Methods
advertisement
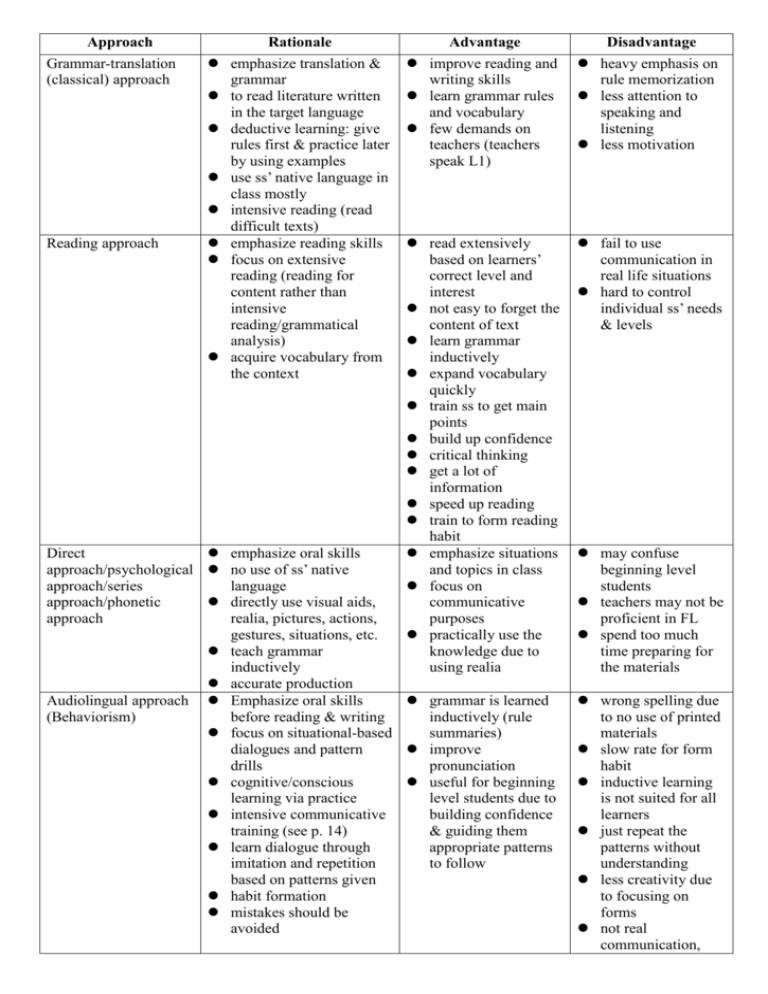
Approach Grammar-translation (classical) approach Reading approach Rationale emphasize translation & grammar to read literature written in the target language deductive learning: give rules first & practice later by using examples use ss’ native language in class mostly intensive reading (read difficult texts) emphasize reading skills focus on extensive reading (reading for content rather than intensive reading/grammatical analysis) acquire vocabulary from the context Advantage improve reading and writing skills learn grammar rules and vocabulary few demands on teachers (teachers speak L1) Disadvantage heavy emphasis on rule memorization less attention to speaking and listening less motivation read extensively based on learners’ correct level and interest not easy to forget the content of text learn grammar inductively expand vocabulary quickly train ss to get main points build up confidence critical thinking get a lot of information speed up reading train to form reading habit emphasize situations and topics in class focus on communicative purposes practically use the knowledge due to using realia fail to use communication in real life situations hard to control individual ss’ needs & levels Direct emphasize oral skills approach/psychological no use of ss’ native approach/series language approach/phonetic directly use visual aids, approach realia, pictures, actions, gestures, situations, etc. teach grammar inductively accurate production Audiolingual approach Emphasize oral skills grammar is learned (Behaviorism) before reading & writing inductively (rule focus on situational-based summaries) dialogues and pattern improve drills pronunciation cognitive/conscious useful for beginning learning via practice level students due to intensive communicative building confidence training (see p. 14) & guiding them learn dialogue through appropriate patterns imitation and repetition to follow based on patterns given habit formation mistakes should be avoided may confuse beginning level students teachers may not be proficient in FL spend too much time preparing for the materials wrong spelling due to no use of printed materials slow rate for form habit inductive learning is not suited for all learners just repeat the patterns without understanding less creativity due to focusing on forms not real communication, Oral-situational approach Cognitive approach Suggestopedia (Affective-humanistic approach) Community language learning Emphasize oral skills before reading & writing Teacher-centered Only use target language in class Teach/grade grammar from simple to complex (systematic planning) Practice situational topics (e.g., at the post office, at the bank, etc.) Learn language by rule acquisition, not habit formation (meaningful practice) Individualized learning Teach grammar deductively or inductively depending on individual ss) Use L2 in class Not emphasize perfect pronunciation Extensive grammar teaching Correct errors constructively in the learning process Teachers should be good models and have good proficiency respect ss’ feelings decrease ss’ negative feelings toward learning integrate fine arts, music, posters infantilization emphasize “whole-person” learning (intellect, feeling, physical reactions, etc) “counseling-learning approach” Teacher’s role is counselor Humanistic approach Client-counselor and just memorization turn ss into parrots boring and reduce motivation Hard to teach grammar from simple to complex Similar with audiolingual method Useful for those general and useful topics Scheduled progress Learners can determine their own learning pace Ss don’t feel ashamed if corrected directly Build confidence Hard for ss to manage their own learning Teachers’ pressure to be good models increase ss’ mental powers by decreasing barriers in learning bright and cheerful classroom by doing role playing, songs, games enhance ss’ self-confidence & motivation understand ss’ fears and help to overcome their negative feelings build good relationship with ss want ss to be responsible for their own learning provide free-pressure if too relaxed and comfortable, hard to facilitate learning unuseful for advanced-level adults not really useful to apply it to all subjects hard to control the learning process if ss are too passive in learning hard to run the class for the relaxing environment Total physical response (TPR) learner-knower relationships focus on listening comprehension similar with Natural approach emphasize “meaning” not “form” Comprehension-based approach (Natural approach) Communicative approach Task-based approach Similar to L1 acquisition Emphasize listening comprehension Get comprehensible/ meaningful inputs (i+1) Don’t push output if not ready Unnecessary to correct errors Use language for real communication (more open-ended answers) Not necessary to use exercise and drills Use authentic materials (e.g., real newspaper article, listen to a live radio, CNN news, ICRT) for functional purpose “Listen and do” sth based on the information received Consciousness-raising environment in learning develop basic communication skills, listening and vocabulary through comprehensible messages more interesting to use realia & pictures allow silent period no requirement for many preparations on materials Useful for beginning learners Silent period is acceptable to decrease anxiety hard to control the appropriate time to give ss modeling and commands hard to judge ss’ learning due to different personalities lack of reading & writing training Hard to judge ss’ performance if they are not ready for output Hard to learn correct forms Hard to prepare for the teaching materials for real hard for beginning communication, ss level ss to express should know target language knowledge of with foreigners linguistic forms, ignore the training meaning, functions, of reading & background writing information no environment of produce real ESL language in daily life difficulty in evaluating ss’ performance Make functional use hard for beginning of the lg immediately level ss Develop higher focus on meaning, cognitive & instead of form metacognitive (manage own learning) strategies