PROTOTYPE DRUG (Colloid): Normal Serum Albumin (Albuminar
advertisement
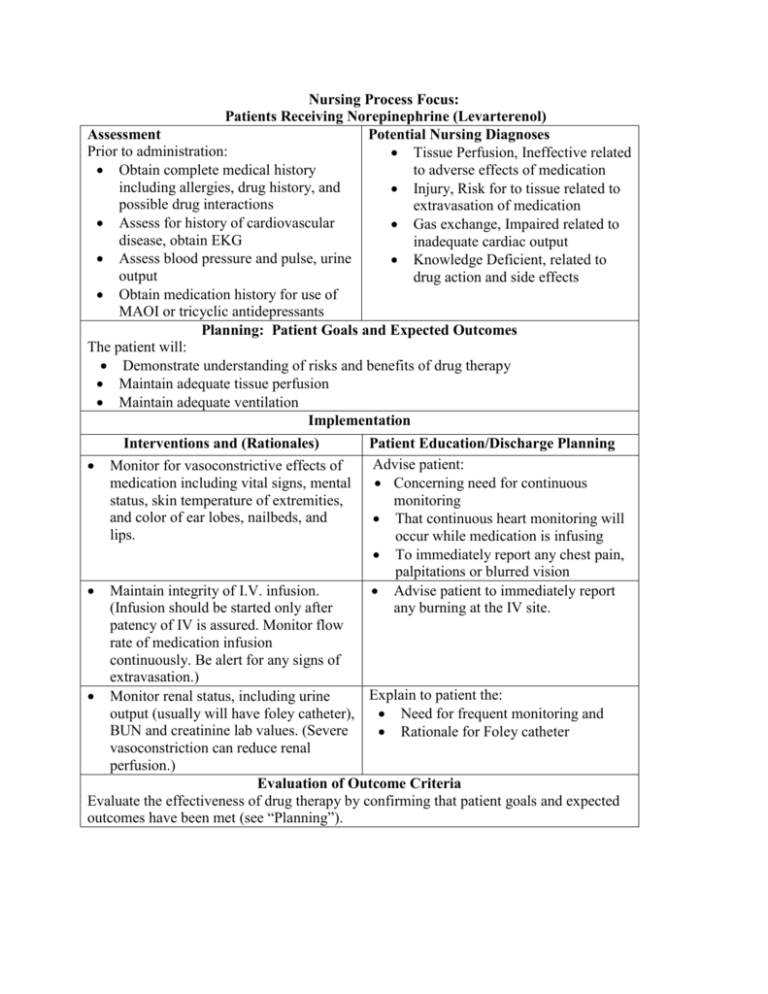
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Norepinephrine (Levarterenol) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Tissue Perfusion, Ineffective related to adverse effects of medication Obtain complete medical history including allergies, drug history, and Injury, Risk for to tissue related to possible drug interactions extravasation of medication Assess for history of cardiovascular Gas exchange, Impaired related to disease, obtain EKG inadequate cardiac output Assess blood pressure and pulse, urine Knowledge Deficient, related to output drug action and side effects Obtain medication history for use of MAOI or tricyclic antidepressants Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Demonstrate understanding of risks and benefits of drug therapy Maintain adequate tissue perfusion Maintain adequate ventilation Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Monitor for vasoconstrictive effects of medication including vital signs, mental status, skin temperature of extremities, and color of ear lobes, nailbeds, and lips. Patient Education/Discharge Planning Advise patient: Concerning need for continuous monitoring That continuous heart monitoring will occur while medication is infusing To immediately report any chest pain, palpitations or blurred vision Advise patient to immediately report any burning at the IV site. Maintain integrity of I.V. infusion. (Infusion should be started only after patency of IV is assured. Monitor flow rate of medication infusion continuously. Be alert for any signs of extravasation.) Explain to patient the: Monitor renal status, including urine output (usually will have foley catheter), Need for frequent monitoring and BUN and creatinine lab values. (Severe Rationale for Foley catheter vasoconstriction can reduce renal perfusion.) Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Dopamine (Dopastat) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Tissue perfusion, Risk for Ineffective related to poor cardiac output Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and Gas exchange, Risk for Impaired related possible drug interactions to inadequate pulmonary blood flow Assess for history of cardiovascular Injury, Risk for (tissue) related to disease, obtain EKG necrosis of local tissue from Assess blood pressure and pulse, urine extravasation of medication output Knowledge Deficient, related to drug action and side effects Assess patient’s weight Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Demonstrate understanding of risks and benefits of medication therapy Maintain adequate tissue perfusion Avoid injury to tissues Maintain adequate ventilation Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Monitor vital signs and tissue integrity frequently. (Vasoconstrictive effects of drug can result in tissue necrosis.) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Advise patient: That continuous cardiac monitoring will occur while patient is receiving medication To immediately report any numbness or tingling in the extremities, or chest pain Inform patient of frequent monitoring and rationale for Foley catheter. Monitor renal status, including urine output (usually will have foley catheter), BUN and creatinine lab values. Ensure patency of IV prior to Instruct patient to immediately report beginning infusion and monitor site any burning at the IV site. frequently. (Extravasation of medication into tissues may result in sloughing of tissue or gangrene.) Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”).








