MODULE 8: HOW IS BANGLADESH`S TEMPERATURE CHANGING
advertisement

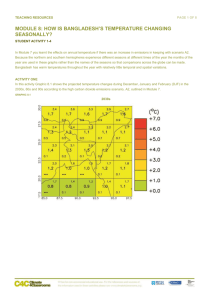
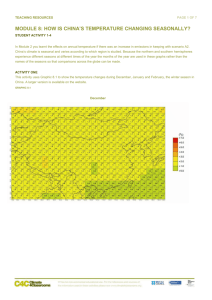
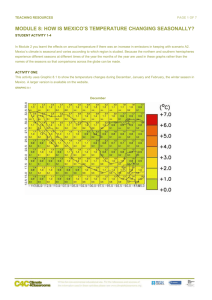
TEACHING RESOURCES PAGE 1 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 In Module 7 you learnt the effects on annual temperature if there was an increase in emissions in keeping with scenario A2. Argentina’s climate is seasonal and varies according to which region is studied. Because the northern and southern hemispheres experience different seasons at different times of the year the months of the year are used in these graphs rather than the names of the seasons so that comparisons across the globe can be made. ACTIVITY ONE In this activity Graphic 8.1 shows the projected temperature changes during December, January and February (DJF) in the 2030s, 60s and 90s according to the high carbon dioxide emissions scenario, A2, outlined in Module 7. GRAPHIC 8.1 2030s PAGE 2 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? | STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 2060s 2090s PAGE 3 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? | STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 All values are temperature anomalies – the variation compared to average temperatures from 1970 to 1999. Areas shaded deep red will be 6- 7°C hotter than average temperatures from 1970 to 1999, whereas, areas shaded green will be the same as the 1970 – 1999 average. The tiny numbers in the centre of each grid box is the average expected temperature; numbers in the upper and lower corners give the maximum and minimum DJF mean temperatures. All the temperatures are in degrees Celsius. The numbers along the y axis are Latitude and the numbers on the x axis are Longitude This information applies to all the graphics in this unit. 1. Which areas are most affected by the temperature changes? ACTIVITY TWO This activity uses Graphic 8.2 to show the temperature changes during March, April and May (MAM) in 2030s, 60s and 90s according the high carbon dioxide emissions scenario A2. See the information about the key to these graphics in Activity one. GRAPHIC 8.2 2030s PAGE 4 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? | STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 2060s 2090s 1. What is the temperature increase for each decade at each of the locations studied in Unit 1? PAGE 5 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? | STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 ACTIVITY THREE This exercise uses Graphic 8.3 to look at the changes during June, July and August (JAJ) in the 2030s, 60s and 90s according the high carbon dioxide emissions scenario A2. See the information about the key to these graphics in Activity one. .GRAPHIC 8.3 2030s 2060s PAGE 6 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? | STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 2090s 1. Describe what is happening to the temperatures at each of the locations from Module 6? PAGE 7 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? | STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 ACTIVITY FOUR This exercise uses Graphic 8.4 to look at the changes during September, October and November (SON) in the 2030s, 60s and 90s according to the high carbon dioxide emissions scenario A2. See the information about the key to these graphics in Activity one. GRAPHIC 8.4 2030s 2060s PAGE 8 OF 8 MODULE 8: HOW IS ARGENTINA’S TEMPERATURE CHANGING SEASONALLY? | STUDENT ACTIVITY 1-4 2090s 1. Describe what is happening at each of the eight locations studied in Module 6? 2. Look at the graphics for the four seasons. Which months have the least projected temperature variation? PERSONAL ACTIVITY Have you noticed that the water in the sea or a lake seems much cooler than the land in spring and warmer in autumn?