CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION UNIT
PROCEDURAL GUIDE
2010
Point of Contact:
Dave Laton (334) 293-4581
Alabama Community College System
Copyright© 2010
All rights reserved
PART I
MISSION, FUNCTIONS, OPERATION, AND 2008 GOALS OF THE DEPARTMENT
OF POSTSECONDARY EDUCATION CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION UNIT
MISSION
The Curriculum and Instruction Unit (CIU) supports instructional functions of the
Alabama Department of Postsecondary Education in career-technical education, health
professions, and academic transfer courses, by developing, implementing, and
maintaining curricula based on validated industry and student needs.
MAJOR FUNCTIONS
Develop course plans of instructions (POIs) comprised of validated competencies
and student learning outcomes.
Coordinate with Alabama Department of Education to develop state-wide
articulation agreements in specified programs of instruction.
Maintain the Common Course Directory to ensure currency of program offerings
throughout the college system.
Assist colleges in delivering faculty development activities pertinent to curricula
implementation and effective student instruction and assessment strategies.
Assist with major initiatives for the Department of Postsecondary Education and its
respective agencies as required.
Provide technical assistance to college administration and instructional staff as
requested related to curriculum development and management.
Provide instructor professional development through the Instructor Skills
Enhancement Program (ISET).
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
UNIT OPERATION
The Assistant Director for Career/Technical Education provides overall supervision for
the CIU with consultation with the Vice Chancellor of Instruction and Student Services,
the Director of Career/Technical Education, the Director of Health Programs, the
Director of Academic Affairs, and representatives from the Alabama Department of
Education.
The Assistant Director for Career/Technical Education, serving as the team manager,
has lead responsibility for developing and implementing a CIU strategic plan and is
responsible for establishing timelines, scheduling work activities, submitting progress
reports, and ensuring that high quality work is performed in a timely manner. The team
manager also represents the Department in developing statewide articulation
agreements with State Department of Education. Although individual team members
have various specific work assignments, all are responsible for developing course plans
of instruction in assigned program areas.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
PART II
DACUM AND IMPLEMENTATION PROCESS FOR
POSTSECONARY EDUCATION CIU
I.0 DACUM Overview
1.1 Description
1.1.1 DACUM is an acronym for “Developing A Curriculum.” It is a process that
brings together the parts necessary to identify duties, tasks, knowledge, skills,
traits, and attitudes necessary to succeed in a given discipline and to transfer
those to success on the job. The occupational analysis of the areas identified
above is the crucial element to the success of this process.
1.1.2 Assumptions:
Experienced and knowledgeable individuals that perform the tasks on a
regular basis are the best source for describing their occupation.
Occupations can be described in terms of knowledge, competencies, and
attitudes that successful workers in an occupation posses or can perform.
All tasks within an occupation are relevant and necessary for the knowledge
and attitudes that workers must have in order to perform the tasks effectively.
1.1.3 Explanation of Competency Based Curricula
Knowledge and skills are based on specific standards with performancebased outcomes.
In competency based curricula students are assessed on their performance,
that is, on whether they have achieved the outcomes related to specific
standards called for in the performance or assessment criteria.
Students may be assessed separately on their knowledge (a test or report) as
well as the performance of skill (demonstration or role play).
Skills and knowledge may also be assessed together (report and presentation
or demonstration with explanation).
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
Competency-based curricula must meet the following criteria:
-
Employers must be involved to identify all needed competencies from the
start of the curriculum development process.
-
Competencies must be identified using Subject Matter Experts.
-
Competencies related to workplace readiness and academically related
areas must be defined using a nationally recognized metric, such as Work
Keys or equivalents.
-
A full competency analysis profile must be conducted to identify
competencies in workplace readiness, academic and related areas, and
areas of technical expertise.
-
Competencies must be converted to a curriculum using a recognized
methodology for instructional design system (DACUM/ISD).
1.2 Purpose of the DACUM Process
1.2.1 The DACUM process is used to develop and revise curricula for new and
existing programs and occupations in effective, quick, and valid manner.
DACUM can also be used to assess curricula in existing programs or
occupations.
1.2.2 DACUM consists of 3 phases:
Phase I - Job Analysis
Phase II - Program Development
Phase III - Program Implementation
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
2.0 Application of DACUM
2.1 Outcomes
Convert existing technical education programs to a standardized and recognized
educationally sound format of competency based outcomes.
Develop new courses as necessary to prepare individuals for entry level
qualifications
Align outcomes with industry and governmental certification requirements (i.e.
NATEF, NIMS, AWS, FAA, CompTIA)
Format curricula into a modular based delivery method.
2.2 Detail Process
Phase I – Job Analysis
Research existing curriculum materials
Research certification standards and requirements
Research occupational studies
Interview Subject Matter Experts (SME’s) from certification agencies, faculty, and
industry
Secondary Education Course of Study with the intent of including their content as
applicable and to facilitate state-wide and local articulation agreements.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
Phase II - Program Development
Form committee of SME’s to include faculty from colleges, industry, and
secondary education (and other individuals as required). Select from this list a
smaller, “core” group. Use the core group to assist with identifying and grouping
topics necessary for instruction and to identify core competencies
If information is unavailable or incomplete, develop industry competency survey
for SME’s to determine needs for individuals at entry level into industry
o
Develop outcomes as competency statements that are clearly observable
and measurable
o
Compile competencies based on criticality and frequency of performance
o
Solicit additional competencies from SME’s
o
Rank completed survey competencies by criticality and frequency
o
Validate with industry and agency requirements
o
Group competencies and determine courses needed to achieve them.
Design course map
o
Group topics together under specific course headings (may be current titles in
use or new titles)
o
Determine core courses based on criticality of competency
o
Determine common courses as optional support knowledge and skills
Develop Plans of Instruction (POIs) for each course
o
Develop outcome statements and enabling objectives to meet identified
competencies
o
Develop modules within course
o
Place modules in logical progression to ensure students attain foundational
knowledge, skills, and abilities
o
Assign proficiency/knowledge level to each competencies and enabling
objective using the Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities code key.
o
Meet with SMEs
o
Review each POI item (currency of content, accuracy of stated outcomes,
feasibility in terms of time and resources, educational soundness)
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
Revise content as needed
o
Review for final approval
o
Oversight Committee approval
Publish on Internet for pre-review
Meet with committee to answer questions and concerns
Revise accordingly
Update course directory
Phase III – Program Implementation
o
Publish approved POIs
o
Conduct In-Service-Training for faculty
o
Faculty review and began necessary adjustments or development of personal
use lesson plans
o
Individual school obtain necessary resources required by course
o
Administration revise catalogue and schedule
Validation
Conduct in-service training for faculty
Faculty teach program according to POIs
Gather data including cognitive tests, performance evaluations, student surveys,
and visual observation of faculty and student performance.
Analyze data to determine need for revisions.
Revise accordingly and publish
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
2.3 Implementation Details
Upon notice to proceed, the development team will publish the curriculum on
the ACCS website making it available to all interested and affected parties.
Revise course directory as needed
Conduct a series of in-service training (IST) sessions to present curriculum
and implementation plan to appropriate faculty and staff.
Provide necessary information for affected schools to update catalogues,
policies, procedures, and other necessary administrative support functions.
Distribute or make available all materials as necessary.
Conduct onsite IST to train instructors on pedagogical and androgogical
delivery methodologies, lesson plan development, test and evaluation
procedures, test analysis, and data gathering process in support of I.E.
reporting.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
3.0 Overview of Validation Process
3.1 Validation must include content and process measurements.
During initial validation, data should be collected at the conclusion of each
module as well as at the end of a course. Data should include observations
of instruction (note: the purpose of observations is to ascertain the ease of
use of the materials from the instructor’s perspective), instructor feedback,
student performance data, and any other relevant observations providing an
overall detailed view of the course and student outcomes. Data may suggest
changes in the format, delivery methodologies, audiovisual support, student
handouts, software improvement, etc. Over time, repeated comments may
lead to revamping the entire course.
Data should be gathered for a minimum of 3 iterations of the course before
making whole scale revisions. Only critical revisions that directly impact on
student success in obtaining objectives or viability of the course are made
prior to 3 iterations.
All data is reviewed by DPE and maintained on permanent file. Before
revising a course, data must be reviewed to ensure any findings and
recommendations are included in the course re-write or revision.
3.2 Develop/Distribute follow-up questionnaires
A critical step, course maintenance is always necessary to keep a course
valid.
A standard evaluation and validation technique is the follow-up
survey/questionnaire. From 6 weeks to a few months after attendance at a
course, students and their supervisors should be surveyed to see if the
course met the education and training needs.
Questions to consider are as follows:
Did the student gain the training needed to do his or her job better?
Was the education and training adequate to the task?
Was the education and training implemented on the job?
What could be improved within the course for future students?
Was the student satisfied with the education and training he or she
received?
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
All areas must be reevaluated for possible course revision. All sources of
data must be reviewed. Student knowledge and skills assessments and
relevant feedback from early presentations of a course and instructor
suggestions should be consolidated into an evaluation report written by
curriculum development. This report will be submitted for review.
Establish a process for periodic review to validate the currency of a course.
DACUM Process
Start
Define Program
Requirements (1)
Gather Data (2)
Developed
Competency and
Needs Analyses
Survey (3)
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
Review by Subject
Matter Expert CoreCommittee (7)
Develop Plans of
Instruction (6)
Design Course Map
(5)
Group Competencies
Into Courses (4)
Review by Full
Subject Matter
Expert Committee
(8)
Review by
Oversight
Committee (9)
Place in Course
Directory (10)
Implement (11)
Stop
Validate (12)
Detail of Process
1. Ensure courses are developed in a manner that maximizes opportunities to receive
college credit through secondary/postsecondary articulation agreements.
2. Research existing curriculum materials including the secondary course of study.
Research certification standards and requirements. Research federal and state
occupational studies. Interview subject matter experts (faculty, industry, certification
agencies).
3. Develop competency statements. Compile survey instruments to determine criticality
and frequency of task. Solicit additional competencies from respondents. Validate
instrument with Subject Matter Experts (SMEs).
4. Designate course titles based on functional grouping and primary activity or concept
and group activities based on CIP code. (Existing course titles, descriptions, and
number will be used whenever possible.)
5. Determine core and common courses and recommend theory and laboratory credit
and contact hours.
6. Include industry competency statements, credit hours, course objectives, outcome
statements, enabling objectives, logical flow of content, assessment table of
specifications, and recommended instructional methodologies, other critical
information as applies.
7. Appoint a core committee to provide initial review and validation of content and
processes outlined on Plans of Instruction (POIs) and to determine validity of course
map.
8. Entire SME committee reviews and provides approval.
9. Oversight committee is provided advanced copies through Internet access.
Conducts a quality review. Provides final approval of program and courses.
10. Department of Postsecondary (DPE) includes in course directory and updates the
DPE Web site.
11.Respective colleges take over implementation process to include necessary revision
of catalogue, advertisement, enrollment and registration.
12 Conduct in-service training on site for faculty and staff. Faculty teaches program as
directed by POI. Gather and analyze data using instructor surveys, class
observations, student surveys, and assessment data.
Revise program as
necessary, publish final version, and maintain.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
DRAFT
Course Prefix and number
Course Name
Plan of Instruction
Effective Date:
Version Number:
COURSE DESCRIPTION:
CONTACT/CREDIT HOURS
Theory Credit Hours
Lab Credit Hours
Total Credit Hours
x hours
x hour
x hours
NOTE: Theory credit hours are a 1:1 contact to credit ratio. Colleges may schedule practical
lab hours as 3:1 or 2:1 contact to credit ratio. Clinical hours are 3:1 contact to credit ratio. (Ref
Board Policy 705.01)
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
PREREQUISITE COURSES
As determined by college.
CO-REQUISITE COURSES
As determined by college.
PROFESSIONAL COMPETENCIES
INSTRUCTIONAL GOALS
Cognitive – Comprehend principles and concepts related to topic.
Psychomotor – Apply principles of topic.
Affective – Value the importance of adhering to policy and procedures related to
topic.
STUDENT OBJECTIVES
Condition Statement: Unless otherwise indicated, evaluation of student’s attainment
of objectives is based on knowledge gained from this course. Specifications may be in
the form of, but not limited to, cognitive skills diagnostic instruments, manufacturer’s
specifications, technical orders, regulations, national and state codes, certification
agencies, locally developed lab/clinical assignments, or any combination of
specifications.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES
MODULE A –
MODULE DESCRIPTION –
PROFESSIONAL COMPETENCIES
A1.0
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
A1.1
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
KSA
KSA
A1.1.1
MODULE A OUTLINE:
MODULE B –
MODULE DESCRIPTION –
PROFESSIONAL COMPETENCIES
B1.0
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
B1.1
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
KSA
KSA
B1.1.1
MODULE B OUTLINE:
MODULE C –
MODULE DESCRIPTION –
PROFESSIONAL COMPETENCIES
C1.0
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
C1.1.1
MODULE C OUTLINE:
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
C1.1
KSA
KSA
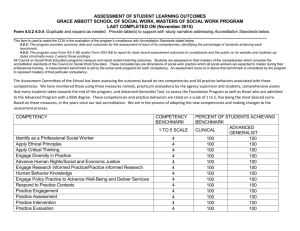
LEARNING OUTCOMES TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS
The table below identifies the percentage of learning objectives for each module.
Instructors should develop sufficient numbers of test items at the appropriate
level of evaluation.
Limited
Knowledge and
Proficiency
1
Module A
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
Moderate
Knowledge
and
Proficiency
2
Advanced
Knowledge
and
Proficiency
3
Superior
Knowledge
and
Proficiency
4
Indicator
1
2
3
4
Learner’s Knowledge, Skills and Abilities
Key Terms
Description
Identifies basic facts and terms about the subject or
competency.
Limited
Knowledge Performs simple tasks associated with the
and
competency. Needs to be told or shown how to do
Proficiency
most tasks.
Requires close supervision.
Identifies relationship of basic facts and states
general principles and can determine step-by-step
Moderate
procedures for doing the competency.
Knowledge
and
Performs most parts of the competency. Needs help
Proficiency
only on hardest parts.
Requires limited supervision.
Analyzes facts and principles and draws conclusions
about the subject to include why and when the
Advanced
competency must be done and why each step is
Knowledge
needed. Can predict outcomes.
and
Performs all parts of the competency. Needs only a
Proficiency
spot check of completed work.
Requires little or no direct supervision.
Can evaluate conditions and make appropriate
Superior
decisions as related to resolving problems.
Knowledge
Performs competency quickly and accurately with no
and
direct supervision and is able to instruct and
Proficiency
supervise others.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
Lesson Plan Template
COURSE TITLE:
Course Title
MODULE:
Module and Title
RECOMMENDED
Total instruction hours for
TIMEFRAME
module
INSTRUCTOR PREPARATION
Materials/Supplies Requirements:
Effective Date
Mo-dayyear
Audiovisual Requirements:
Equipment Requirements
Handouts/Supplemental Materials
Classroom/Lab/Clinical Set Up Requirements
Evaluation Methodology
Clinical/Lab Skills
Insert appropriate information in each cell above. Cells will expand as information is
entered.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
COMPETENCIES AND OBJECTIVES
COMPETENCY
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
A1.0 Insert the competency (s) for A1.1 Insert the performance objective (s) for
this module.
this module.
Instructor Notes:
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
A1.1.1 Insert learning objectives related to this module from the Plan of instruction.
Instructor Notes:
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
LESSON DEVELOPMENT
Theory = T
Lab = L
Clinicals = C
MAIN POINTS
T
L
C
Main point 1 detailed outline
T
L
C
Main point 2 detailed outline
T
L
C
Main point 3 detailed outline
Insert appropriate
abbreviation for each
main point. This
indicates where main
point is taught.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
ASSIGNMENTS AND DUE DATES
Insert appropriate information for this module.
SUMMARY AND REVIEW
Insert appropriate information for this module.
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved
Format for Common Course Directory
DPT
CRS.
COURSE TITLE
BASIC MACHINING
MSP
101
TECHNOLOGY
Course Description Course Description
THEORY
LAB
COURSE
1
4
5
Updated
Oct 12, 07
PREREQUISITE: As determined by college.
COREQUISITE: As determined by college.
NOTE: There is an approved standardized plan-of-instruction for this course.
This course introduces machining operations as they relate to the metalworking industry. Topics include
machine shop safety, measuring tools, lathes, drilling machines, saws, milling machines, bench grinders,
and layout instruments. Upon completion, students should be able to safely perform the basic operations
of measuring, layout, drilling, sawing, turning, and milling. NDC CORE
DPT
CRS.
COURSE TITLE
INTERMEDIATE MACHINING
MSP
102
TECHNOLOGY
Course Description Course Description
THEORY
LAB
COURSE
1
4
5
Updated
Oct 12, 07
PREREQUISITE: As determined by college.
COREQUISITE: As determined by college.
NOTE: There is an approved standardized plan-of-instruction for this course.
This course provides additional instruction and practice in the use of precision measuring tools, lathes,
milling machines, and grinders. Emphasis is placed on setup and operation of machine tools including the
selection and use of work holding devices, speeds, feeds, cutting tools, and coolants. Upon completion,
students should be able to perform basic procedures on precision grinders and advanced operations of
measuring, layout, drilling, sawing, turning, and milling. NDC CORE
ACCS Copyright © 2010
All Rights Reserved