechanical properties of composites. To prepare active electronic components such as p–n junction and logic gates. Important role in future of digital computing. 16. List any four nano-materials. Carbon nano tubes Nano wire Quantum dots Dendrimers 17. Mention some uses of CNTs. Battery technology and used as catalyst in industries. Light weight shielding materials for protecting electronic equipments. Drug delivery Used as composites. 18. What is the basic principle involved in solvothermal synthesis of nano-materials. Solvothermal synthesis involves the use of solvent under high temperature (between o 100 C to 1000oC) and moderate to high pressure (1 atm to 10,000 atm) that facilitate the interaction of precursors during synthesis. 19. Mention some characteristics of nano wires. One dimensional material. Nano wire is less than that of the corresponding bulk materials. It exhibits distinct optical, chemical, thermal and electrical properties due to this large surface area. 20. Define Nanotechnology. It is defined as the design, characterization, production and applications of structures, systems and devices by controlling size and shape at 10-9 m scale or the single-atomic level. PART – B 1. Describe the preparation of any two methods of carbon nanotubes. (A.U. Dec 2014)-(2 times) 2. Distinguish molecules, nano particles and bulk materials. (A.U. Jan 2014) 3. Discuss various types of synthesis involved in the preparation nanomaterials. (A.U. Jan 2014) Subject Code/ Name: CY6151 / Engineering Chemistry - I 4. Explain (1) Nano cluster (2) Nano wire with examples. (A.U. Jan 2014) 5. Describe the synthesis of nano materials by precipitation and thermolysis methods. (A.U. Dec 2012) 6. Explain about the size dependent properties of nano materials. (A.U. Dec 2012) 7. Discuss any four applications in the nanotechnology. (A.U. Dec 2014)-(2 times) 8. Write notes on properties of nano particles. (A.U. Dec 2012) 9. Describe the hydrothermal and electrodeposition techniques for the synthesis of nano particles. (A.U. June 2013) 10. Discuss the CVD and laser ablation techniques for the synthesis of nano particles. (A.U. Dec 2014) –(2 times) 11. Write an informative note on the properties and applications of nano particles. (A.U. June 2013) 12. Define the terms: nano rods, nano tubes, nano wires and nano clusters. (A.U. June 2013) 13. What are nano materials? Discuss the types of carbon nano tubes and their applications. (A.U. June 2012) 14. How are carbon nano tubes synthesized? What are its applications? (A.U. Dec 2011) 15. Explain briefly the applications of nano materials. ************* (A.U. Jan 2009)