Supplementary Material Anterior insular cortex is necessary for
advertisement

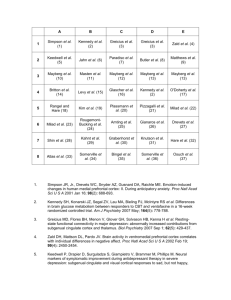
Supplementary Material Anterior insular cortex is necessary for empathetic pain perception Xiaosi Gu1-3*, Zhixian Gao4, Xingchao Wang4, Xun Liu1,5, Robert T. Knight7,8, Patrick R. Hof 2,3, and Jin Fan1-3,6 1 Department of Psychiatry, 2Fishberg Department of Neuroscience, and 3Friedman Brain Institute, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, New York 10029 4 Department of Neurosurgery, Beijing Tiantan Hospital of Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050, China 5 Key Laboratory of Behavioral Science, Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China 6 Department of Psychology, Queens College, The City University of New York, Flushing, NY 11367 7 Helen Willis Neuroscience Institute and 8Department of Psychology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 *Current affiliation: Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute, Roanoke, VA 24016 This PDF file includes Supplementary Table 1 & 2 Supplementary Fig 1 Supplementary Table 1 Demographics of included studies in the meta-analysis. Reference # of subjects Task (Akitsuki and Decety, 2009) 26 Valence rating (Botvinick et al., 2005) 12 Observation (Cheetham et al., 2009) 16 Button press (Costantini et al., 2008) 13 Observation (Decety et al., 2010) 22 Observation (Gu and Han, 2007) 12 Valence rating (Gu et al., 2010) 18 Valence rating (Han et al., 2009) 24 Valence rating (Jackson et al., 2005) 15 Valence rating (Jackson et al., 2006) 34 Valence rating (King et al., 2006) 12 Empathetic decision making (Lamm et al., 2007) 17 Perspective taking (Lamm et al., 2007) 18 Valence rating (Lamm and Decety, 2008) 18 Valence rating (Lamm et al., 2010) 24 Valence rating (Mathur et al., 2010) 28 Valence rating (Morrison et al., 2004) 11 Observation (Morrison et al., 2007) (Morrison and Downing, 2007) (Ochsner et al., 2008) 14 Observation 16 Hit/miss judgment 13 Observation (Olsson et al., 2007) (Osborn and Derbyshire, 2010) (Saarela et al., 2007) 14 Observation 15 Valence rating 12 Observation (Singer et al., 2004) 16 Observation (Singer et al., 2006) 16 Observation (Ushida et al., 2008) 15 Observation (Xu et al., 2009) 33 Valence rating (Zaki et al., 2007) 13 Observation Supplementary Table 2. Brain regions involved in empathetic pain perception Voxel ALE x y z Area Label 2405 0.084 -40 14 0 L anterior insula 0.041 -30 -4 -14 L amygdala 0.036 -16 -8 -8 L globus pallidus 0.033 -38 -2 4 L middle-posterior insula 0.029 -48 8 8 44 L inferior frontal gyrus 0.028 -46 0 24 6 L premotor area 0.026 -38 -2 16 L middle-posterior insula 2298 0.084 40 20 -4 47 R inferior frontal gyrus 0.032 46 28 6 45 R inferior frontal gyrus 0.032 26 -2 -14 R amygdala 1999 0.075 -2 24 32 32 L anterior cingulate cortex 0.057 0 -2 36 24 Anterior cingulate cortex 0.050 -8 6 40 32 L anterior cingulate cortex 0.031 0 10 54 6 L supplementary motor area 506 0.053 52 -30 34 2 R somatosensory cortex 408 0.047 -54 -28 34 40 L inferior parietal lobule 0.020 -44 -38 38 40 L inferior parietal lobule 302 0.033 12 -6 12 R thalamus 154 0.041 -2 42 18 9 L medial prefrontal cortex 150 0.028 -42 -68 -8 19 L fusiform gyrus 0.027 -44 -72 6 37 L inferior temporal gyrus 143 0.038 -38 -48 50 40 L inferior parietal lobule 131 0.040 36 -4 14 R middle-posterior insula 117 0.027 48 4 30 6 R premotor area 0.024 44 2 42 6 R premotor area 55 0.026 -10 -12 6 L thalamus 40 0.028 30 -82 2 19 R middle occipital gyrus 35 0.027 -30 -64 -26 L cerebellum PFDR < 0.05, k > 30, voxel size = 2x2x2 mm. L, left; R, right. A NC BDC AIC ACC Overall accuracy 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 BD C AI C 1 AI C 2 AI C3 AC C 1 AC C 2 AC C 3 BD C N NC 0.0 B Overall RT (ms) 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 2 C 3 AC C 1 AC C 2 AC C 3 AI C AI 1 C AI C 0 Supplementary Fig. 1 (A) Overall response accuracy across all experimental conditions. AIC patients had marginally lower accuracy than NC (P = 0.05) and BDC (P = 0.06). ACC patients did not show statistical alternation compared to NC and BDC (both Ps > 0.05). (B) Overall RT across all experimental conditions. There is no statistically significant difference between AIC or ACC patients and controls (all Ps > 0.05). Error bars (where relevant) represent 95% confidence interval. Supplementary References Akitsuki Y, Decety J. Social context and perceived agency affects empathy for pain: an event-related fMRI investigation. Neuroimage. 2009 Aug 15;47(2):722-34. Botvinick M, Jha AP, Bylsma LM, Fabian SA, Solomon PE, Prkachin KM. Viewing facial expressions of pain engages cortical areas involved in the direct experience of pain. Neuroimage. 2005 Mar;25(1):312-9. Cheetham M, Pedroni AF, Antley A, Slater M, Jancke L. Virtual milgram: empathic concern or personal distress? Evidence from functional MRI and dispositional measures. Front Hum Neurosci. 2009;3:29. Costantini M, Galati G, Romani GL, Aglioti SM. Empathic neural reactivity to noxious stimuli delivered to body parts and non-corporeal objects. Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Sep;28(6):1222-30. Decety J, Echols S, Correll J. The blame game: the effect of responsibility and social stigma on empathy for pain. J Cogn Neurosci. 2010 May;22(5):985-97. Gu X, Han S. Attention and reality constraints on the neural processes of empathy for pain. Neuroimage. 2007 May 15;36(1):256-67. Gu X, Liu X, Guise KG, Naidich TP, Hof PR, Fan J. Functional dissociation of the frontoinsular and anterior cingulate cortices in empathy for pain. J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 10;30(10):3739-44. Han S, Gu X, Mao L, Ge J, Wang G, Ma Y. Neural substrates of self-referential processing in Chinese Buddhists. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2009 Jun;5(2-3):332-9. Jackson PL, Brunet E, Meltzoff AN, Decety J. Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44(5):752-61. Jackson PL, Meltzoff AN, Decety J. How do we perceive the pain of others? A window into the neural processes involved in empathy. Neuroimage. 2005 Feb 1;24(3):771-9. King JA, Blair RJ, Mitchell DG, Dolan RJ, Burgess N. Doing the right thing: a common neural circuit for appropriate violent or compassionate behavior. Neuroimage. 2006 Apr 15;30(3):1069-76. Lamm C, Batson CD, Decety J. The neural substrate of human empathy: effects of perspectivetaking and cognitive appraisal. J Cogn Neurosci. 2007 Jan;19(1):42-58. Lamm C, Decety J. Is the extrastriate body area (EBA) sensitive to the perception of pain in others? Cereb Cortex. 2008 Oct;18(10):2369-73. Lamm C, Meltzoff AN, Decety J. How do we empathize with someone who is not like us? A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Cogn Neurosci. 2010 Feb;22(2):362-76. Lamm C, Nusbaum HC, Meltzoff AN, Decety J. What are you feeling? Using functional magnetic resonance imaging to assess the modulation of sensory and affective responses during empathy for pain. PLoS ONE. 2007;2(12):e1292. Mathur VA, Harada T, Lipke T, Chiao JY. Neural basis of extraordinary empathy and altruistic motivation. Neuroimage. 2010 Jul 15;51(4):1468-75. Morrison I, Downing PE. Organization of felt and seen pain responses in anterior cingulate cortex. Neuroimage. 2007 Aug 15;37(2):642-51. Morrison I, Lloyd D, di Pellegrino G, Roberts N. Vicarious responses to pain in anterior cingulate cortex: is empathy a multisensory issue? Cognitive, affective & behavioral neuroscience. 2004 Jun;4(2):270-8. Morrison I, Peelen MV, Downing PE. The sight of others' pain modulates motor processing in human cingulate cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2007 Sep;17(9):2214-22. Ochsner KN, Zaki J, Hanelin J, Ludlow DH, Knierim K, Ramachandran T, et al. Your pain or mine? Common and distinct neural systems supporting the perception of pain in self and other. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2008 Jun;3(2):144-60. Olsson A, Nearing KI, Phelps EA. Learning fears by observing others: the neural systems of social fear transmission. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2007 Mar;2(1):3-11. Osborn J, Derbyshire SW. Pain sensation evoked by observing injury in others. Pain. 2010 Feb;148(2):268-74. Saarela MV, Hlushchuk Y, Williams AC, Schurmann M, Kalso E, Hari R. The compassionate brain: humans detect intensity of pain from another's face. Cereb Cortex. 2007 Jan;17(1):230-7. Singer T, Seymour B, O'Doherty J, Kaube H, Dolan RJ, Frith CD. Empathy for pain involves the affective but not sensory components of pain. Science. 2004 Feb 20;303(5661):1157-62. Singer T, Seymour B, O'Doherty JP, Stephan KE, Dolan RJ, Frith CD. Empathic neural responses are modulated by the perceived fairness of others. Nature. 2006 Jan 26;439(7075):466-9. Ushida T, Ikemoto T, Tanaka S, Shinozaki J, Taniguchi S, Murata Y, et al. Virtual needle pain stimuli activates cortical representation of emotions in normal volunteers. Neurosci Lett. 2008 Jul 4;439(1):7-12. Xu X, Zuo X, Wang X, Han S. Do you feel my pain? Racial group membership modulates empathic neural responses. J Neurosci. 2009 Jul 1;29(26):8525-9. Zaki J, Ochsner KN, Hanelin J, Wager TD, Mackey SC. Different circuits for different pain: Patterns of functional connectivity reveal distinct networks for processing pain in self and others. Social neuroscience. 2007;2(3-4):276-91.