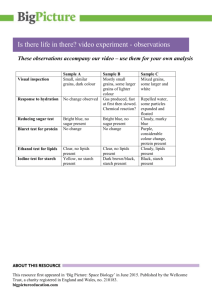
Human Biology Chemical Composition of Cells
advertisement

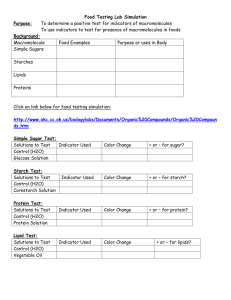
Human Biology Chemical Composition of Cells Label this diagram a. nucleus b. nucleolus c. plasma membrane Carbohydrates include sugars and molecules that are chains of sugars ________ is a monosaccharide. Starch is a __________. Which reagent is needed to test for protein? What would you use benedicts reagent to test for? How could you test for lipids? During ________ bonds are broken as water is added. What is an emulsifier? Potato is a ________ Maltose is a _________ Olive Oil is a ______ What is tonicity? Small molecules diffuse across a membrane from an area of ________ concentration to an area of _________ concentration. Why are controls used in experiments? What type of protein speeds chemical reactions? What is starch composed of? Why did you use water as a control? Match: 1. Test starch a. Biuret reagent 2. Albumin b. Emulsifier 3. Olive oil c. Contain carbohydrates 4. Potato d. Lipid 5. Pepsin e. Benedict’s reagent 6. Test for protein f. Enzyme 7. Cause fat disperse in water g. Iodine 8. Test for sugar H. Contain protein A fat molecule is formed by: A protein molecule is composed of? To test whether a sample contains starch, what reagent should be used? Explain the function of enzymes. True or False. Lipids are not soluble in water. What molecules make up or form carbohydrates? Amino acids can join together and form what? Primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure are all different levels of organization of a ___________. Benedict’s reagent is used to test for ____________. [10 pts] Fats, oils, steroids, and cholesterol are all categorized as __________. [9 pts] Starch is a polysaccharide, how does it differ from a monosaccharide such as glucose? [9 pts] What does the Biuret reagent test for? What does the iodine solution test for? What does the Benedict's reagent test for? What is the term used to describe what happens to large organic molecules when they break down into monomers when water was added to their bonds? True or False. Enzymes are classified as proteins? True or False. Lipids are soluble is water. What color of the testing solution indicates high sugar concentration? Name the disaccharide with two sugar units. What substance causes fat to dissolve in water? What enzyme breaks starch down into maltose? Label this diagram d. nucleus e. nucleolus f. plasma membrane Tests: Unknown #1 Unknown #2 Benedicts (-) (-) Biuret (-) (+) Iodine (+) (-) Wax Paper (-) (-) Table 1 – Results of various tests to determine the identity of unknowns #1 and #2 (1) Unknown #1 is a ______________. sugar, protein, lipid) Possible choices: (starch, simple Unknown #2 is a ______________. sugar, protein, lipid) Possible choices: (starch, simple (2) The enzyme Pepsin was introduced into a test tube with unknown #1 and then incubated at 37oC for 15 minutes. EXPLAIN what effects (if anything) the Pepsin had on unknown #1. If there was no effect, you must explain why not. (3) The enzyme Pepsin was introduced into a test tube with unknown #2 and then incubated at 37oC for 15 minutes. EXPLAIN what effects (if anything) the Pepsin had on unknown #2. If there was no effect, you must explain why not. (4) Would the result from question #3 have been different if the incubation had occurred at 100oC rather than at 37 oC? Explain why it would or why it would not have made a difference. An FIU biologist decides to test her lunch from the Graham center to see if the suspicious meat she received at the cafeterias all you can eat buffet really does contain proteins. She sets up an experiment where she tests three things: (1) a sample of genuine meat from Publix, (2) her lunch, (3) a glass of pure water. a) In her experiment, the positive control is the ________________________ and the negative control is the _________________________. [5 pts] b) What was the purpose of using the negative and positive control? If you wanted to wash some oil off of your hands by only using water, most of the oil would not wash off. To get it all off, you would also have to use a soap that was a good _____________. [Hint: the word starts with the letter “E”] [10 pts] What do Bile salts do in the digestive tract? Do potatoes contain more starch than glucose? What color does Biuret reagent turn in the color of proteins? What sub-units make up proteins? What kinds of proteins speed up biological reactions? What is the experimental controls significance? Name a monosacharide sugar? Which reagent will be used to test for sugars? What is the function of ribosomes? How do buffer’s affect pH? How do enzymes affect biological reactions? Name two types of lipids. What causes lipids to disperse in water? What yellow-brown colored reagent turns blue black in the presence of starch? Name a disaccharide To test whether a sample contains starch, what reagent should be used? Explain the function of enzymes. True or False. Lipids are not soluble in water. What molecules make up or form carbohydrates? Amino acids can join together and form what? Explain the function of an emulsifier. What is the function of fat in animal cells? If a substance turns blue/black when iodine is added to it, what does that substance contain? What type of bond joins amino acids to make peptides? List the following in order of least to greatest in sugar content: maltose, starch, water, and glucose. Name 2 kinds of controls used in the design of experiments. Proteins are made up of ______________. True/False. Lipids are soluble in water. What are the basic units of carbohydrates? Explain the function of enzymes. 1. What goes through all the steps of an experiment but lacks the factor being tested? a) Subunit b) Control c) Enzyme d) Lipid