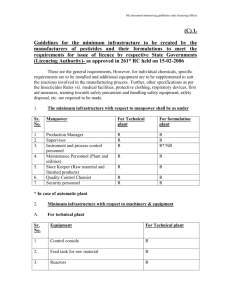
Procedure for - LSU Fire and Emergency Training Institute
advertisement

Issue Date: South Adams County Fire Department Rev No.: June 29, 2002 Standard Operating Guideline: 1 NA Document Title: Gasoline Tank Truck Emergencies – Guidelines & Procedures 1. PURPOSE To provide emergency response personnel with information, instructions, and training as required by NFPA 472. 2. LEARNING OBJECTIVES 2.1 COMMON TRAINING OBJECTIVES Describe the basic design and construction features of the MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank truck. Explain the design, construction, and operation of each of the following safety devices which may be found on a MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank truck: Internal safety valve or external valve with accident protection, including method of activation (air, cable) Shear-type breakaway piping Fusible links or nut assemblies Emergency remote shut-off device Pressure and vacuum relief protection devices Dome cover design Vapor emission controls Overturn protection Describe the normal methods of loading and unloading the MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank, including: Top loading Bottom loading Vapor recovery system List and describe at least three safety features that are installed on product loading racks and/or cargo tank trucks in order to prevent overfills during transfer operations. Given a MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank involved in an emergency, identify the factors to be evaluated as part of the damage assessment process, including: 1 Type of cargo tank (MC or DOT specification) Number of compartments Type of tank metal (e.g., aluminum vs. stainless steel) Nature of the emergency (e.g., rollover, vehicle accident, struck by object, etc.) Container stress applied to the cargo tank Type and nature of tank damage (e.g., puncture, dome cover leak, valve failure, etc.) Amount of product released and remaining in cargo tank Given a MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank, identify and describe the likely methods of container breach and release: Given an incident involving an MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank truck, describe the methods, procedures, risks, safety precautions, and equipment required to implement spill and leak control procedures. Describe the methods for containing the following leaks on an MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank: Puncture Irregular-shaped hole Split or tear Dome cover leak Valves and piping Pressure relief devices (e.g., vents, burst disc, etc.) Identify the methods and precautions used when controlling a fire involving an MC-306/DOT-406 aluminum shell cargo tank. Describe the methods and procedures for the grounding and bonding of flammable liquids from an MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank, including: Selection of proper equipment Sequence of grounding and bonding connections Proper testing of grounding and bonding connections Describe the safe and proper procedures for the following methods of product removal and transfer from an MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank: Remove via drilling Removal via unloading lines Removal via vapor recovery lines Removal via internal safety valve 2 Dome funnel (i.e., Canadian Bag) Describe the methods and procedures for the safe removal and transfer of product from a MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank truck, including the use of: Portable pumps (air, electrical, gasoline/diesel) Vehicles with power-take-off (PTO)-driven pumps Vacuum trucks Given an overturned MC-306/DOT-406 cargo tank, describe the factors to be evaluated for uprighting, including: 2.2 Type of cargo tank and material of construction Condition and weight of the cargo tank Type and nature of stress applied to the cargo tank Preferred lifting points Selection of lifting straps and/or air bags Lifting capabilities of wreckers and cranes Site safety precautions SITE SPECIFIC TRAINING OBJECTIVES As Required 3. EMPLOYEE INFORMATION 3.1. Obtain a copy of the Textbook "Gasoline Tank Truck Emergencies, Guidelines and Procedures 2nd Edition". 4. TRAINER'S INFORMATION 4.1. Materials Needed for training 4.1.1. Textbook "Gasoline Tank Truck Emergencies, Guidelines and Procedures 2nd Edition" 4.1.2. Video "Incidents Involving Fuel Tank Trucks”, Action Training Systems, Inc. 4.1.3. PowerPoint Presentation " Gasoline Tank Truck Emergencies" 4.2. Practical Exercises 4.2.1. As Required 5. VIDEO INFORMATION “Incidents Involving Fuel Tank Trucks is the fourth program in the Hazardous Materials Containment Series. This program presents information about tank trucks and offers procedures to follow in the event of an emergency involving a fuel tank truck. The program is divided into four training objectives: 1. To describe the structure and safety features of fuel tank trucks - 3 The tank truck designated as “Motor Carrier 306” (or MC306) by the U. S. Department of Transportation is a common sight on most highways in North America. These trucks transport millions of gallons of low-pressure fuels to gas stations, and other end-user fuel distribution points. This program examines the structure of MC306 tank trucks, and gives special attention to the four types of safety features: pressure relief devices, shutoff valves, overturn protection, and valve protection devices. 2. To present the four types of incidents that can occur There are four types of incidents in which an MC306 could be involved: A spill without ignition, a spill with ignition, an overturned truck, or a fire in a truck part, such as a tire or brake pad. In the program, you will see examples of different types of fuel tank truck emergencies and will learn the unique response tactics for each type. 3. To demonstrate basic procedures for controlling leaks in low pressure tank trucks The program shows responders how to slow or stop leaks in the tank shell, as well as, leaks that occur in pipes, valves, caps, and other fittings. The leak control procedures presented are designed to minimize the loss of product which will result in less imminent danger and less environmental clean-up. 4. To show safety rules for responding to incidents involving fuel tank trucks Incidents involving fuel tank trucks can be especially dangerous because of the potential destructive power of the product, and because these incidents often occur on busy public roadways making scene control a difficult task. The program stresses proper hazardous materials control operations. Remember, procedures vary from department to department. This program presents suggestions for responding to incidents involving fuel tank trucks. Always follow your department’s standard operating procedures for responding to hazardous materials incidents in your jurisdiction. Suggested Review Questions 1. Describe the physical features of the MC306 2. What types of hazardous materials can be carried in MC306 trucks: 3. Name three tank shell materials that are used on MC306’s. What is the most common tank shell material for fuel tank trucks? 4. What often happens to aluminum tanks that are impinged by fire? 5. How much vapor space must be left in each compartment when a fuel tank truck is filled? Why is it necessary? 6. How can you determine the number of compartments in a fuel truck? 7. What are the types of safety devices on fuel tank trucks? 8. Where would you find the secondary control for the tank shut-off valves? 4 9. Name the four types of incidents involving fuel tank trucks. 10. What are the four steps that you should take immediately at all incidents involving fuel tank trucks? 11. How should you disconnect the truck’s battery? 12. What must always be finished before an overturned fuel tank truck is righted? 13. What two materials could you use to slow or stop a small dripping leak in a pipe? 14. Why is it often difficult to maintain scene security in fuel tank truck incidents? 15. When is a “let burn” decision appropriate? 16. What is “bonding” and “grounding”? Answers can be found in the video program. 5 GUIDE CHECK SHEET FOR TANK TRUCK RESPONSE PRELOAD INSPECTION Check capacity of trailer for contents to be transferred. Check inspection of empty trailer – gaskets, inspection, construction, equipment, safety items. Compatibility of product to transfer equipment (MC 307, SS, Alum, etc.). Check hose and fittings. Tie or tape all connections. Chock and ground equipment. Proper tags and placards available for product. Check suction and discharge lines on pump. Type of transfer going to be made (open or closed dome). Type of protective gear needed for this transfer. Check arrangements for venting of tank truck or tank car used in transfer. DURING TRANSFERS Check for leaks. Drip pans or pads at connections (hose and pump). Monitor filling levels - eliminate all possible vapors. Eliminate all possible contamination to product during transfer. All hose tied securely to prevent movement. Monitor damaged equipment for movement or leaks that may occur as product is being transferred. Position of equipment may change as loads increase or decrease (accident site may vary with each incident). POST TRANSFER After transfer is complete, walk each hose three times to eliminate all possible product from hose before breaking connections. 6 Secure all closures, seal dome and outlet areas Proper tags and placards are applied to both vehicles (reverse placards on tank cars – you do not reverse tank trucks). Fill out a Bill of Lading for the loaded trailer. Check Bill of Lading on empty vehicle for corrected information All collected material properly disposed of or transportation arrangements have been made. Protective equipment used in transfer have been decontaminated or properly contained for later cleanup and storage. 7