Questions for 360 Teacher Assessments
advertisement

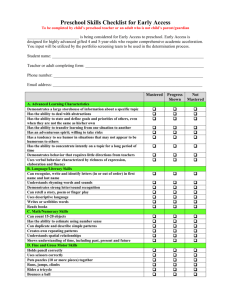
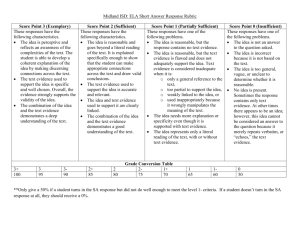
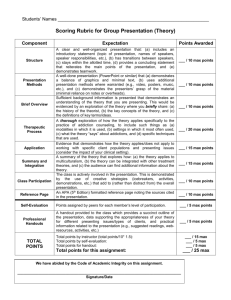
360 Degree Teacher Assessment Competencies and Questions ©Educational Impact 2007 360 Degree Teacher Assessment Responses Below is a list of the questions that appear in the Educational Impact 360 Degree Teacher Assessment. The questions are connected with 38 teacher competencies that were developed using the Danielson framework and other state teaching standards Responses to all Competency questions are: In depth knowledge/ very capable Considerable knowledge / capable Basis knowledge / somewhat capable Little knowledge / not very capable No evidence of knowledge / incapable Each Competency question also requires that the respondent answer the following question: How important is this competency for the success in this person’s position? Mission Critical Very Important Somewhat useful / nice to have Less Important Not Important Questions for 360 Degree Teacher Assessment (There are three different types of competencies) Instructional Competencies 1. Content Knowledge Displays extensive content knowledge; understands the central concepts of the discipline and is able to create learning experiences that make the subject matter meaningful for all students 2. Establishing Instructional Goals Establishes appropriate instructional goals for each lesson; instructional goals are capable of assessment and clearly align with curriculum framework and standards; teacher solicits information about students’ experiences, learning behaviors, and progress from former teachers and parents and considers these inputs in formulating appropriate instructional goals. 3. Creating Learning Activities Uses learning activities that are highly relevant to the students and the instructional goals; activities emphasize “problem based learning” and are designed to encourage student choice, initiative and higher level thinking. Learning activities include both group and individual interaction 4. Instructional Materials and Resources Demonstrates the ability to evaluate the resources and curriculum materials for appropriateness; uses materials and resources that support the instructional goals and engage the student in meaningful learning. 5. Engages Students in Learning Demonstrates the ability to conduct classroom lessons that include discussions that actively engage the students in their own learning; students formulate questions and make significant contributions to the classroom discussion. 6. Structure and Pacing Demonstrates the ability to conduct classroom lessons that have a clearly defined structure around which learning activities are organized; pacing of lessons is appropriate for all students; students do not feel rushed in their work, nor does time drag while students are completing their assignments 7. Assessment Selects, constructs, and uses assessments that are appropriate for measuring all instructional goals and learning outcomes; appropriate assessment types (i.e. standardized tests, peer and student self assessments, surveys, performance tasks, interviews, student work, teacher made tests, etc) are selected based on the learning outcomes. 8. Differentiated Instruction Is effective in differentiating instruction; can create assignments and learning activities to meet the needs of diverse students; can assist in the design of instruction that meets the needs of students with varying learning skills. 9. Special Needs Students / Differentiated Instruction Understands the unique requirements of special needs students; effectively plans for their inclusion in the classroom; is effective in differentiating instruction, creating assignments and learning activities to meet the needs of diverse student groups; can assist in the design of instruction that meets the needs of students with varying learning skills, including gifted students 10.Technology Integration Has a good understanding of how to use technology; whenever appropriate integrates the use of technology into classroom lessons, assignments and student learning; encourages students to use technology for problem solving; uses a variety of media and communication tools to enrich learning opportunities 11.Classroom Management Standards of conduct are clear to all students; monitoring by teacher is subtle and preventative. The classroom is arranged purposefully for learning activities; routines for handling materials and supplies are seamless; transitions are seamless; resources are equally accessible to all students 12.Brain Based Instruction Demonstrates knowledge of brain based research and how it applies to student learning; adjusts instruction to accommodate different learning styles (i.e. Auditory, Visual and Kinesthetic learners). 13.Intervening with Struggling Students Actively uses comprehension checks, assessment, and other instructional strategies to identify struggling students; using an extensive repertoire of strategies, persists in seeking alternative approaches for students who need help. Where appropriate, seeks additional assistance from other teachers and/or special education specialists. 14.Data Utilization Demonstrates knowledge of how to use student data (test results, observations, student work, etc) to drive instruction; is able to measure student performance and evaluate the results based on the data - then make thoughtful and accurate assessments of ones own teaching and instruction; has demonstrated the flexibility to make changes to instruction, learning activities, and lesson plans based on the ongoing evaluation of student data 15.Providing Student Feedback Feedback to students is consistently provided in a timely manner and is pertinent to the ongoing instruction or learning activity; encourages students to make prompt use of the feedback in their learning. 16.Using Graphic Organizers and Visual Tools Demonstrates knowledge of all types of graphic organizer and visual tools; understands their application and which visual tools are appropriate for specific situations; actively integrates visual tools and graphic organizers into classroom instruction to enhance student understanding; Encourages students to use visual tools to organize their thinking and comprehension. 17.Teaching “English as a Second Language” students Demonstrates knowledge of specific instructional strategies needed to teach ESL students; uses extra-linguistic cues, sheltered lessons, linguistic modifications, comprehension checks and cooperative learning to effectively provide instruction to the ESL students. 18.Creating Opportunities for Self Directed Learning Provides opportunities for students to assume responsibility for their own learning; students are responsible for identifying and choosing self directed learning opportunities that are relevant to them. Makes self directed learning available to students. 19.Preventing Student Cheating Demonstrates knowledge of student cheating techniques; actively employs assessment and classroom strategies to prevent cheating; is aware of the opportunities for plagiarism made available via the internet. Clearly establishes and communicates polices and penalties for students who engaged in academic dishonesty. 20.Teaching AD/HD Students Demonstrates the ability to recognize the signs that a student has AD/HD; is able to employ specific instructional strategies geared toward teaching AD/HD students: has a working knowledge of the prescribed treatments for AD/HD including both pharmacological and behavioral approaches 21.Interdisciplinary Approaches Demonstrates the ability to create lessons and learning activities in multiple disciplines that link together; when appropriate, works with other teachers to maximize interdisciplinary opportunities Interpersonal Competencies 22.Teacher / Student Interaction Demonstrates genuine caring and respect for individual students; maintains a positive learning environment that is conducive to learning and open communication; student’s exhibit respect for teacher; 23.Managing Defiant Students Demonstrates the ability to deal effectively with disruptive students; is not afraid to deal with disruptive students head on; willing to take a tough stance with a disruptive student, if necessary. 24.Enthusiasm Conveys genuine enthusiasm for the subject being taught; encourages students to actively participate and take pride in their work. Enjoys working hard; is action oriented and full of energy for the day to day job of being a school teacher 25.Communicating Demonstrates the ability to provide clear directions, instructions and explanations to students; communications contain an appropriate level of detail; teacher is expressive with well chosen vocabulary that is understood by all students. 26.Dealing with Parents Frequently provides parents with information about instructional programs and their child’s academic progress; engages with parents to collaboratively encourage student learning; is not afraid to involve parents in decision making when necessary; makes optimum use of technology to improve communication with parents 27.Collaboration with Colleagues Demonstrates the ability to effectively work with school faculty members and school administrators; can work through complex situations that involve collaboration with other faculty members; uses diplomacy and tact; is open to suggestions when appropriate; can represent his/her own interest yet be fair to others involved in the process. 28.Resolving Student Conflict Is effective in resolving student conflicts and disagreements; can hammer out tough agreements and settle disputes equitably; can find common ground and get cooperation; acts fairly and doesn’t give preferential treatment when reaching a resolution 29.Student Motivation Effectively encourages and motivates students to reach their potential; creates a climate where each student feels that their work is important; can access each student’s “hot button” to get the best out of them; creates relevance for students by linking learning with students real life experiences 30.Student Social Development Encourages student social development and understands the role of the school in influencing student character and personal responsibility; is interested in the non school lives of students and encourages them to be positive members of the community 31.Diversity Displays knowledge of the interests or cultural heritage of each student; demonstrates the ability to deal effectively with students and other teachers of all races and ethnic origin; supports equal and fair treatment of all regardless of nationality, culture; age or sex. When appropriate, uses knowledge of different cultural contexts within the community (socio-economic, ethnic, and cultural) to create multiple perspectives within each classroom lesson and activity. Professional and School Wide Competencies 32.Mentoring Demonstrates ability to act as a mentor to another teacher and/or a student teacher; capable of judging quality teaching and provides constructive feedback to other teachers seeking assistance. 33.School Law Has a good working knowledge of basic school law as it relates to the student / teacher interactions; considers legal implications when making decisions; demonstrates knowledge of the documentation that is required for serious inappropriate student conduct. 34.School Safety Understands the importance of school safety and actively addresses anything that threatens the safety of students within his/her class. Understands proper procedure to follow in the event of a crisis; knows when it is appropriate to involve law enforcement 35.Supervisions of Volunteers and Paraprofessionals Insures that volunteers and paraprofessionals make a substantive contribution to the classroom environment 36.Professional Development Is committed to the continuous improvement of him/herself and life long learning; seeks out opportunities for professional development to enhance content knowledge and pedagogical skills; considers a variety of delivery systems to maximize learning options and retention 37.Professional Responsibilities Volunteers to participate in school events, making substantial contributions; assumes a leadership role in at least some aspect of school life 38.Professionalism / Integrity Exhibits professionalism in dealing with all school stakeholders; acts with integrity, fairness and in an ethical manner; is widely trusted; is seen as a truthful individual; keeps confidences; does not misrepresent him/herself for personal gain; adheres to an appropriate and effective set of core values regardless of the circumstances