Prophylactic Antibiotics (policy & attach)
advertisement
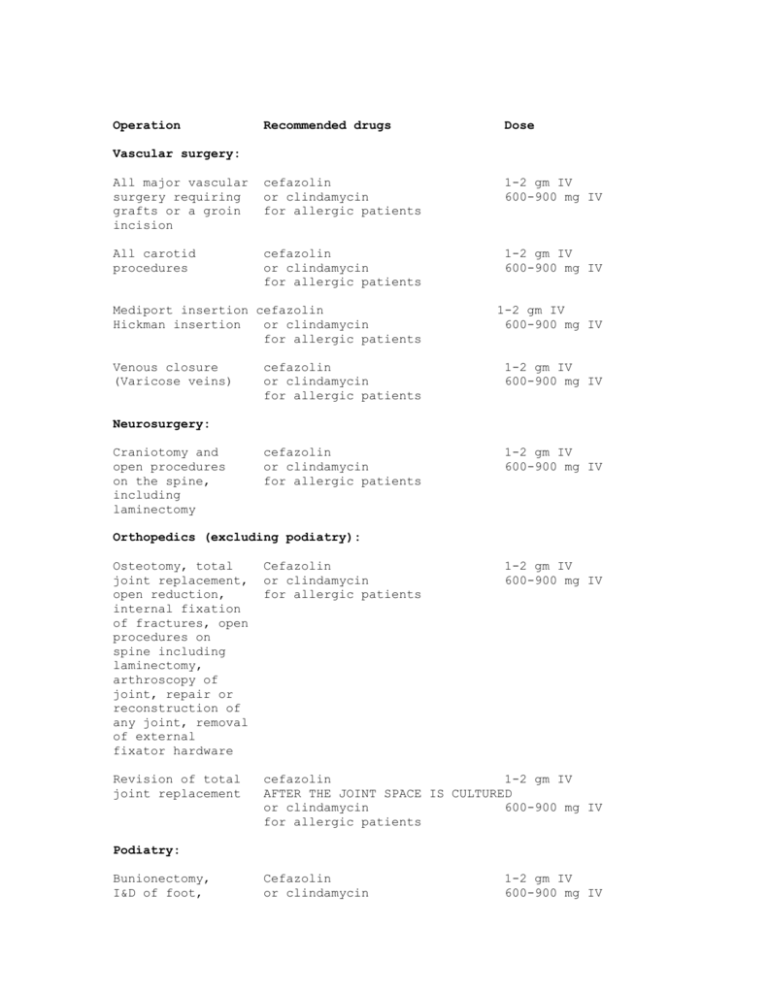
Operation Recommended drugs Dose All major vascular surgery requiring grafts or a groin incision cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV All carotid procedures cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Mediport insertion cefazolin Hickman insertion or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Vascular surgery: Venous closure (Varicose veins) cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Neurosurgery: Craniotomy and open procedures on the spine, including laminectomy Orthopedics (excluding podiatry): Osteotomy, total joint replacement, open reduction, internal fixation of fractures, open procedures on spine including laminectomy, arthroscopy of joint, repair or reconstruction of any joint, removal of external fixator hardware Cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Revision of total joint replacement cefazolin 1-2 gm IV AFTER THE JOINT SPACE IS CULTURED or clindamycin 600-900 mg IV for allergic patients Podiatry: Bunionectomy, I&D of foot, Cefazolin or clindamycin 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Lapidus procedure open reduction, internal fixation, excision of bone, tarsal tunnel release for allergic patients Plastic surgery: Abdominoplasty, breast implant, breast reconstruction, face lift, excision of hydradentitis, liposuction, mammoplasty Cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Ophthalmology: Per surgeon Topical antibiotic General surgery: Herniorrhaphy when mesh is utilized cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Breast surgery which involves needle localization cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Splenectomy cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Biliary and gastroduodenal cefazolin or clindamycin and gentamicin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV 1.7 mg/kg IV* Gastric bypass cefazolin or clindamycin and gentamicin for allergic patients 2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV 1.7 mg/kg IV* Colorectal Oral prophyaxis: neomycin and erythromycin base 1 gm of during day PO 2, and each pre-op at 1, 11 pm Parenteral prophylaxis: 2 Appendectomy Ampicillin-sulbactam 3 gm IV or metronidazole and ciprofloxacin for allergic patients 500 mg IV 400 mg IV ampicillin-sulbactam or clindamycin and gentamicin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV 1.7 mg/kg IV* Oral surgery: Per surgeon Urology: Bladder suspension cefazolin (Slings, TVTs) or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg Radical Prostatectomy cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg Lithotripsy ciprofloxacin or ampicillin-sulbactam for allergic patients 400 mg IV 1-2 gm IV Otolaryngoscopy: Per surgeon Thoracic surgery: Thoracotomy, cefazolin Pleurodesis, or clindamycin Esophagogastrectomy for allergic patients Lung resection, 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Cardiology: Pacemaker cefazolin or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg IV Gynecology: Hysterectomy, vaginal and abdominal cefazolin or clindamycin with gentamicin for allergic pts. 1 gm IV 600-900 mg 1.7 mg/kg* 3 Bladder suspension cefazolin (Slings, TVTs) or clindamycin for allergic patients 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg D&C’s following Missed abortions or terminations. doxycycline for allergic patients consult gynecologist 100 mg IV cefazolin or clindamycin and gentamicin for allergic pts 1-2 gm IV 600-900 mg 1.7 mg/kg* Obstetrics: Cesarean section NB: Use of the Group B Strep. Protocol during labor is not sufficient for maternal wound prophylaxis * Maximum dose = 200 mg 4 NEWTON-WELLESLEY HOSPITAL NEWTON, MASSACHUSETTS EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/09 POLICY TYPE: ADMIN CLINICAL DEPARTMENTAL X-IC PROPHYLACTIC ANTIBIOTICS IN ELECTIVE SURGERY, ADMINISTRATION OF PURPOSE: The purpose of this policy is to define guidelines for the selection and timely administration of prophylactic antibiotics to all patients undergoing elective surgery. SCOPE: This policy applies to anesthesiologists, surgeons, and obstetricians caring for patients undergoing elective surgery and requiring administration of prophylactic antibiotics. POLICY & PROCEDURE STATEMENT: Newton-Wellesley Hospital supports optimum patient care by defining guidelines for the timely administration of prophylactic antibiotics. DEFINITIONS: Prophylactic antibiotic - an antibiotic administered in the absence of infection, for the purpose of preventing bacterial infection. Protocol - a predetermined set of antibiotic choices, doses, and administration times for patients having elective surgery selected on the basis of published studies or a strong theoretical rationale. PROCESS: I. II. Patients having the operations identified in Attachment I should routinely receive the recommended prophylactic antibiotics in the absence of a specific order to the contrary. The only exception to the recommended timing of antibiotic administration is for: A. Revision of joint prostheses, for which antibiotics are administered after a culture has been obtained; III. Surgeons who do not want the antibiotic guidelines followed must write an order and inform the anesthesia team that no antibiotic prophylaxis is to be given or that an alternative is to be substituted for the protocol drug. IV. The Medical Letter on Drugs and Therapeutics and the Surgical Infection Prevention Guideline were used as the primary references for Attachment I. However, there may be some differences between the Guidelines and the Appendix that are based on recommendations by the Infectious Disease Service. V. Because of concern about development of vancomycin resistance in the hospital, and, because of difficulties with administration of vancomycin by rapid intravenous infusion, the Infection Control Committee has recommended and the Executive Committee of the Medical 5 Staff has approved an alternative antibiotic for most patients who are allergic to penicillins and cephalosporins. Clindamycin will be administered rather than vancomycin. Prophylaxis with vancomycin should be considered for patients who are receiving orthopedic prostheses and are known to be colonized by methicillin-resistant Staph. Aureus. Preoperative consultation with the Infectious Diseases service is encouraged for such patients. VI. If the patient requires endocarditis prophylaxis an endocarditis prophylaxis protocol will be followed and surgical prophylaxis will be overridden. Please see Attachment II for Endocarditis Prophylaxis. VII. Please see Attachment III, Selection of Antibiotics for a discussion of the management of penicillin allergic patients. VIII. Calculation of dose by weight: A. When 1-2 gm is the recommended dose, 1 gram will be given if the patient weighs 50-80 kg and 2 grams will be given if the patient weighs more than 80 kg. B. When 600 - 900 mg is the recommended dose, 600 mg will be given if the patient weighs 50-80 kg and 900 mg will be given if the patient weighs more than 80 kg C. Recommended antimicrobials for pediatric patients are the same as for adults. Pediatric dosages should be adjusted on a weight basis and guidelines can be found in Appendix IV. IX. Unless stated otherwise, prophylactic antibiotics should be administered within 1 hour prior to incision. POLICY REVISIONS: I. II. These policies and appendices will be reviewed by the Infection Control Committee and the Department of Anesthesiology at least once every three years. Interim changes to the policy, such as addition, deletion, or modification of items contained in Attachment I, must be proposed by the Chairs or Chiefs of the relevant services and approved by the Infection Control Committee and the Department of Anesthesiology. REFERENCES: Current Joint Commission Standards The Medical Letter on Drugs and Therapeutics, 2002 Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Recommendations for preventing the spread of vancomycin resistance. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1995; 16(2):105-13. Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 1999; 20(4):247-78. American Academy of Pediatrics, The Red Book, 2002 Rx Epocrates 6 Surgical Infection Prevention Guideline: ORIGINATOR: Director of Infection Control and Epidemiology ORIGINATION DATE: SPONSOR: 2006 01/08/96 Direction of Infection Control COLLABORATORS: Chairman, Department of Anesthesia Chairman, Department of Surgery Chairman, Department of Obstetrics-Gynecology Chief of Infectious Diseases Infection Control Committee REVIEWED: 2/17/04 REVISED: 03/01/96 03/15/96 04/10/96 12/10/96 09/11/97 10/31/97 11/24/97 05/04/98 05/20/98 06/29/98 08/28/98 10/20/98 04/01/99 CROSS-REFERENCES: 05/28/99 09/16/99 10/19/99 05/03/00 11/05/01 02/22/05 04/07/06 12/12/06 10/28/08 01/09 N/A APPROVED BY: Patient Services Executive Committee 05/10/06, 12/10/08 Executive Committee of the Medical Staff 05/16/06; 12/17/08 Infection Control Committee 10/28/08 CANCELLATION: EFFECTIVE: N/A 08/03/06 KEY SEARCH WORDS: Infection control, prophylactic, antibiotic, IC, administration of prophylactic, elective surgery ATTACHMENTS: Attachment I: Attachment II: Attachment III: Attachment IV: List of Recommended Drugs Endocarditis Prophylaxis Selection of Antibiotics for Surgical Prophylaxis in penicillin – Allergic Patients Pediatric doses for recommended antibiotics 7 Endocarditis Prophylaxis For dental procedures, procedures that involve the manipulation of gingival tissue, periapical region of teeth or perforation of the oral mucosa or procedures that involve incision or biopsy of the respiratory tract: Endocarditis prophylaxis is now recommended only for the following cardiac conditions: 1. Prosthetic cardiac valve 2. Previous history of infective endocarditis 3. Some forms of congenital heart disease (unrepaired cyanotic CHD, completely repaired CHD with prosthetic material or device for 6 months, repaired CHD with residual defects at site or adjacent to site of prosthetic patch or device) 4. Cardiac transplantation recipients who develop cardiac valvulopathy. Genitourinary or gastrointestinal procedures: Endocarditis prophylaxis is no longer routinely recommended. For procedures on infected skin or musculoskeletal structures: Endocarditis prophylaxis is recommended for patients listed above Table 1. Antibiotic Regimens for Infective Endocarditis Prophylaxis Situation Agent Adults Children 2 g 50 mg/kg 2 g 50 mg/kg 600 mg 20 mg/kg 500 mg 15 mg/kg Ampicillin 2 g Im or IV 50 mg/kg IM or IV Cefazolin; or 1 g IM or IV 25 mg/kg IM or IV 600 mg IM or IV 20 mg/kg IM or IV Oral Amoxicillin Penicillin or ampicillin allergic- oral route Cephalexin*#; Unable to take oral Penicillin or ampicillin allergic and unable to take oral medication * Regimen: Single dose 30 to 60 minutes before dental procedure or Clindamycin; or Azithromycin or clarithromycin. Clindamycin Or other first –or second- generation oral cephalosporin in equivalent adult or pediatric dosage. 8 # Cephalosporins should not be used in an individual with history of anaphylaxis, angioedema, or urticaria with penicillins or ampicillin. References: 1. Wilson, W. et al. Prevention of Infective Endocarditis – Guidelines from the American Heart Association. Circulation (online publication); April 19, 2007 found at http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/reprint/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.183095 9 SELECTION OF ANTIBIOTICS FOR SURGICAL PROPHYLAXIS IN PENICILLIN – ALLERGIC PATIENTS 1. If the patient has had adverse reactions to cephalosporins(1) in the past, administer alternative prophylaxis (2). 2. If neither the patient nor the medical record reports a history of allergy to penicillins, administer standard cephalosporin prophylaxis. (3) 3. If the patient or the medical record reports an allergy to penicillins, the nature of the reaction must be investigated: If the reaction to penicillin was a maculopapular rash or was of a non-allergic nature (4), ask if the patient has tolerated cephalosporins (1) in the past without adverse effects: If the patient has tolerated cephalosporins in the past, or cannot recall receiving cephalosporins in the past, administer standard cephalosporin prophylaxis. If the nature of the reaction to penicillins suggests anaphylaxis or immediate-type (IgE-mediated) hypersensitivity - DO NOT ADMINISTER CEPHALOSPORINS OR PENICILLINS. Administer alternative prophylaxis (2). Footnotes: (1) e.g., Keflex, Ceclor, Kefzol, Mefoxin, Ceftin (cephalexin, cefaclor, cefazolin, cefoxitin, cefuroxime). (2) Usually clindamycin (3) Usually, cefazolin for general, gynecological, vascular, and orthopedic surgery; ampicillin-sulbactam (Unasyn) for colon surgery. (See the Protocol Table above.) (4) e.g., nausea, vomiting, headache, non-specific symptom 10 Pediatric doses for recommended antibiotics Agent Dose Cefazolin Cefuroxime Clindamycin Erythromycin base Gentamicin Neomycin Vancomycin 20 mg/kg 35 mg/kg 10 mg/kg 20 mg/kg 2.5 mg/kg 25 mg/kg (3 doses 1 day before surgery) 20 mg/kg (max. 1000 mg) 11