Beneficiary Report
advertisement

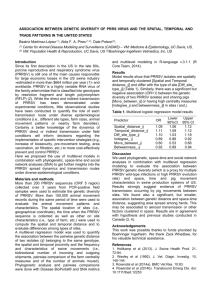
Purpose of Visit The aim of this work is to define whether there are differences in target cells that become infected with PRRSV, and to dissect the immunological host responses at both transcriptional and translational levels. Immunological responses in lungs, blood and lymphoid tissues of pigs infected with several PRRSV strains with a different clinical outcome, including subclinical infections with European type PRRSV strain Lelystad (Netherlands) and a recent Belgian isolate, alongside strains with overt clinical signs, a European type PRRSV strain LENA (Belarus). With this research it is aimed to find an explanation for the higher virulence of some strains. The work completed at the Central Veterinary Institute (CVI), The Netherlands, makes up part of a larger EU project (PoRRSCon) which is being split between three separate sites, the CVIthe Veterinary Laboratories Agency, UK, and the Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, China. The purpose of the visit to the CVI was not only to help process the samples and carry out immediate lab work but to observe if any problems arose that could be addressed before the experiment started at the VLA. It was also important to observe laboratory methods to ensure that they are kept as consistent as possible throughout the different sites. Description of work carried out during visit Three European strains of PRRSV were selected, Lena, a highly pathogenic Belarus strain, a recent field isolate from Belgium (07V063) and the European reference strain Lelystad virus, which will be used across all three sites to act as a control. For each virus strain, and the uninfected control group, sixteen randomly selected male pigs were used, four piglets from one sow were spread between each group, to provide an even genetic background. Each pig was inoculated intranasally with 105 TCID50 of the respective virus, with controls inoculated with PBS. The animals were clinically scored and had temperatures taken daily. Oropharyngeal samples were taken at days 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,10,14, 21, 26 and 33, the swabs were proceesed and the samples stored at -80°C for analysis of viral load by qPCR. Blood samples were taken at days 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, 21, 26 and 33. EDTA blood was used for automated cell counts, non-treated blood was used to collect serum which was aliquoted and stored at -80°C for later analysis, blood was taken into paxgene tubes and frozen at 20°C, finally heparin-preserved blood was taken and used for the isolation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). PBMCs were phenotyped by flow cytometry, and used for quantification of PRRSV and aujeszky’s disease virusspecific IFN-γ responses by ELISpot assay. PRRSV Ab were determined in serum by ELISA. At 3, 7 and 35 dpi, four pigs (eight at day 35, to include four vaccinated at days 7 and 21) were euthanized and tissues collected for a full histopathological and virological screening as well as tissues to be examined for host gene expression by microarray. Description of main results PRRSV Antibodies All animals in the trial were negative for PRRSV Ab before infection and the control group remained negative throughout. All groups were positive for PRRSV Ab by day 10 post-infection with levels peaking at day 21. PRRSV Ab 2.5 Lena Belgium 07V063 Leystad Virus Control S/P Ratio 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 33 26 21 14 7 10 -0.5 5 3 0 0.0 d.p.i Figure 1. Detection of PRRSV-specific Ab by IDEXX ELISA, in serum from pigs infected with Lena, Belgium 07V063, the Lelystad virus strains of PRRSV and uninfected controls. An S/P value of >0.4 is considered as a positive for PRRSV Ab. Mean data for each group is presented and error bars represent the SEM. PBMC Phenotyping and IFN-γ Responses. Results were obtained from flow cytometry with two sets of triple staining with the following monoclonal antibody panels; CD3/CD4/CD8 and SWC1/SWC3/SWC8. These stains provided data on populations of memory and naive CD4 T cells, γδ-T cells, CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, natural killer cells, neutrophils, monocytes and B cells. The IFN-γ ELISpot was performed with PBMCs plated and stimulated with media, ConA, the PRRSV strain which the pig was originally infected with and the Aujeszky’s disease virus reference strain (NIA-3). The data from both the phenotyping of PBMCs and the ELISpot assays are currently being analysed. Production of Samples for Later Analysis The animal experiment has produced numerous samples which have been stored as it was impossible to perform all analysis during the 2 month visit. Virus load and distribution is being quantified in tissues, serum and oropharyngeal swabs by qPCR, those samples which are positive will then be used to perform virus isolation to determine the amount of infectious virus. Tissue samples will also be stained for PRRSV antigen. The humoral immune response to secondary infection will be determined by looking at levels of Aujeszky’s disease virus-specific Ab in serum by ELISA. Cytokine profiles will be determined for pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-α, IL-1, IL-6 and TNFα) and other relevant cytokines (including IL-10) by qPCR. Protein levels may be investigated in those samples which display changes in expression levels. RNA extracted from lymphoid tissues will be analysed by microarray to assess the transcription level of different genes during infection. Differences in gene expression between PRRSV strains may explain different viral replication kinetics related to virulence. Expression profiling will be performed within the UK Centre for Functional Genomics in Farm Animals (ARK-Genomics) based at Roslin. With this information relevant transcripts and pathways will be re-examined in the animal tissues with in situ hybridisation and immunohistochemistry. Alongside the data that was produced, or will be produced from analysis of the samples which were collected during the experiment, the visit has allowed me to become accustomed to the laboratory work which we will be aiming to replicate in the experiment at the VLA. Also it has allowed us to identify areas of the original protocol which may benefit from slight alterations, so that further experiments can run more smoothly. Future Collaboration with host institute Collaboration with the host institute will carry on through the EU PoRRSCon project, with the possibility of staff members from the CVI coming to the VLA to help with our experiment. Also the CVI has invited me back to help with analysis of the samples obtained as well as to perform any ex vivo experiments we may be interested in performing. Projected publications The results of the experiment described above will be published the coming year.. Confirmation of successful completion of mission Sophie Morgan assisted during the animal trial at the CVI for the PoRRScon project. The experiment was very successful and the collaboration with Sophie was perfect. During the course of the experiment there was an excellent exchange of knowledge. We would be happy to continue this collaboration with the VLA.