BIOCHEMISTRY
advertisement
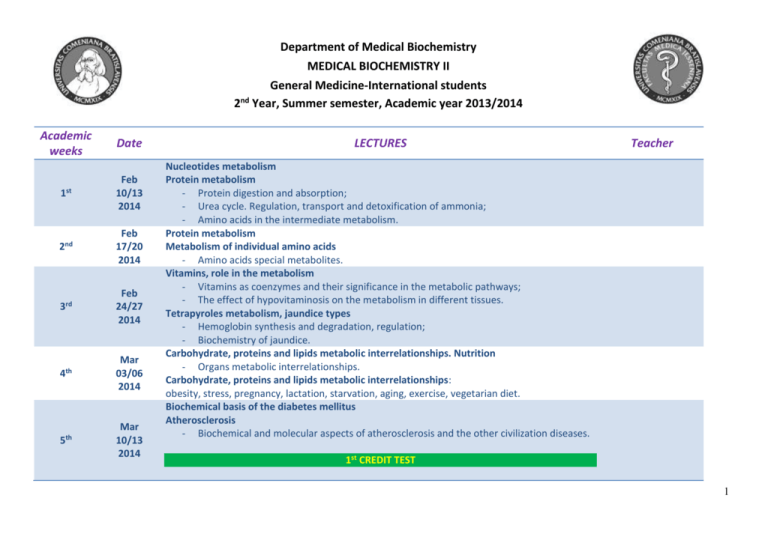
Department of Medical Biochemistry MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY II General Medicine-International students 2nd Year, Summer semester, Academic year 2013/2014 Academic weeks Date 1st Feb 10/13 2014 2nd Feb 17/20 2014 3rd Feb 24/27 2014 4th Mar 03/06 2014 5th Mar 10/13 2014 LECTURES Teacher Nucleotides metabolism Protein metabolism - Protein digestion and absorption; - Urea cycle. Regulation, transport and detoxification of ammonia; - Amino acids in the intermediate metabolism. Protein metabolism Metabolism of individual amino acids - Amino acids special metabolites. Vitamins, role in the metabolism - Vitamins as coenzymes and their significance in the metabolic pathways; - The effect of hypovitaminosis on the metabolism in different tissues. Tetrapyroles metabolism, jaundice types - Hemoglobin synthesis and degradation, regulation; - Biochemistry of jaundice. Carbohydrate, proteins and lipids metabolic interrelationships. Nutrition - Organs metabolic interrelationships. Carbohydrate, proteins and lipids metabolic interrelationships: obesity, stress, pregnancy, lactation, starvation, aging, exercise, vegetarian diet. Biochemical basis of the diabetes mellitus Atherosclerosis - Biochemical and molecular aspects of atherosclerosis and the other civilization diseases. 1st CREDIT TEST 1 6th 7th Mar 17/20 2014 Mar 24/28 2014 8th Mar/Apr 31/03 2014 9th Apr 07/10 2014 10th Apr 14 2014 11th Apr 24 2014 Cell signaling, signal molecules Hormones and neurohormonal regulation - Relationship between the hypotalamus, the anterior pituitary and target organs. Steroid hormones Hormones of the thyroid and parathyroid glands Peptide hormones Free radicals in the living system - Production of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species in cells; - Oxidative damage to lipids, proteins and DNA; - Antioxidant systems; - Oxidative stress in various pathological states. Neurochemistry, neurotransmitters, synapse Plasma enzymes and their diagnostic importance, isoenzymes Blood proteins, erythrocyte metabolism - Blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Minerals, role in the metabolism - Transformation of Na+, K+, Cl-; - Transformation of Ca2+, Mg2+, PO43-, regulation, parathyrin, calcitonin, calcitriol; - Transformation of Fe2+, transport proteins, receptors; - Transformation of Cu , Zn, Mn, Se, Cr and another trace elements. Biochemical function of the kidney, urine production Acid-base balance. Buffer systems - Regulation of acid-base balance; - Metabolic acidosis and alkalosis; - Respiratory acidosis and alkalosis. 2 12th Apr 28 2014 Connective tissue biochemistry Muscle biochemistry - Metabolism of muscle contraction; - Effect of hormones and regulation of muscle biochemistry. 2nd CREDIT TEST 13th May 05 2014 Biochemical functions of the liver - Endogenous and exogenous functions of the liver; - Xenobiochemistry and biotransformation reactions. The neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders of compound lipids 14th May 12/15 2014 Biochemistry of immune system The select functions of plasmatic enzymes 15th May 19/22 2014 The compensatory lecture 3 Academic weeks Date 1st Feb 10-14 2014 2nd 3rd 4th 5th Feb 17-21 2014 Feb 24-28 2014 Mar 03-07 2014 Mar 10-14 2014 Seminars [S] – Lab. practicals [LP] – PP presentations [PPT] S: Integration of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Regulation. LP: Estimation of proteins in serum by the biuret reaction. S: Metabolisms of purines and pyrimidines nucleotides. Regulation. LP: Estimation of the uric acid in serum. PPT: 1. Genetic defects of purines metabolism, basic divide. 2. Role of antimetabolites in medicine. S: Metabolism of proteins. Urea metabolism. Nitrogen fixation. Glutamine cycle. LP: Estimation of urea in serum. PPT: 1. Hyperammonemia and ammonia toxicity. 2. Glutamine as an alternative substrate for extrahepatic tissues. 3. Pathological conformational changes in proteins – relationship to particular diseases. S: Amino acids metabolism, inborn error of the amino acids metabolism. P: Production of creatin from amino acids and detection of creatinine in serum. PPT: 1. Metabolism of sulfur containing amino acids in connection with some pathological processes. 2. Metabolic diseases of catabolism of aromatic amino acids. 3. Amino acids as signal molecules. S: Vitamins, role in the metabolism. Hypovitaminosis. PPT: 1. Nicotinic acid (niacin) and metabolism of lipoproteins. 2. Antioxidative vitamins and their conjugation to metabolism. 3. Osteoporosis and calciferols. 4. Deficit of folic acid in some pathologically diseases. 1st CREDIT TEST Teacher Assoc. Prof. RNDr. Peter RAČAY, PhD.; prof. RNDr. Ján LEHOTSKÝ, D.Sc. prof. RNDr. Peter KAPLAN, PhD. Mgr. Radovan MURÍN, PhD. prof. RNDr. Peter KAPLAN, PhD. Assoc. Prof. RNDr. Peter RAČAY, PhD. Mgr. Radovan MURÍN, PhD. prof. RNDr. Ján LEHOTSKÝ, D.Sc. Assoc. Prof. Mgr. Eva BABUŠÍKOVÁ, PhD. Ing. Zuzana TATARKOVÁ, PhD. 4 6th 7th 8th 9th Mar 17-21 2014 Mar 24-28 2014 Mar/Apr 31-04 2014 Apr 07-11 2014 S: Hemoglobin metabolism. Tetrapyroles. P: Bilirubin estimation in plasma. PPT: 1. Hyperbilirubinemia connected with increased production of unconjugated bilirubin. 2. Biochemical diagnostic tests for liver diseases. 3. Secretion of bile and its failure. S: Metabolic interrelationships, nutrition. Energy metabolism during the fasting and overweight. P: Estimation of transaminase activity in serum. PPT: 1. Biochemical aspects of obesity and stress. 2. Metabolism during aerobic and anaerobic exercise. 3. Function of different organs in the metabolic interrelationship. 4. Metabolic interrelationship during aging and pregnancy. S: Diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis. P: Estimation of glucose by glucometer. Oral glucose tolerance test. PPT: 1. OxyLDL and atherosclerosis. 2. Incretins and their utilization in pharmacology. 3. Non-enzymatic glycation of proteins. 4. Metabolism of proteoglycans and diabetes mellitus. S: Metabolic pathways of hormonal regulation. P: Estimation of 17-oxosteroids in urine. PPT: 1. Parameters describing thyroid function. 2. Ovary and regulation of reproduction cycle. 3. Function of IP3 in metabolism. 4. Role of catecholamines in the heart. Assoc. Prof. Mgr. Eva BABUŠÍKOVÁ, PhD. Ing. Zuzana TATARKOVÁ, PhD. Mgr. Radovan MURÍN, PhD. Assoc. Prof. Mgr. Eva BABUŠÍKOVÁ, PhD. Ing. Zuzana TATARKOVÁ, PhD. prof. RNDr. Ján LEHOTSKÝ, D.Sc. 5 10th 11th Apr 21-25 2014 12th S: Plasma enzymes and proteins. Importance for clinical diagnostics. PL: Determination of GMT in serum. Estimation of the urine and an unknown sample. PPT: 1. Role of cytokines in the metabolism. 2. Role of proteins in inflammation. S: Plasma enzymes and proteins. Importance for clinical diagnostics. PL: Determination of GMT in serum. Estimation of the urine and an unknown sample. PPT: 1. Role of cytokines in the metabolism. 2. Role of proteins in inflammation. S: Minerals metabolism. P: Iron and transferrin estimation in the blood. PPT: 1. Imbalance of calcium homeostasis. 2. Imbalance of potassium homeostasis. 3. The role of chrome, selenium and manganese in cells. Assoc. Prof. Mgr. Eva BABUŠÍKOVÁ, PhD. Ing. Zuzana TATARKOVÁ, PhD. Assoc. Prof. Mgr. Eva BABUŠÍKOVÁ, PhD. Ing. Zuzana TATARKOVÁ, PhD. Mgr. Radovan MURÍN, PhD. 2nd CREDIT TEST 13th 14th 15th May 05-09 2014 May 12-16 2014 May 19-23 2014 S: Acid-base balance. Biochemical functions of the kidney, urine production. (Seminar is realize on the Department of Clinical Biochemistry in Hospital) Retake of credit tests Compensatory laboratory practicals, credits prof. Dušan DOBROTA, M.D., PhD.; Daniel ČIERNY, M.D. RNDr. Jozef HATOK, PhD. RNDr. Jozef HATOK, PhD. 6 REQUIREMENTS FOR CREDITS General Medicine-International students nd 2 Year, Summer semester, Academic year 2013/2014 Department of Medical Biochemistry provides these rules to grant 9 credits for the subject “Medical Biochemistry” in summer semester in conformity with Act 131/2002 Coll. and Study regulation of Comenius University in Bratislava, Jessenius Faculty of Medicine in Martin, Article 22 and Article 23. 1. 100 % attendance at seminars and practical exercises. All absences due to diseases must be excused by a medical confirmation and substitute in the substitution week (one excused absence is without any substitution). Maximal number of absences is 3. During the time of a seminar/lab. practical (substitution week) only one seminar/lab. practical can be substituted at that time. 2. During the semester are written two credit tests. From each of the test 60 % of total score points is necessary. Maximal number of points for the one test is 50. It is possible to obtain 100 points from two credit tests and 10 points from a student presentation. Credit tests can be substituted maximally two times. 3. Exam from the subject “Medical Biochemistry” is composed from two parts, written and oral*. Written part is one or two days before the oral part and the test consists of 40 questions. 60 % of total score points is necessary for continuing in the oral part of the exam. Final evaluation of the exam consists from the results of oral and written parts as well as total results from the summer semester. 4. *If a student obtained from both tests and presentations classification “A” – will not do the written test, only oral form of exam! Study and test results: A (1) 100 – 91 % B (1.5) 90.9 – 81 % C (2) 80.9 – 73 % D (2.5) 72.9 – 66 % E (3) 65.9 – 60 % Fx less than 60 % 100 – 91 points 90 – 81 points 80 – 73 points 72 – 66 points 65 – 60 points 59 and less points 7