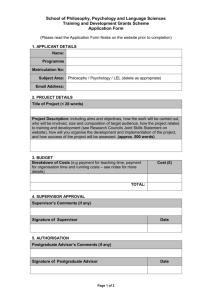
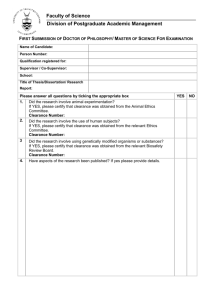
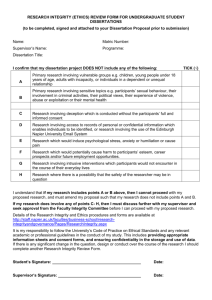
PREPARING FOR THE DOCTORAL DEFENSE
advertisement

A MANUAL FOR MASTERS AND DOCTORAL STUDIES FACULTY OF EDUCATION UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS AND SUPERVISORS NOVEMBER 2004 Message from the Dean In recent years, the Faculty of Education at the University of Pretoria has received hundreds of applications for advanced studies in education at the Masters and PhD levels. Such applications have originated from every continent and brought to the Faculty some of the most outstanding postgraduate students talent in the field of education. In response, the Faculty of Education has decided to enter into a much more rigorous process for selecting students so that ONLY the best and the brightest students are admitted to these advanced programmes in educational theory and research. Accordingly, no student will be selected for M and D studies without passing through an in-depth personal interview with senior academics in the Faculty. Furthermore, every doctoral student will be required to pass a searching public defence of a comprehensive research proposal at the end of the first year of studies. And every M and D student will have to demonstrate some level of participation in the host of research seminars, colloquia and workshops organised annually by the Faculty. Most important, every M and D student must participate in the Annual Postgraduate Research Indaba of the Faculty of Education. In short, the Faculty endeavours from its side to ensure that when you graduate, you will be proud to carry with you a world-class degree in education that should enable you to compete in any university or professional setting with competence and confidence. That is our commitment to our advanced students. In return, we expect you to follow closely the ‘guidelines and procedures’ documented in this Manual for it will enable you to enjoy and take the maximum benefits out of this training programme. With these words, I welcome you warmly to the M and D programmes of the Faculty of Education. Prof J Jansen Dean ii Note from author The purpose of this Manual is to provide supervisors and students with guidelines and procedures that apply to admission, research support, supervision and the finalisation of postgraduate studies in the Faculty of Education. The Manual incorporates the General Rules and Regulations of the University as well as the decisions taken by the Postgraduate Committee, Faculty Board and allied structures of the Faculty of Education pertaining to postgraduate studies. The contributions of all those who have made information available are sincerely appreciated. updated on an annual basis. Jan Nieuwenhuis Coordinator: Master’s and Doctoral Programmes iii This Manual will be reviewed and LIST OF CONTENTS 1 PROCEDURES FOR APPLICATION, SELECTION AND ADMISSION TO MASTER’S AND DOCTORAL DEGREE STUDIES 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Admission requirements Recognition of prior learning Application procedures Selection procedures Admission Additional requirements and support to students studying at postgraduate level 1 1 2 2 3 PROCEDURES FOR DEVELOPMENT AND APPROVAL OF RESEARCH PROPOSAL Purpose of the research proposal Distinguishing between a dissertation and thesis Assessment criteria for a research proposal Technical specifications for a research proposal Content of a research proposal Support to students Procedures for approval of a research proposal Procedures for registration of a title of a dissertation/thesis 5 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 3 4 5 5 6 7 7 8 9 13 PROCEDURES FOR ETHICAL STATEMENT AND PREVENTING PLAGIARISM Purpose of ethical statement Procedures for completing ethical statement Preventing plagiarism 15 20 4.1 4.2 PROCEDURES FOR FINALISATION OF DISSERATIONS AND THESES Monitoring and ensuring progress with studies Submission of dissertation/thesis 5 5.1 5.2 DEFENSE OF DOCTORAL THESIS Purpose and rationale for defence Procedures for doctoral defence 22 22 22 6 6.1 6.2 THE ROLE AND FUNCTION OF THE SUPERVISOR Allocation of supervisors Role and function of supervisor 24 24 24 7 7.1 RESPONSIBILITY OF STUDENTS Rationale 25 25 3.1 3.2 3.3 4 iv 15 16 17 20 20 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 Specific responsibilities Guidelines for writing and getting your dissertation chapters approved Submission of a dissertation/thesis for examination Publishing your dissertation/thesis in electronic format 25 26 29 29 FORMS 31 Application for approval of research involving human respondents Shortened guidelines for submission of thesis/dissertation Preventing plagiarism form 31 34 37 v GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 1 PROCEDURES FOR APPLICATION, SELECTION AND ADMISSION TO MASTER’S AND DOCTORAL DEGREE STUDIES 1.1 ADMISSION REQUIREMENTS 1 Admission requirements are set out in the General Regulations and in the Regulations and Syllabi for the Faculty of Education. Additional requirements set by the Faculty are indicated in this Manual. 2 Applicants for the master’s degree must have obtained an average of at least 60% at honours or related degree level. 3 All students applying for admission to master’s or doctoral studies will be screened and selected on the basis of merit by the relevant academic department on behalf of the Faculty of Education. Selection will be based on documentation submitted by the candidate and personal interviews conducted by the relevant department. The final decision rests with the Faculty and no student will be admitted without an in-depth interview to judge academic readiness and quality of the candidate. 4 The selection process must be seen as an integral part of the quality assurance function of the Faculty and no student will be admitted to postgraduate studies simply on the basis of meeting the minimum requirements laid down. 5 All students enrolling for the Master’s degree (both dissertation only and coursebased Masters students) register for and attend classes for Research Methodology (NME810) and Education Development and Globalisation (OOG810). In exceptional cases, exemption may be granted by the Dean and then only on the basis that the candidate had recently completed a course of comparable standard. 6 All decisions pertaining to the selection and admission of students will be fair and transparent. 1 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 1.2 PROCEDURES FOR THE RECOGNITION OF PRIOR LEARNING 1 Applicants who are not in possession of the minimum academic qualifications set out in the Regulations and Syllabi for the Faculty may apply for the recognition of prior learning. 2 Applications must be directed to the relevant Head of Department. 3 Regulation G.62 stipulates as follows: "In terms of section 10.A of the Universities' Act the Senate may: (a) grant a graduate of another university (either in the Republic or elsewhere) a status at the University that is equivalent to the status the student has at such other university. (b) admit a person, who – (i) has passed examinations at another university or institution (either in the Republic or elsewhere) which the Senate deems equivalent to, or higher than the examinations prescribed for a degree at the University, which are set as a prerequisite for admission to a particular postgraduate course of study, or for the admission of such a person as a research student; or (ii) in another manner has reached a standard of competence the Senate considers adequate for the purposes of postgraduate study or research at the University, as a student for a postgraduate degree or a postgraduate diploma." The regulation provides two alternative routes with regard to the admission of students at postgraduate level in cases where they do not comply with the prescribed requirements: 1. A first possibility is via the academic route where a student has proven himself/ herself on the basis of academic achievement. 2. The second possibility refers to a standard of competence that would make a student eligible to continue with postgraduate studies. With regard to the viewpoint set out above candidates may, inter alia, be evaluated according to the following criteria: Master's studies 1. The application of a student who is not in possession of the required honours degree which would admit him/her to study for the master's degree, but has an academically advanced background, may be considered on grounds of: – the successful completion of an oral/written entrance examination; 2 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES – in which one or more external examiners were involved; and – a submission to the Senate. or 2. In cases where a standard of competence was reached in another manner, status may be granted by means of: – a written motivation by the student which was compiled in conjunction with the head of the department and/or study supervisor, and a recommendation; – the successful completion of an oral/written entrance examination in which one or more external examiners were involved; and – a submission to the Senate. Doctoral studies 1. The application of a student who is not in possession of the required master's degree which would admit him/her to doctoral study, but has an academically advanced background, may be considered on the grounds of: – the successful completion of an oral/written entrance examination; – in which one or more external examiners were involved; and – a submission to the Senate. or 2. In cases where a standard of competence was reached in another manner, status may be granted by means of: – a written submission compiled in conjunction with the head of the department and/or study supervisor in which the standard of competence is indicated; – a report by an external reference(s) motivating the merits of admission to doctoral study; – the successful completion of an oral/written entrance examination in which one or more external examiners were involved; and – a submission to the Senate.” 1.3 APPLICATION PROCEDURES 1 Applicants must apply for admission into master’s or doctoral degree studies before 30 September of the preceding year on the appropriate application and selection form obtainable from Student Administration. (Groenkloof Campus) 2 The application must be accompanied by a typed, two page outline of the theme/topic of the proposed study, the problem statement, and a preliminary 3 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES indication of the importance of the intended research as well as the methodology to be used in the research. The purpose of this preliminary proposal is to assist departments in their selection process. 3 The complete transcript of previous studies must accompany the application. 4 All applications must be handed in at Student Administration. Administration will attach the selection form to the application form and forward all applications to the relevant department for selection purposes. 5 Applicants will not be allowed to submit their applications directly to an academic department. 6 1.4 No applications received after 31 October will be considered. SELECTION PROCEDURES 1 Application and selection forms will be sent to the head of the department. 2 The head of the department will convene a meeting with senior academics in the department to do a coarse sieve selection. This implies that all candidates that do not meet the minimum requirements set by the department will be weeded out. 3 The head of the department will appoint a selection committee to undertake the final selection. 4 Candidates who meet the requirements set by the department will be invited for an interview with the selection panel. The task of the panel is to assess the potential of the candidate to successfully complete his/her studies within the required time frame and of a quality required by the department. 5 The selection panel will in the interview also establish the field of interest of the potential student with the view of identifying a possible supervisor who could assist the student. The following guidelines may serve as a basis for the selection of students: a) The ability to write coherently. b) The ability to interpret research findings. 4 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES c) A working knowledge of their proposed field of study (e.g. what are the current “burning issues”; which are the most respected journals; who are the most respected authors) d) Computer literacy and access to the internet 6 Departments may also request the supervisor of the master’s degree of a PhD candidate or a lecturer from the institution where an applicant did his/her honours degree to submit a confidential report on the applicant (See Forms in Annexure). 7 The chairperson of the selection panel will complete the Admission to post graduate studies form with respect to all the candidates interviewed. This form together with all the other documentation of the student must be signed by the head of the department and forwarded to the Dean’s office for final approval. 8 The selection committee will identify a suitable supervisor for the candidates selected. The name of the candidate and supervisor recommended must be submitted to the Postgraduate Committee of the Faculty for approval. 1.5 DESIGNATION OF SUPERVISORS OR CO-SUPERVISORS 1 The Postgraduate Committee, on the recommendation of the head of the department concerned, designates a supervisor and/or co-supervisor from within the faculty for a particular candidate. Should the Postgraduate Committee refuse to confirm the recommendation by the head of department, the matter is referred to the Dean for a final decision. 2 A person designated as supervisor should hold the necessary qualifications and have the appropriate stature and experience to supervise postgraduate candidates. 3 A person designated as supervisor, must be associated with the University as a full-time lecturer, unless adequate justification can be submitted to the committee as to why an external person should be designated. 5 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 4 On the retirement or resignation of a supervisor from the University's service, he or she may, with approval of the Postgraduate Committee concerned, and after consultation with the head of the department, for a period of not longer than two years after retirement or resignation, still act as supervisor for the student for which he or she was appointed as supervisor, in order to enable such a student to complete his or her dissertation/thesis. For this purpose and for this period such a supervisor will be deemed to be an accredited lecturer of the University. If on the retirement or resignation of a supervisor from the University's service, he or she is no longer prepared to act as supervisor for the student for which he or she was appointed as supervisor, a new supervisor is appointed. 5 The names of all candidates selected and the supervisors approved must be submitted to the Faculty Board for notification. . 1.6 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR DOCTORAL DEGREE STUDIES 1. All students registered for the PhD in Education would be required to pass a doctoral-level course in statistics in education (quantitative research requirement). 2. All students registered for the PhD in Education would be required to pass a doctoral-level course in qualitative studies in education (qualitative research requirement). 3. All students registered for the PhD in Education would be required to submit and pass a substantial theoretical paper that synthesizes the key ideas in the chosen field of study e.g., educational psychology. 4. In specific circumstances, and with adequate and full motivation, students could be exempted from one or more of these requirements 5. In addition, the Faculty encourages all doctoral students to: a) form “theme groups” in which students with similar theoretical or methodological interests meet on a regular basis. b) participate actively in the Monthly Research Seminars and the Annual Research Indaba. 6 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 1.7 ADMISSION 1 Student Administration will finalise the registration of the student on receipt of the approved forms from the Dean’s Office. 2 Student Administration will inform the student in writing of the outcome of the application. 1.8 ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS AND SUPPORT TO STUDENTS STUDYING AT POSTGRADUATE LEVEL 1 The purposes and intent of postgraduate studies (especially at doctoral level) is not only to do research on a specific research topic, but also to contribute to the scholarly development of the student. This will be achieved through the creation of opportunities to advance students’ development (research seminars and a research-support programme) 2 A postgraduate research-support programme to assist students with their studies is offered. The support programme focuses on the following aspects: 3 a) Grounding in advanced topics in educational theory and educational issues b) Improved understanding of research methodological aspects c) Epistemological and ontological aspects in educational research d) Qualitative and quantitative research approaches e) Academic writing skills f) Proposal writing skills Attendance of research support sessions is compulsory for all postgraduate students for the full duration of their studies. 4 Students’ attendance and participation in these sessions will be taken into consideration for purposes of the approval for the continuation of their studies. 7 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 2 PROCEDURES FOR DEVELOPMENT AND APPROVAL OF RESEARCH PROPOSAL 2.1 PURPOSE OF THE RESEARCH PROPOSAL 1 A research proposal is a document that outlines how a person proposes to undertake a specific research project. 2 The research proposal is a crucial step in the research process and must be put through intensive scrutiny to ensure (a) that quality assurance is built into the research process at an early stage in order to optimise the quality of the research that will flow from the approved research proposal; and (b) that the correct supervisor is allocated to the student. 3 The research proposal should therefore reflect the student’s thinking about an identified problem at the start of the research process and must give evidence that the student has a firm grasp of the problem to be studied and has consulted a sufficient body of literature on the topic to be able to develop a substantive proposal. 2.2 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN DISSERTATIONS AND THESES 2.2.1 MASTER’S DEGREE 1 The main purpose of a master’s degree is to train and educate researchers who can contribute to the development of knowledge at an advanced level. 2 A master’s degree may be earned either by completing a single advanced research project, culminating in the production and acceptance of a dissertation or by successfully completing a course work programme requiring a high level of theoretical and intellectual engagement and a research project. 3 Master’s degree graduates must be able to deal with complex issues systematically and creatively, make sound research judgements based on data and 8 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES information, and communicate their conclusions clearly in a dissertation of high quality. 4 The research proposal at master’s degree level should be such that the execution thereof will enable the student to demonstrate the ability to conduct scientific research independently. 5 A dissertation of full scope should be indicative of the ability of the student to conduct research at a master’s degree level and should reflect a critical understanding of the theoretical underpinning of his/her area of focus and of the apposite research methodologies needed to generate data, apply sound data analysis techniques and report comprehensively on the findings of the research in a document of approximately 150 pages. 6 A dissertation of limited scope should reflect the candidate’s ability to conduct independent research at a master’s degree level and should display insight and understanding in the theoretical underpinning of his/her field of study and the research approach needed to execute the research and report on the findings in a dissertation of approximately 75 pages. The units of analysis, the variables, the number of respondents, may be less, but the scientific rigor and standard of work produced must be of comparable standard to that of a full dissertation. 2.2.2 1 DOCTORAL DEGREE At doctoral degree level candidates must be able to undertake research at the most advanced level and with scholarly excellence to produce, defend and get a thesis accepted. The defining characteristic of this qualification is that the graduate must demonstrate high-level research capability and make a significant and original contribution at the cutting edge of the education applicable to his/her field of specialisation. 3 At a PhD level the research proposal should be indicative of more advanced work that engages critical philosophical reflection and will enable the student to make a contribution to our knowledge or understanding of a specific phenomenon within the specialisation field or that will lead to the development of educational 9 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES technology (e.g. the development of a new teaching strategy or assessment method, the development of a measuring instrument, or the development of new interactive computer teaching). 4 A thesis is a scientific research study of a high quality that reflect the ability to deal with concepts and data at an advanced level depicting the thorough grounding of the student in the theoretical underpinning of the field of study as well as research competence to deal with research at a doctoral level and to report comprehensively in approximately 240 pages on the new knowledge and insights gained through the study. 2.3 ASSESSMENT CRITERIA FOR A RESEARCH PROPOSAL 1 Although there are no hard and fast rules on what constitutes a good proposal, the following should be considered: a) Is the topic fresh, stimulating and intellectually challenging? b) Is the research proposal feasible, viable and operationalisable? c) Is the research design appropriate and defensible? d) Is the research relevant to current educational debates and discourses applicable to the programme area? e) Is the research proposal well articulated, concise and direct? f) Does the proposed research have practical applicability that could lead to further research or a better understanding or insight into a specific phenomenon? 2.4 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS FOR A RESEARCH PROPOSAL 1 All research proposals must be typed in 12pt font and 1.5 spacing with 2.5cm margins. 2 All sources consulted must be properly referenced and listed under “References” at the end of the proposal (see reference techniques). 10 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 3 The length of a research proposal for master’s degree studies should be approximately 20-30 pages and for PhD studies, 30-40 pages. The length of a proposal does not necessarily reflect quality. The quality of the proposal is the key aspect to be considered. 4 Attention must be paid to the language use in the proposal. Not only should the proposal be free of grammatical errors, but the scientific and technical language used must be apposite to the standard set for a good proposal. 2.5 CONTENT OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL Although there are no fixed guidelines for a research proposal, most research proposals will include at least the following aspects: 1 The proposed title: The title must be sufficiently clear to reflect the nature and intention of the research. 2 Background/rationale: Provide a succinct outline of the reasons why the study should be undertaken and the general objectives of the study. 3 Preliminary literature review: Should reflect the student’s reading on the topic that helped him/her to narrow down and formulate the research problem. 4 Problem statement: The problem of the study must be stated in clear and unambiguous terms and is often formulated in terms of a central research question with a number of sub-questions or as a number of research hypotheses. 5 Aims/objectives of the study: This section answers the question: What is it that you want to achieve? Students should guard against over ambitious or exaggerated statements of what they want to achieve and should rather focus on tangible concrete outcomes for the research that are appropriate and in line with the level at which the study is conducted. 6 Research design: The research design should clearly answer the key question: What type of research and methodological approach would be best suited to study the problem identified in the problem statement? This is a vital part of the proposal as it maps out the process that will flow from the research proposal. 11 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 7 Research methods: Specific attention must be given to: the unit(s) of analysis, the research techniques (measuring instruments, data-collection methods) to be used; sampling; data analysis; and presentation of data. 8 Timeframe: A realistic outline of the milestones to be achieved in the research specifying the dates on which these milestones will be achieved. This will form the basis of the contract between the supervisor and the student. 9 Provisional outline of chapters 10 References: This is a list of the sources referred to in the text of the research proposal and not a reading list of possible sources that the student will consult. 2.6 SUPPORT TO STUDENTS 1 All of the departments responsible for the supervision of postgraduate students must ensure adequate supervisor guidance and support to assist students. The guidance and support could be linked to the research-support programme offered, but should not be limited to the support programme. 2.7 PROCEDURES FOR APPROVAL OF RESEARCH PROPOSAL 1 The objective of establishing procedures for the approval of research proposals is to enhance the quality of postgraduate studies and all inputs and constructive criticisms forwarded should be aimed and improving the quality of the end product. This does not take away the responsibility of the supervisor and student to ensure that they produce quality proposals. It is not the task of any committee appointed to write the proposal on behalf of a student. 2 All students must successfully complete and defend their research proposal during the first year of registration. 12 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 3 Master’s degree (course work option): a) All students enrolled for the course work or dissertation option for the master’s degree must do Research Methodology (NME 810). One of the outcomes of this course is a research proposal that may (or may not) serve as the basis for the dissertation of limited scope. b) Successful completion of this course may also serve as the formal approval of the research proposal, but departments may request students to also present their proposals at department level. c) In exceptional cases where students have been granted exemption from doing the research methodology course (see 1.1 (4)) these students will be required to prepare and defend their proposals before a departmental committee. d) The “Registration of title form” (“Dwarsvorm”) for the registration of the title and external examiners must be completed and signed by the head of the department as soon as the research proposal has been approved (See 2.8 regarding the process for approval of Titles). An abstract of 500 words on the contents of the study must be attached to enable the external examiner to determine whether he/she will be able to examine the study. 4 Master’s degree (full dissertation) a) The student, with the help and guidance of the supervisor, must draft a research proposal of an acceptable standard. b) Once the supervisor and student are satisfied with the proposal, the student must defend the proposal before an internal departmental committee. c) The following documents must be made available one week prior to the meeting: The research proposal Ethic statement Research timeframe d) All academic staff from the department will be invited to attend the defence of the proposal, but each department must ensure that they appoint a committee of academics on an annual basis to serve as an examining committee. This is to ensure consistency in standards of quality to be applied. 13 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES e) At the meeting, the student will be given twenty minutes to present his/her proposal and forty minutes will be allocated for questions and discussions. The aim of the question and discussion session is to provide inputs and suggestions aimed at improving the quality of the proposal. f) The departmental meeting must include at least the following staff members to enable the defence and approval of the proposal: Chair (Co-ordinator of MEd studies) Head of the department (or representative) Supervisor g) At the conclusion of the defence, the meeting will decide whether the proposal is: Approved. Provisionally approved, provided that changes must be made to the satisfaction of the supervisor. Not accepted, but the student will get the opportunity to rework and resubmit the proposal for defence. Student fails and his/her continuation of studies is terminated. h) On approval of the proposal at the departmental meeting, the student can formally start with his/her research. i) The supervisor will register the approved title and external examiners by completing the Registration of Title form (“Dwarsvorm”) and submitting it to head of the department. (See 2.8 regarding the process for approval of Titles). j) The approved ethic statement must be submitted to the Ethics committee for approval on successful defence of the proposal. 14 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 5 Procedures for doctoral thesis a) The student with the help and guidance of the supervisor must draft a research proposal of an acceptable standard. b) Once the supervisor and student are satisfied with the proposal, the student must defend the proposal before an internal departmental committee who will scrutinise the proposal and make recommendations for the improvement of the proposal. These suggestions should be incorporated into a revised proposal. c) After departmental approval has been secured, the student must defend the proposal at a Faculty meeting. d) The following documents must be made available one week prior to the Faculty meeting: The research proposal Ethic statement Research timeframe e) The Faculty will appoint an "examining committee" of academics representing all the schools and departments in the Faculty on a yearly basis. This committee will consist of the appointed academics, the two research coordinators (ex officio) and the Dean (or his representative). f) All academic staff and doctoral students will be invited to attend the defence of the proposal. g) At the meeting, the student will be given twenty minutes to present his/her proposal and forty minutes will be allocated for questions and discussions. The aim of the question and discussion session is to provide inputs and suggestions aimed at improving the quality of the proposal. h) The Faculty meeting must consist of at least the following staff members to enable the defence and approval of the proposal: Chair (Co-ordinator of PhD studies) The Dean (or representative) Head of the department Supervisor Member of Postgraduate Committee 15 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES Member of Ethics Committee Appointed academics i) At the conclusion of the defence, the meeting will decide whether the proposal is: Approved. Provisionally approved, provided that changes must be made to the satisfaction of the supervisor. Not accepted, but the student will get the opportunity to rework and resubmit the proposal for defence. Student fails and his/her continuation of studies is terminated. j) On approval of the proposal at the Faculty meeting, the student can formally start with his/her research. k) The supervisor will register the approved title and external examiners by completing the Registration of Titles form (“Dwarsvorm”) and submitting it to head of the department. (See 2.8 regarding the process for approval of Titles). k) 2.8 PROCEDURES FOR REGISTRATION OF A TITLE FOR DISERTATION/THESIS 1 On approval of the research proposal of the student, the supervisor must complete the Registration of Title form (“dwarsvorm”) and submit it to the head of the department for approval. 2 The head of the department must ensure that the title and nominated external examiners meet the criteria set for the title as well as those set for external examiners before signing the “dwarsvorm” 3 The following guidelines should serve as a basis for the approval of titles for dissertations and theses: a) Keep the title short (e.g. A conceptual analysis of the concept ‘life-long learning’) b) Do not refer to the details of the locale or area within which the study will be conducted (this demarcation seldom impinges on the study detail and will be demarcated in the substance of the study) 16 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES c) Ensure that the title reflects and projects the nature of the problem being studied (e.g. The efficacy of school governing bodies, OR How new teachers navigate their way through the first year of teaching) d) Avoid vague statements (e.g. Learning problems of foundation phase student teachers) e) The title should reflect a new or innovative focus of study. Avoid topics that are completely over-studied and exhausted (e.g. The implementation of OBE, OR The characteristics of effective principals) f) The title should reflect a topic that is intellectually deep and theoretically promising. Avoid topics that represent ‘fads’ or populist trends in education (e.g. TQM, OR De Bono’s thinking hats) g) Avoid apostrophes (e.g. not Principals’ understanding of continuous assessment, but rather How high school principals understand continuous assessment) h) 4 Ensure correct grammatical usage. The head of department must send the approved “dwarsvorm” to Student Administration. 5 Student Administration will submit the forms to the Postgraduate Committee and then to the Dean for the final approval of the title and the approval of the external examiners. 6 Student Administration submits the approved titles to the Faculty Board for ratification where after it will be registered with the HSRC/NRF. 7 Administration will inform the student and supervisor in writing of the approved title. 8 The student and supervisor must ensure that the exact wording of the approved title appears on the dissertation/thesis. 9 Should the need arise to change an approved title, the same procedure as set out in 1-7 must be followed. 17 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 3 PROCEDURES FOR ETHICAL STATEMENT AND PREVENTING PLAGIARISM 3.1 PURPOSE OF ETHICAL STATEMENT 1 The purpose of ethical review is to ensure that human respondents participate in research freely and without unreasonable risk. Where there is some degree of risk, the process of ethical review has to ensure that the potential benefits outweigh the risk and that the participation of human respondents enjoys the full and informed consent of these respondents. 2 The process of ethical review is intended to protect the researcher as well as the participating human respondents. At a higher level, the process is also intended to elevate the quality of research in the Faculty of Education—where research is conceived not simply as a set of techniques, but as a well-considered, ethically grounded process that builds values such as trust, respect, empathy and dignity among both the researcher and the researched. In such a process, participants are treated as authentic “respondents” in the research endeavour and not simply as “objects” to be studied. 3 The broader goals of the ethical review of research proposals in the Faculty of Education are the following: a) to develop a high standard of ethics and ethical practice in the conceptualisation and conduct of educational research among students and researchers. b) to cultivate an ethical consciousness among scholars especially in research involving human respondents. c) to promote, among researchers, a respect for the human rights and dignity of human respondents in the research process. 4 The ethical review process is guided by the following principles common to research involving human respondents: a) the principle of voluntary participation in research, implying that the participants might withdraw from the research at any time. 18 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES b) the principle of informed consent, meaning that research participants must at all times be fully informed about the research process and purposes, and must given consent to their participation in the research. c) the principle of safety in participation; put differently, that the human respondents must not be placed at risk or harm of any kind e.g., research with young children. d) the principle of privacy, meaning that the confidentiality and anonymity of human respondents must be protected at all times. e) the principle of trust, which implies that human respondents will not be respondent to any acts of deception or betrayal in the research process or its published outcomes. 3.2 PROCEDURES FOR COMPLETING AN ETHICAL STATEMENT 1 It is essential that the academic department approves the ethical statement completed by the student before the student starts with his/her research. This is not the final approval of the ethical statement, but is needed to protect the interest of the student and the Faculty. Master’s degree studies: 2 a) The student must complete the ethics statement and submit it to his/her supervisor prior to the defence and approval of the research proposal. b) The supervisor must scrutinize the ethical statement and ensure that the research proposed will not in any way violate the research code of ethics before signing it and submit it to the head of department for approval. c) The head of the department will approve the ethic statement after the candidate has successfully defended the research proposal where after it must be forwarded to the Ethics Committee of the Faculty. 3 Doctoral degree studies: a) The student must complete the ethics statement and submit it to his/her supervisor prior to the defence and approval of the research proposal 19 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES b) The supervisor will scrutinize the ethical statement and ensure that the research proposed will not in any way violate the research code of ethics before signing it and submitting it for approval by the head of department. c) The ethical statement will serve with the research proposal at the Faculty defence of the proposal. d) The Faculty Committee will approve the ethic statement and research proposal where after it must be forwarded to the Ethics Committee of the Faculty. The Faculty’s representative on the Ethics Sub-committee of Senate will compile 4 a report on the approved ethical statements for Senate. 3.3 PREVENTING PLAGIARISM The following information is reprinted from the UP Anti-Plagiarism website: http://upetd.up.ac.za/authors/create/plagiarism.htm The following information is also available: Guidelines for Staff: http://upetd.up.ac.za/authors/create/plagiarism/staff.htm Guidelines for Students: http://upetd.up.ac.za/authors/create/plagiarism/students.htm 1 In academic writing such as assignments, dissertations, theses, research articles and reports it is standard practice to give an overview of the current knowledge about a topic and to provide evidence to support the points that you make. These ideas will form the foundation for your own arguments and will be integrated into your own work by 2 quoting (using the exact words of another), paraphrasing (using the ideas of another in your own words), or summarising (using the main points of another). If you do not acknowledge them correctly it indicates that either you have not yet mastered the skill of referencing (citation) - which can be learned with the help of your lecturers, or you have given in to cheating - which will have to be unlearned because it is a crime. In either case you may be accused of PLAGIARISM which 20 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES can have serious consequences for your academic career and eventually for your professional career. 3 What is plagiarism? a) You commit plagiarism when you present someone else's ideas - published or unpublished - as if they were your own. People's ideas may be contained in written text articles, books, dissertations, theses, newspapers, magazines, notes, course material, co-students' projects, e-mail messages, data, computer code, everything on the Internet, etc. c) visual text fine art, graphics, photographs, etc. multimedia products websites, video productions, films, CDs, design projects, etc. music compositions, lyrics, CDs, music or sound bytes on the Internet, etc. spoken text speeches, audio recordings, lectures, interviews, etc. Plagiarism is a serious offence. If you are found guilty of plagiarism you may be suspended from the University, criminally charged, or a civil claim may be brought against you. d) All master’s and doctoral students of the Faculty of Education must complete Form A (Preventing Plagiarism) (see Annexure). 5 What is referencing? a) Referencing is a standardised way of identifying sources of information used in academic writing. It is also the way to "get permission" from the author to use her/his ideas by acknowledging the fact that s(he) is the owner of these ideas. 21 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES b) This is done by citing the source in the text whenever you quote, paraphrase, summarise or copy someone else's ideas as part of your work and by including the reference in the list of references at the end of your dissertation. 6 Why should you reference? a) Correct referencing demonstrates that you are familiar with developments in your field that you have read widely, and know who the leading subject specialists are. b) Correct referencing shows that your ideas are related to those of the experts, adding authority to your arguments. Correct referencing enables your readers to locate and consult the sources you have used in order to verify your data and to read more about it. Correct referencing is necessary to avoid plagiarism. 7 Referencing technique (Harvard method) For more information, visit: http://www.ais.up.ac.za/edu/guideref.htm 7.1 How resources are referred to in text (Text referencing) The author, year of publication and page number/s are stated. Remember to acknowledge the sources in detail in your list of references at the end of document. EXAMPLES: Books cited in text (surname year: page no.) e.g.: (Malta 1977:3) or (Behrens 2000:74; Gates 1994:84) or (Allen, Bartlett & Colegrove 1967:15-21) or more than three authors (Esterhuyse et al 1987). If author(s) name appear as part of sentence then: “According to Gagiano (1981:156), the …” Government publications or acts cited in text: e.g. (South Africa 1994, Section.38a), or (SA Parliament: Hansard 1986) or (South Africa 2002) or (White Paper, 1996) or (Department of Education 1999: 25) Theses & Dissertations cited in text: e.g. (Louw 2001: 28) Dictionaries & Encyclopedias cited in text: e.g. (Torsten & McNamarra 1986) Journal articles cited in text: e.g. (Miller 1998: 63) or (Rosen & Sauter 2000: 506-508) 22 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES Newspaper articles in text: e.g. (Meyer 2004: 51) or if no author indicated (Star 2004: 12) Author for a web-site: e.g. “Thomas (1997) summarises …” or if no author indicated (www.edu.com/newsday/25May/html) 7.2 List of References Your References is a list of publications and other information sources referred to in the text, and are included at the end of your assignment, document or dissertation. It should be arranged alphabetically according to the first component of the description (for example the author) and all sources referred to in text must be included in your list of references. Sources that you have read, but you have not referred to them specifically should not be included. In other words, a list of references is not a bibliography. BOOKS The particulars of every entry for a book in the list of sources must be stated in the following order: Author(s) (surname and initials, separated by a comma), Year of publication, Title (in italics, Edition (except the first), Place of Publication and Publisher FOR EXAMPLE: Bogdan, R. 2003. Qualitative research for education: an introduction to theory and methods, (4th edition). Boston: Allyn and Bacon. Carroll, S.R. & Carroll, D.J. 2002. Statistics made simple for school leaders: data-driven decision making. Lanham, Md.: Scarecrow Press. Taylor, J., Marais, D. & Kaplan, A. 1997. Action-learning for development: use your experience to improve your effectiveness. Cape Town: Juta. In cases where more than three authors the first author’s name can be used, together with et al. E.g. Miller, P. et al. 1997. Action-learning. Cape Town: Juta. GOVERNMENT/OFFICIAL PUBLICATIONS Department of Education. 2002. Curriculum 2005 assessment guidelines for inclusion. Pretoria: The Department. Republic of South Africa. 1996. South African Schools Act, 84. Pretoria: Government Printer. BOOKS WITH EDITORS Boil, P.P & Watt, E. (Editors) 2003. Introduction to Qualitative Research. Harvard: University Press. Reference to author in a book with editors: Rowland, J.F.B. 1975. Chemical structure retrieval. In Handbook of special librarianship and information work. Edited by W.E. Batten. 4th ed. London: Aslib: 376-387. 23 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES TRANSLATED BOOKS Mayr, H. 1992. A guide to fossils. Translated by D. Dineley & G. Windsor. Princeton: University Press. THESES/DISSERTATIONS Smithers, R.H.N. 1970. The mammals of Botswana. DSc thesis. University of Pretoria. ENCYCLOPAEDIA ARTICLES The particulars of an article from an encyclopaedia must be stated in the following order: Author(s) (surname and initials, separated by a comma), Year of Publication, Title of the article, Name of the encyclopaedia (in italics), Edition (except the first), Volume, Page(s) on which the article appears Varley, D.H. & Immelman, R.F.M. 1972. Libraries. Standard Encyclopaedia of Southern Africa, vol.6: 618-619. Phoenicia. 1958. The Encyclopaedia Americana, vol.6: 28. JOURNAL ARTICLES The particulars of an article from a journal must be stated in the following order: Author(s) (surname and initials, separated by a comma), Year of Publication, Title of the article, The Journal’s name (italics - it may be abbreviated in line with ISO-standard ISO 4), Month/season, date, Volume, Number, Page(s) on which the article appears EXAMPLE: Boons, J.K. & Blackwood, M. 1998. Classroom instruction: New approaches. Educational Review. Vol.22 (3): 24-28. Hamilton, J.B. & Hoch, D. 1997. Ethical standards for business lobbying. Business Ethics Quarterly, vol.7(3): 117-129. NEWSPAPER ARTICLES The particulars of a newspaper article must be stated in the following order: Author(s)/heading of the report , Year, Title of the article, Title of the newspaper (in italics), Edition date, Page(s) EXAMPLE: Peterson, C. 1987. Falklanders fear weakening of UK resolve, Pretoria News, 21 January: 12. Star. 2004. Teacher strike in perspective (Editorial) 23 July 2004: 8. WORLD WIDE WEB SITES O’Dell, C. & Grayson, C.J. 1997. If we only knew what we know: identification and transfer of internal best practices. Houston, Tex.: American Productivity and Quality Center, 1977. Also available at: http://www.apqc.org/download/kmpaper.pdf (accessed 25 May 1999). Stoffle, C. 1999. The emergence of education and knowledge management as major functions of the digital library. Available at: http://www.ukoln.ac.uk/services/papers/follett/stoffle/paper.html (accessed 25 May 1999). 24 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES Online Journal: Liberman, K., Rich, J.L. & Stewart, T.T.W. 2000. The foundations of a virtual library. Online training, 5(1):1-10. Available: http://lcweb.loc.gov.catdir/pcc (accessed 25 May 1999). ELECTRONIC MAIL Please note: E-mail addresses should never be cited without permission of the owner of the address. FOR EXAMPLE: Thomson, Barry. “Virtual Reality.” Personal e-mail (25 Jan. 1999). Students may also use APA referencing technique. It is your responsibility to verify the referencing technique to be used with your supervisor. 25 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 4 PROCEDURES FOR FINALISATION OF DISSERATIONS AND THESES 4.1 MONITORING AND ENSURING PROGRESS WITH STUDIES 1 It is the responsibility of the supervisor to ensure that the following approvals have been secured before the student commence with his/her research: a) The research proposal has been approved b) The ethical statement has been approved c) The title and external examiners have been approved 2 All students must submit a progress report to the supervisor before the end of each academic year. The supervisor must verify the contents of the report and recommend to the head of the department whether the student could be allowed to continue with his/her studies based on satisfactory progress made during the year. Attendance and participation in the research support programme could also be taken into account. 3 Supervisors must annually submit a progress report to the head of department with regard to all students being supervised (see Annexure for template). 4 Heads of departments must annually submit an integrated progress report of all postgraduate students in the department to the Postgraduate Committee. Heads of department will advise the Dean of the names of students who have not made satisfactory progress. These students may be advised that they will not be allowed to continue with their studies after such a decision has been taken by the Postgraduate Committee. 5 The Postgraduate Committee must prepare a yearly report for the Faculty Board regarding the progress of postgraduate students. 6 Students should be reminded that there is no automatic progress from one year to the next, but that continued participation in the degree programme will be based on progress made during the preceding year. 26 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 4.2 SUBMISSION OF DISSERTATION OF LIMITED SCOPE, DISSERTATION AND THESIS PLEASE NOTE: A dissertation of limited scope in the Faculty of Education is handled in the same manner as a full dissertation 1 The supervisor has the responsibility to ensure that the dissertation/thesis is properly prepared by the student. 2 No student will be allowed to submit a dissertation or thesis for examination before the supervisor has approved it. In cases where a student disputes the decision of the supervisor, the student may appeal to the Postgraduate Committee to review the decision. The decision of the Postgraduate Committee is final. 3 The student must inform Student Administration in writing (three months in advance) of his/her intention submit his/her dissertation or thesis. Student Administration will verify that the external examiners are still available and will provide the student with all the necessary forms needed to submit the dissertation/ thesis. 4 Before the student submits his/her dissertation/thesis, the supervisor will check all the documentation to be handed in and sign the required checklist as well as the declaration that must accompany the article. 5 The correct number of copies of the dissertation/thesis is submitted to the Head: Student Administration, before the closing date for the various graduation ceremonies as announced annually. 6 A student for the master's degree/doctorate, on submission of the dissertation/thesis, has to declare the following before a Commissioner of Oaths: "I declare that the dissertation/thesis, which I hereby submit for the degree ........................ at the University of Pretoria, is my own work and has not previously been submitted by me for a degree at this or any other tertiary institution." 7 For examination purposes, a student must, in consultation with the supervisor, submit a sufficient number of bound copies of the dissertation/thesis, printed on 27 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES good quality paper and of good letter quality, to the Head: Student Administration. 8 If a dissertation/thesis is accepted, but the student is required to make certain amendments in accordance with the examiners' decisions, the amendments should be made to all copies to the satisfaction of the supervisor concerned, who must submit a declaration to this effect to the Head: Student Administration at least one month prior to the graduation ceremony at which the degree is to be conferred. 9 In addition to the copies mentioned in above, each successful student must submit a bound paper copy as well as two electronic copies of the approved dissertation/thesis to the Head: Student Administration in the format specified by the faculty and in accordance with the minimum standards set by the Academic Information Services (AIS) at least one month prior to the graduation ceremony at which the degree will be conferred, failing which the degree will not be conferred. 4.3 1. TECHNICAL EDITING OF THE DISSERTATION AND THESIS The technical editing of a dissertation/ thesis should comply with the following requirements: 1.1 Title page The title page of the copies of the dissertation/thesis submitted should contain the following: (a) (The full title of the dissertation/thesis)………………………………… by (b) (Full name of the student) ……………………………………………… (c) Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree ..………… or Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree ………….……... in the Faculty of ........................……………………, University of Pretoria (d) (Year and date of submission)…………………………………….…….. 28 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 1.2 Format and cover The dissertation/thesis should be submitted in a format not larger than A4. The bound copies must be bound in a hard cover, on which the title of the dissertation/thesis and the name of the student are printed. The name of the student and the year of submission of the dissertation/thesis should appear on the spine of each bound copy. 1.3 Abstract/.summary of the dissertation or thesis (a) A summary of the dissertation/thesis in English of not more than 500 words should be compiled and included by the student in each bound copy of the dissertation/thesis. (b) In addition to the summary in, an abstract, in English, of the doctoral thesis (350 words), as well as a copy of the title page in English, should be submitted together with the examination copies of the thesis. The title of the abstract referred to in contains the following: The full title of the thesis ………………………………………….. by Full name of the student .………………………………………….. Name of the supervisor……………………………………………. Name of the co-supervisor ………………………………………… Department …………………………………………………………... Degree for which the thesis is submitted …………………. A list of key terms to ensure retrieval of the source should also be submitted together with the examination copies of the dissertation/thesis. 1.4 The student submits the summary of the dissertation, and the summary and abstract of the thesis for approval by the supervisor before final presentation thereof. 1.5 For guidelines for the submission and technical aspects relating to dissertation and theses see Annexure 29 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 4.4 1 DRAFT ARTICLE FOR PUBLICATION Unless the Senate, on the recommendation of the supervisor, decides otherwise, a student, before or on submission of a dissertation must submit at least one draft article for publication in a recognized academic journal and in the case of a thesis, must submit proof of receipt of an article by an accredited journal, to the Head: Student Administration. The draft or accepted article, as the case may be, should be based on the research that the student has conducted for the dissertation/thesis and be approved by the supervisor if the supervisor is not a co-author. The supervisor shall be responsible for ensuring that the paper is taken through all the processes of revision and resubmission, as may be necessary. Conferment of the degree may be made subject to compliance with the stipulations of this regulation. 2 The procedures for the submission of the draft article: a) MEd students submit their articles within six (6) weeks after submission of the examination copies but not later that one (1) month prior to the graduation ceremony; b) PhD students submit their articles within three (3) months after submission of the examination copies but not later than one (1) month prior to the graduation ceremony; c) Students submit one (1) copy of the article as well as the completed declaration to the student administration for record purposes. The supervisor will be responsible for submitting the article to the relevant journal. 4.5 1 Intellectual property right All rights in regard to intellectual property that is produced by a student during his/her studies or as a result of any research project conducted at the University or through the use of the equipment of the University, vest in the University, in terms of the contract entered into by the student and/or his/her parents or guardians at registration. This stipulation applies inter alia where the student works under study guidance or as a member of a project team of the University. 30 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 2 A student and the University may conclude an agreement regarding the publication of an essay, a dissertation, thesis and/or draft article for publication. Should the copyright of the essay, dissertation, thesis and/or draft article for publication be the only exploitable intellectual property that arises from such essay, dissertation, thesis and/or draft article for publication, the University would normally transfer the copyright to the student, subject to certain conditions. 3 The University has the right to reproduce and/or publish, in any manner it may deem fit, the essay, dissertation, thesis and/or draft article for publication and to distribute such reproduction. 4 On publication of the essay, dissertation, thesis or the draft article, or an adaptation thereof, it should be stated that it emanates from a bachelor's/master's/doctoral study at the University. The name of the supervisor/promoter and the department, in which the study was completed, should also be acknowledged. Reprints should state the title and date of the original publication. 31 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 5 EXAMINATION OF DISSERTATION/THESIS 5.1 APPOINTMENT OF EXAMINERS 1. The supervisor in consultation with the head of the department concerned compiles a list of names of potential examiners both inside and outside of South Africa from which the Postgraduate Committee appoints examiners in the following manner: (i) For dissertations: At least one internal examiner and at least one external examiner from outside the University. (ii) For theses: At least one internal examiner and at least two external examiners from outside the University, of whom at least one must preferably be from outside South Africa. 2 An external examiner should not be associated in any way with the candidate or in any way be involved in the research that the candidate has done previously. 7 As soon as a potential examiner has accepted his appointment as examiner, he/she is supplied with a formal letter of appointment as well as documentation on the policy of the University concerning examinations. Examiners must sign an acceptance form which is to be returned to the Head: Student Administration. 8 The identity of the examiners, other than the internal examiners, may not be revealed to the candidate until the examination process has been completed and then only with the consent of the examiner and the Postgraduate Committee. 5.2 CRITERIA FOR EVALUATION 1 A dissertation must be proof of a candidate’s ability to work independently. 2 A thesis must contain proof of a candidate’s ability to conduct original research that contributes to the development of new knowledge and expertise. (a) A dissertation/thesis is also evaluated on the following and should otherwise also comply with the requirements stipulated by faculties: i scientific and academic standard of research; research procedures and techniques; methodology; definition and extent of research; theoretical 32 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES foundation; coverage of literature and comprehension of field of research; ii scientific and academic quality of processing; presentation, analysis and synthesis of data, structure and logical development and arrangement of content; as well as critical findings, conclusions and recommendations; iii editing and use of language; iv technical finish and layout which must meet the requirements set by faculties; and v whether the dissertation/thesis or parts thereof is publishable. 5.3 EXAMINERS’ REPORTS 1 Every examiner independently and individually submits a report to the Head: Student Administration. The reports are treated confidentially. 2 Every report has to contain one of the following recommendations, namely: (i) that the degree be conferred without any changes to be made by the candidate to the dissertation/thesis; (ii) that the degree be conferred as soon as minor changes have been made to the dissertation/thesis by the candidate, to the satisfaction of the head of the department; (iii) that the degree be conferred as soon as the candidate has made major changes to the dissertation/thesis to the satisfaction of the examination panel; (iv) that the dissertation/thesis is not of the required standard and that the candidate be invited to resubmit it for re-examination after reviewing the dissertation/thesis; (v) that the dissertation/thesis be rejected and that the candidate does not pass; (vi) that the candidate should be called for oral questioning by the examination panel prior to finalisation of the result; (vii) in addition to the above in the case of dissertations, the mark that the candidate has achieved: on condition that at least 50% be regarded as a pass mark and 75% as a pass with distinction. 33 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES (b) The reports are made available to the head of the department by the Head: Student Administration. 3 In the case of a dissertation, the supervisor and the head of the department review the examiners’ reports and submit a consolidated report with recommendations to the Postgraduate Committee: In the case of a thesis, the examiners’ recommendations made are preliminary in 4 nature and subject to the successful completion of an oral examination by the candidate. The supervisor arranges an oral examination chaired by the Dean during which the candidate is required to defend his/her thesis. The examiners appointed constitute the examination commission for the oral examination. If an examiner cannot participate in the examination, the Postgraduate Committee appoints an additional external examiner for the purpose of this examination. 5 The panel will consist of the following people who will conduct the oral defence: 6 a) All the external Examiners b) The supervisor (and co-supervisor) c) The Chair of School d) The Head of Department e) Departmental Representative f) The Dean The panel will have the following documentation at their disposal: a) All the external examiner reports b) the supervisors’ reports 7 The duration of the oral defence is normally two hours. 8 After the presentation by the candidate, the examination commission constitutes a closed meeting to consider the success of the candidate’s representation, to review all the examiners’ reports and to submit a consolidated report with a recommendation to the Postgraduate Committee. 9 The content of the reports of the examiners and the examination committee may only be reveal to the candidate on approval of the external examiners and the Postgraduate Committee. 34 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES No examiner’s report may be ignored. In the event of a dispute, the Dean in 10 consultation with the Postgraduate Committee and the head of department will appoint an additional external examiner of international standing on the topic of the research. The appointed examiner will submit his/her report to the Postgraduate Committee. The Postgraduate Committee will submit a recommendation to the Dean for approval. The Dean in consultation with the Postgraduate Committee will reach a final decision on the outcome of the 5.4 PURPOSE AND RATIONALE FOR DEFENCE 1 The successful defence of a doctoral degree forms an integral part of the degree study and will focus on the following three aspects: the intellectual component of the defence: does the candidate demonstrate sufficient intellectual depth, breadth and dexterity of knowledge and understanding to qualify as a doctor of the University of Pretoria? the textual component of the defence: does the candidate understand with sufficient nuance and insight the complexities underlying the theoretical and methodological substance of the thesis? the personal component of the defence: does the candidate express a disposition appropriate for a new scholar in the course of conducting the defence? 2 The doctoral defence forms part of the quality assurance function of the university and students must realise that i) ii) iii) iv) They can fail the doctoral defence despite a well written thesis They can fail the degree despite a good oral defence They can fail despite positive reports by the South African examiners It is very likely that they may be asked to make editorial and/or substantive changes to their thesis. 35 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 6 ROLE AND FUNCTION OF THE SUPERVISOR 6.1 ROLE AND FUNCTION OF SUPERVISOR 1 The supervisor and co-supervisor will act as advisers, guides, quality controllers and "pastors". It remains their main responsibility to ensure that all postgraduate studies are of a high quality and they should aspire to instil in their students a sense of striving for excellence. 2 It is the responsibility of the student to initiate the first contact with the supervisor after the student has been informed of the name of the supervisor allocated. 3 During the first meeting, the supervisor and student must reach an agreement in terms of how they will interact and the supervisor should clearly spell out his/her expectations of the student. This first interaction should serve as a basis for a working contract between the supervisor and student. 4 It is the supervisor’s responsibility to ensure that the procedures set out in terms of the development and approval of a research proposal, the development of an ethics statement, the defence of proposals, the submission of the final dissertation/ thesis is adhered too. 36 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 7 RESPONSIBILITIES OF STUDENTS 7.1 RATIONALE 1 Postgraduate studies remain the primary responsibility of the student. This includes initiating contact with the supervisor, knowing and understanding University and Faculty administrative requirements, and maintaining interest and commitment. 2 All postgraduate students of the Faculty are expected to be computer literate and have adequate Internet access. One of the primary means of communication between the supervisor and students will be computer-based. 7.2 SPECIFIC RESPONSIBILITIES 1 All postgraduate students registering for the first time for the MEd or PhD must attend the Orientation day at the start of the academic year. During this event students will be introduced to the graduate centre, the library, Faculty research foci, funding opportunities, and supervisors. 2 Specific research support sessions will be held during the course of the year. It is important to attend these sessions, as the main objective is to assist students in their scholarly development as well as with proposal writing, literature surveys, defending a proposal, etc. 3 All students must defend their research proposals. This exercise is aimed at sharpening your research skills and to improve the quality of your research. All students must successfully defend their proposals before they will be allowed to continue with their studies. Students who fail their defence will be requested to terminate their studies. 4 The purpose of the proposal presentation is for the student to give account of the philosophical underpinnings of the proposed work, how it links up with international, national and local realities and to conceptualise the research methodology. The student should be able to defend the selected methodology, 37 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES based on its merits and demerits, and should also be able to reject the most obvious alternative methodologies. 5 The research proposal must be successfully defended during the first year of study. Failure to do so may result in a student not being allowed to continue with their studies. 6 All students must complete the ethics statement prior to their research proposal being defended. 7 Conducting the fieldwork for the research is the main responsibility of the student, but all data gathering instruments to be used must be approved by the supervisor prior to the fieldwork. 8 The student must submit annual progress reports. Unsatisfactory progress may lead to the student being refused to continue with his/her studies. 9 Students must, on completion of their studies, write and submit an article for publication in a journal. This article is published under the name of the student, supervisor and co-supervisor (in that sequence). It stands to reason that the involvement of authors should be reflected by the sequence of names. 7.2 GUIDELINES FOR WRITING AND GETTING YOUR DISSERTATION CHAPTERS APPROVED (These guidelines are based on some hard lessons learnt in recent times from students submitting dissertation chapters and even full drafts for evaluation by their supervisors and, eventually, for external examination. Please study it with all due attention to avoid painful delays and even failure to cross the final hurdles in the research process.) 1. You cannot expect that your first draft of a chapter will be accepted as is. Prepare yourself to accept that your supervisor would probably have seen a number of drafts for detailed feedback and rewriting. This further means that you and your supervisor should have had at least 3-5 detailed feedback discussions on the individual drafts of each and every chapter even before the full draft dissertation, as a whole, goes through this process of feedback and rewriting. A dissertation 38 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES /thesis must pass through a decent incubation period, under the heat of scrutiny, before it is ready to leave the baking oven for quality control. 2. You must take care of the basic language editing. Supervisors do not have the time, and should not be distracted into making comments on spelling errors and faulty sentence constructions. Do not hand-in any chapters or full drafts of your dissertation unless you did your own spell-checks and had a language editor work through the manuscripts; in this regard, choose a decent language editor and not someone for whom English is a second language. Simple things like making sure every page is numbered, every sentence is complete, and every argument is linked, can really frustrate a supervisor. 3. The most important chapters in your dissertation/thesis are the 2-4 chapters representing the actual data from the original research. These chapters must occupy most of the “space” in the dissertation – do not take more than 40-60 pages before you get to these data chapters. Too many students spend all their time describing the nature of the study, the literature review, the methodology etc without getting to the substance of the dissertation/thesis itself - what did you find or discover (the data chapters) and what does it all mean (the final chapter)? 4. It is important in your data chapters that you adopt an acceptable mode of writing in these sections. Do not use too many sub-headings and, worse, do not write a line-by-line report on each item’s results in your questionnaire or interviews e.g., 18% of learners say they like ice-creams; 12% say they are diabetic etc. Use these guidelines: 4.1 write in narrative form i.e., coherent stories written in a logical and sequential narrative throughout. 4.2 weave the data from various sources (interviews, questionnaires, observations, statistics, profiles, dairies etc) into the storyline. 4.3 identify the key claim from the data and state that claim with authority e.g., ‘the majority of teachers have great difficulty understanding the language of outcomes based education.’ 4.4 describe the supporting evidence to back the claim using the full range of data from the various sources (literature, interviews, questionnaires, 39 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES observations, statistics, profiles, dairies etc). For each claim, you need a substantial description of the evidence that runs for at least five pages per claim. For example, the judicious use of quotations from teachers (in this OBE example) could really give powerful insights into the difficulties of teachers in understanding the language of outcomes based education 4.5 Develop a narrative around the evidential statements i.e., it does not help to simply put down one table of statistics after another, or one quotation after another, without an embedded narrative that explains, analyses, interprets— and also connects—one set of evidence after another. 5. When you describe the methodology or methods for your study, please refrain from simply listing the published literature on the subject. Rather, explain how exactly you went about collecting data for the study; justify why you chose a particular sample (substantiate based on literature); describe the purpose of each particular method for data collection; outline the validity checks applied in the inquiry (substantiate based on literature); and identify the limitations of these methods, and how you dealt with them i.e., the limitations. 6. The final chapter is really where you bring the theory and the data into conversation; it is a synthesis or summary of the data presented in the previous data chapters that are now interpreted in the light of the theoretical or conceptual framework described in an earlier chapter. This final chapter is absolutely crucial since it takes the data beyond the specific case or instance or country that you studied, and interprets its meanings in the broader international context of scholarship on the subject. It is this chapter that often determines if the study was worthwhile at all, and whether it deserves to be passed. So you cannot simply rattle-off some concluding remarks in this final chapter; it deserves careful and detailed attention as you think back over the data presented in the context of the theoretical stance adopted in the study. It is in this chapter that you must grapple with the question that will be posed in the oral examination: “after four or more years of research for this dissertation, what do we (the community of international scholarship) now know about your topic that we did not know before your started this inquiry?). This question penetrates the superficial. 40 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 7. It is not uncommon for students, especially those working in a qualitative mode, to have to rewrite earlier chapters based on what happens in later chapters— even modifying or dropping one or more of the original research questions. You should feel comfortable with this possibility. 8. A typical division of chapters—and creative students need not be limited to either these divisions, their sequencing or their titles: 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Literature Review 8.3 Theoretical or Conceptual Framework 8.4 Research Design and Methodology 8.5 Presentation of Findings (research question 1) 8.6 Presentation of Findings (research question 2) 8.7 Presentation of Findings (research question 3) 8.8 Synthesis 7.3 PUBLISHING YOUR DISSERTATION OR THESIS IN ELECTRONIC FORMAT (see http://upetd.up.ac.za/ETD-db/) 1 Students are encouraged to consider this very seriously because it is far less cumbersome to do this (or to have it done) on a computer than to have to deal with printers, copiers and binders, 3 a web thesis/dissertation costs far less than a stack of paper copies, the accessibility of your work increases a enormously. If the thesis/dissertation has been created on MS Word or some other text/word processing package it will be converted to PDF which can be read the world over with Adobe Acrobat. 4 All the necessary instructions are available on our web site (http://upetd.up.ac.za): UP Postgraduate Students. One needs approximately one hour per chapter. 5 If your thesis/dissertation has been put on the web you are exempted from the two copies which have to be delivered to the Academic Information Service. 41 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 8 ACADEMIC WRITING 8.1 GENERAL GUIDELINES 1. Assorted, diverse observations on a topic are not enough to make an accomplished academic essay. An essay should have an argument. It should answer a question or a few related questions (see 2 below). It should try to establish something - develop a single "thesis" or a short set of closely related points - by reasoning and evidence, especially including apt examples and confirming citations from any particular text or sources your argument involves. Gathering such evidence usually entails some rereading of the text or sources with a question or provisional thesis in mind. 2. Your first effort should be to formulate as exactly as possible the question(s) you will seek to answer in your study. Next, develop by thinking, reading, and jotting a provisional thesis or hypothesis. Don't become prematurely committed to this first answer. Pursue it, but test it even to the point of consciously asking yourself what might be said against it - and be ready to revise or qualify it as your work progresses. (Sometimes a suggestive possible title one discovers early can serve in the same way.) 3. There are many ways in which any particular argument may be well presented, but an dissertation/thesis's organisation - how it begins, develops, and ends - should be designed to present your argument clearly and persuasively. (The order in which you discovered the parts of your argument is seldom an effective order for presenting it to a reader.) 4. Successful methods of composing a chapter are various, but some practices of good writers almost invariably include a combination the following: 42 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES a) They start writing early, even before they think they are "ready" to write, because they use writing not simply to transcribe what they have already discovered but as a means of exploration and discovery. b) They don't try to write a chapter from beginning to end, but rather write what seems readiest to be written, even if they're not sure whether or how it will fit in. c) Despite writing so freely, they keep the chapter's overall purpose and organisation in mind, amending them as drafting proceeds. Something like an "outline" constantly and consciously evolves, although it may never take any written form beyond scattered, sketchy reminders to oneself. d) They revise extensively. Rather than writing a single draft and then merely editing its sentences one by one, they attend to the whole chapter and draft and redraft - rearranging the sequence of its larger parts, adding and deleting sections to take account of what they discover in the course of composition. Such revision often involves putting the chapter aside for a few days, allowing the mind to work indirectly or subconsciously in the meantime and making it possible to see the work-in-progress more objectively when they return to it. e) Once they have a fairly complete and well-organised draft, they revise sentences, with special attention to transitions - that is, checking to be sure that a reader will be able to follow the sequences of ideas within sentences, from sentence to sentence, and from paragraph to paragraph. Two other important considerations in revising sentences are diction (exactness and aptness of words) and economy (the fewest words without loss of clear expression and full thought). Lastly, they proofread the final copy. 8.2 UNDERSTANDING THE TOPIC OF YOUR STUDY 1 Before you plunge into research or writing, think through the specific topic you are dealing with. Remember, you are not being asked just to 43 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES collect facts, but to develop and display your powers of reasoning. You can save yourself time and frustration by beginning this reasoning early in the process. Here are some steps: a) Note the key terms, including those naming parts of the topic and those giving directions for dealing with it. Look especially for words that define the kind of reasoning you should be using: why, how, analyse, compare, evaluate, argue, etc. Be sure you understand the specific meanings of these terms. Analyse means that you have to look behind the surface structure of your source material. See the relationship of parts to whole. Be able to recognise relationships such as cause and effect, even if it's unstated in what you read. Look for underlying assumptions and question their validity. How and why imply an answer reached by analysis. Compare means that you have to find differences as well as similarities. You will need to formulate the aspects which you are looking at in each item; consider organising your paper by using these aspects as headings. Evaluate stresses applying your judgement to the results of your analysis. It asks for an opinion based on well-defined criteria and clearly stated evidence. Wording such as to what extent also asks for an evaluation of an idea. Argue (or agree or disagree) likewise asks you to take a stand based on analysis of solid evidence and explained by clear reasoning. You will need to consider other possible viewpoints and defend your own in comparison. b) Note which concepts or methods the topic asks you to use. Are you to argue a point with others, or to explore your own responses? Does the topic ask you to go into depth about some material already 44 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES covered, or does it suggest that you evaluate a theory or model by applying it to an example from outside the module-specific material? Whatever the design, an essay assignment expects you to use module-specific concepts and ways of thinking; it encourages you to break new ground for yourself in applying module-specific methodology. c) To generate ideas from which you can choose the direction of your research or preliminary analysis, ask yourself questions about the specific topic in terms of the concepts or methods that seem applicable. Looking for controversies in the material will also help you find things worth discussing. You may want to look at some general articles in reference works such as encyclopaedias to see how others have framed questions or seen problems to discuss. 2 The key to making sense of your research topic is very simple: Read the topic with care, it tells you what you need to do. Take your time figuring the topic out! Many students' research proposal problems begin with failing to analyse the topic carefully at the start of the project. It's also a good idea to refer frequently to the topic as you go along, to ensure that you stay on track. 3 In course work modules you will be expected to submit assignments in essay format. Although careful analysis of essay topics will usually help you work out what your lecturer wants you to do with a particular assignment, it's not an infallible approach.. 4 Here are a few key questions you can ask: What is the purpose of this assignment? Is its purpose to allow you to demonstrate what you can do or what you know? How does it relate to the overall exit-level outcomes of the module? How does the lecturer want you to do the assignment? What kind of process does the lecturer suggest you use (i.e. with respect to prewriting, writing, and revising)? Is the subject clear? What form should the essay 45 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES take? Should it be mainly expository, analytical, comparison/contrast, critical, or some other mode or combination of modes? For whom are you writing? Who is the audience? Just the lecturer? Your peers? Everyone in the field of Educational Psychology? The audience for whom you write determines many aspects of your essay, particularly with regard to the inclusion of background information and the citation of sources; it is essential information, and is seldom specified in essay topics. How will the assignment be assessed? What would constitute a successful response? An outstanding response? A merely adequate response? A failure? 5 Using thesis statements: When you write a dissertation/thesis, your reader will probably expect a clear statement of your position. Here are some characteristics of good thesis statements. Note that good thesis statements indicate a theoretical basis and promise substantial support. It makes a definite and limited assertion that needs to be explained and supported by further discussion (e.g. “The success of the last scene in Midsummer Night's Dream comes from subtle linguistic and theatrical references to Elizabeth's position as queen.”) It shows the emphasis and indicates the methodology of your argument (e.g. “Neither neo-protectionism nor post-industrial theory explains the steep reversal of fortune for the South African National Qualifications.”) It shows awareness of difficulties and disagreements (e.g. “Dutch laws on euthanasia have been rightly praised for their attention to the principles of selfdetermination. Recent cases, however, show that they have not been able to deal adequately with issues involving technological intervention of unconscious patients. Hamarckian strategies can solve at least the question of assignation of rights.”) 46 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 6 Developing coherent paragraphs. Paragraph structures provide a map for your ideas, guiding readers through your reasoning. Keep this simple set of principles in mind while you write, and use it as a checklist when you're revising. Use Topic Sentences: State the central idea of each paragraph explicitly in a topic sentence. That's one way of demonstrating that you have thought through your material. In academic writing, the topic sentence nearly always works best at the beginning of a paragraph so that the reader knows what to expect. Don't count on your readers to guess what your paragraph is going to be about. Expand on the Topic Sentences. The body of a paragraph develops and demonstrates what your topic sentences state. Here are some common patterns: o Explain more fully what you mean, giving definitions or indicating distinctions. o Offer details, examples, or relevant quotations (with your comments). o Follow through a logical sequence, showing the connections among your ideas in a recognisable pattern such as cause and effect or comparison and contrast. Show Connections. Be sure your intended logic is clear. Often the simplest words do the most to pull together ideas. Pronouns such as it and they and this keep the focus on the ideas announced at the beginning of the paragraph - as long as they are clearly linked to specific nouns. Deliberate repetition of key words also helps (but guard against clumsy formulations in using repetitive words). Certain specialised linking words (e.g. in addition, moreover, more importantly, however, in contrast, etc.) can also be powerful tools for pulling ideas together. But don't just sprinkle them into your sentences - use them to support your logic. Relating your topic sentences to your thesis can help strengthen the coherence of your chapter. If you include a thesis statement in your introduction, then think of incorporating a keyword from that statement into the topic sentence. But you need not be overly explicit when you echo the thesis statement. Better to be subtle rather than heavy-handed. Do not forget that your topic sentence should do more than just establish a connection between your paragraph and your thesis. Use a topic sentence to show how your paragraph contributes to the development of 47 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES your argument by moving it that one extra step forward. If your topic sentence merely restates your thesis, then either your paragraph is redundant or your topic sentence needs to be reformulated. If several of your topic sentences restate your thesis, even if they do so in different words, then your work is probably repetitive and than scholarly quality. Choose appropriate paragraph length. A series of long paragraphs can you’re your work dense and unpleasant to read. Check any paragraph that is longer than a page to see if it would work better as two or more paragraphs. Break it at a logical place (e.g., where your focus shifts), and see whether you need to create new topic sentences to make the shift clear. Also look out for paragraphs that are only two or three sentences long. They make academic writing seem disjointed or skimpy. Try combining a few short paragraphs into one, using a single topic sentence to hold them together. 7 What is a review of the literature? a) A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. A literature review forms an integral part of dissertation and thesis writing. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries. b) Besides enlarging your knowledge about the topic, writing a literature review lets you gain and demonstrate skills in two areas: information seeking: the ability to scan the literature efficiently, using manual or computerised methods, to identify a set of useful articles and books critical appraisal: the ability to apply principles of analysis to identify unbiased and valid studies. 48 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES c) A literature review must be organised around and related directly to the thesis or research question you are developing, synthesise results into a summary of what is and is not known, identify areas of controversy in the literature and formulate questions that need further research d) Know what type of literature review you will be conducting? Are you looking at issues of theory, methodology, policy, or quantitative/ qualitative research? Pay specific attention to the scope of the literature review (must be comprehensive without getting bugged down in trivialities or irrelevant detail). The level and rigor of the analysis is also essential elements to consider. e) Be critical and reflective in your analysis of the literature. Follow through a set of concepts and questions, comparing items to each other in the ways they deal with them. 8 How does “critical reading” relate to “critical writing”? Critical writing depends on critical reading. Your work will involve reflection on written texts - the thinking and research that has already been done on your subject. In order to write your own analysis of this subject, you will need to do careful critical reading of sources and to use them critically to make your own argument. The judgments and interpretations you make of the texts you read are the first steps towards formulating your own approach. a) Critical Reading: To read critically is to make judgements about how a text is argued. This is a highly reflective skill requiring you to "stand back" and gain some distance from the text you are reading. Reading should not be based on reading for information, but it is aimed at looking for ways of thinking about the subject matter. Avoid approaching a text by asking "What information can I get out of it?" Rather ask "How is the evidence (the facts, examples, etc.) used and interpreted? How does the text reach its conclusions? Here are some hints: 49 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES Determine the central claims or purpose of the text (its thesis). A critical reading attempts to assess how these central claims are developed or argued. Begin to make some judgements about context. What audience is the text written for? In what historical context is it written? Distinguish the kinds of reasoning the text employs. What concepts are defined and used? Does the text appeal to a theory or theories? Is any specific methodology laid out? If there is an appeal to a particular concept, theory, or method, how is that concept, theory, or method then used to organise and interpret the data? You might also examine how the text is organised: how has the author analysed (broken down) the material? Be aware that different disciplines (i.e. Psychology, Sociology, Philosophy, Theology) will have different ways of arguing. Examine the evidence (the supporting facts, examples, etc) that the text employs. Supporting evidence is indispensable to an argument. How is the evidence is used to develop the argument and to control claims and concepts. What counts as evidence in this argument? Is the evidence statistical? Literary? Historical? etc. From what sources is the evidence taken? Are these sources primary or secondary? Critical reading involves evaluation. Your reading of a text is already critical if it accounts for and makes a series of judgments about how a text is argued. If the argument is strong, what is it that makes it strong? Could it be better or differently supported? Are there gaps, leaps, or inconsistencies in the argument? Is the method of analysis problematic? Could the evidence be interpreted differently? Are the conclusions warranted by the evidence presented? What are the unargued assumptions? Are they problematic? What might an opposing argument be? When you begin to think about how you might use a portion of a text in the argument you are forging in your own paper, try to remain aware of how this portion fits into the whole argument from which it is taken. Paying attention to context is a fundamental critical move. 50 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES When you quote directly from a source, use the quotation critically. This means that you should not substitute the quotation for your own articulation of a point. Rather, introduce the quotation by laying out the judgments you are making about it, and the reasons why you are using it. Often a quotation is followed by some further analysis. Critical reading skills are also critical listening skills. In your lectures, listen not only for information, but also for ways of thinking. Your lecturer will often explicate and model ways of thinking that are appropriate to your field of specialisation. b) Taking notes from “research reading” If you take notes efficiently, you can read with more understanding and also save time and frustration when you come to write your paper. These are three main principles: Know what kind of ideas you need to record Focus your approach to the topic before you start detailed research. Then you will read with a clear purpose in mind, and you will be able to sort out relevant ideas. Review the commonly known facts about your topic, and also become aware of the range of thinking and opinions on it. Make a preliminary list of the subtopics you would expect to find in your reading. These will guide your attention and may come in handy as labels for notes. Your research question should allow for reasoning as well as gathering of information - not just what the most important factors are that may influence educational policy, for instance, but how applicable and relevant these factors are for our understanding of the development of education policies. c) Summarise rather than quote. Copy out exact words only when the ideas are memorably phrased or surprisingly expressed - when you might use them as actual quotations. Otherwise, compress ideas in your own words. Paraphrasing word by word is a waste of time. Choose the most important ideas and write them down as labels or headings. Then fill in with a few sub points that explain or exemplify. 51 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES d) Label your notes intelligently. Whether you use cards or pages for notetaking, take notes in a way that allows for later use. e) Save bother later by developing the habit of recording bibliographic information in a master list when you begin looking at each source (don't forget to note book and journal information on photocopies). Then you can quickly identify each note by the author's name and page number; when you refer to sources in the essay you can fill in details of publication easily from your master list. Keep a format guide handy. f) Try as far as possible to put notes on separate cards or sheets. This will let you label the topic of each note. Not only will that keep your note-taking focussed, but it will also allow for grouping and synthesising of ideas later. g) Articles can be complex. Not everything the author says will be a positive conclusion or a premise in support of his conclusion. Sometimes he'll be supporting his view with a thought-experiment. Sometimes he'll be arguing for a distinction which his positive view relies on. Sometimes he'll be arguing that another philosopher's views or arguments ought to be rejected. Sometimes he'll be defending a view against somebody else's objections. Philosophers often provide auxiliary arguments, arguments for important premises they appeal to in support of their main conclusion. The key to getting it right is to read and reread the whole article. When you've figured out what the main conclusion of an article is, and what the overall structure of the article is, go back and read the article carefully. Pay attention to how the various parts fit together. Most importantly, figure out what the author's central argument(s) are. What reasons does he / she offer in support of his / her conclusions? Where in the article does he / she put these reasons forward? h) In your notes, you might make a quick outline of the article's major argumentative "pieces." Draw arrows to diagram how you think those pieces fit together. Obviously, you're only in a position to evaluate an author's argument when you've done the work of figuring out what it is 52 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES he's really saying, and how his arguments work. When you come to that point, you can start asking questions like these: Do you agree with the author? If not, what do you think is wrong with his reasoning? Does he appeal to some premise which you think is false? (Why do you think it is false?) Is there some assumption which the author does not make explicit, but which you think is false? Does his argument equivocate or beg the question? i) The focus of a dissertation/thesis should be on your understanding of the topic. Note that most scientific writing relies on summary rather than quotation. If you include too much quotation in your dissertation, it takes on an eclectic character where your voice is swamped by others’ ideas. Consider quoting a passage from one of your sources if any of the following conditions holds: The language of the passage is particularly elegant or powerful or memorable. You wish to confirm the credibility of your argument by enlisting the support of an authority on your topic. j) The passage is worthy of further analysis. You wish to argue with someone else's position in considerable detail. If an argument or a factual account from one of your sources is particularly relevant to your paper but does not deserve to be quoted verbatim, consider paraphrasing the passage if you wish to convey the points in the passage at roughly the same level of detail as in the original or summarising the relevant passage if you wish to sketch only the most essential points in the passage k) Don't just parachute quotations into your dissertation without providing an indication of who your source is. Letting your reader know exactly which authorities you rely on is an advantage: it shows that you have done your research and that you are well acquainted with the literature on your topic. l) Please observe the forms of punctuation used to introduce the quotations. When you introduce a quotation with a full sentence, you should always 53 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES place a colon at the end of the introductory sentence. When you introduce a quotation with an incomplete sentence, you usually place a comma after the introductory phrase. However, it has become grammatically acceptable to use a colon rather than a comma (e.g. Arendt writes: "we must turn to Roman antiquity to find the first justification of war…") If you are blending the quotation into your own sentence using the conjunction that, do not use any punctuation at all (e.g. Arendt writes that "we must turn to Roman antiquity to find the first justification of war…."). Finally, note that you can deviate from the common pattern of introduction followed by quotation. Weaving the phrases of others into your own prose offers a stylistically compelling way of maintaining control over your source material. Moreover, the technique of weaving can help you to produce a tighter argument. m) If your quotation is lengthy, you should almost always introduce it with a full sentence that helps capture how it fits into your argument. If your quotation is longer than four lines, do not place it in quotation marks. Instead, set it off as a block quotation. The full-sentence introduction to a block quotation helps demonstrate your grasp of the source material, and it adds analytical depth to your dissertation. But the introduction alone is not enough. Long quotations almost invariably need to be followed by extended analysis. Never allow the quotation to do your work for you. Usually you will want to keep the quotation and your analysis together in the same paragraph. Hence it is a good idea to avoid ending a paragraph with a quotation. But if your analysis is lengthy, you may want to break it into several paragraphs, beginning afresh after the quotation. n) If you need to alter your quotations in any way, be sure to indicate just how you have done so. (e.g. If you remove text, then replace the missing text with an ellipsis - three periods surrounded by spaces: In ‘The Mirror and the Lamp’, Abrams comments that the "diversity of aesthetic theories… makes the task of the historian a very difficult one"). If you need to alter or replace text from the original, enclose the added text 54 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES within square brackets. You may, for example, need to alter text to ensure that pronouns agree with their antecedents. o) Whenever you paraphrase, remember these two points: You must provide a reference and the paraphrase must be entirely in your own words. You must do more than merely substitute phrases here and there. You must also completely alter the sentence structure. It can be difficult to find new words for an idea that is already well expressed. The following strategy will make the job of paraphrasing a lot easier: When you are at the notetaking stage, and you come across a passage that may be useful, do not copy the passage verbatim unless you think you will want to quote it. Make a note only of the author's basic point and rewrite the rest in your own words ensuring that you do not distort the original idea or argument. Make sure to include the page number of the original passage so that you can make a proper reference later on. p) When you summarise a passage, you need first to absorb the meaning of the passage and then to capture in your own words the most important elements from the original passage. A summary is necessarily shorter than a paraphrase. 55 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES FORMS 56 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES ANNEXURE A FACULTY OF EDUCATION UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA FACULTY RESEARCH ETHICS COMMITTEE STUDENT APPLICATION FOR APPROVAL OF RESEARCH INVOLVING HUMAN RESPONDENTS APPLICATION FORM 1. SUMMARY OF THE RESEARCH Please provide a brief summary of the nature and purpose of the research in non-technical language (1-2 pp.) 2. PARTICIPATION OF HUMAN RESPONDENTS 2.1 describe who will be participating in the study in terms of race, sex, age range, institutional affiliation, and other special criteria 2.2 describe how will you select the participants in the study; indicate whether participation is voluntary or not; and state what inducements (if any) will be offered to human subjects to participate in this study 2.3 describe what the respondents will be expected to do, or what will be done to them, or what information will be required; indicate how many times observations, tests, questionnaires etc., will be administered; and state how long their participation will take for each specified task 3. SUBJECT APPROVAL AND INFORMED CONSENT 3.1 indicate whether you have received permission to conduct this research from the relevant authority: Yes the provincial department of education the school other authority (specify) _______________________ ____ ____ No ___ ____ ___ ___ 3.2 describe how you will explain the research to respondents, and how you will obtain their informed consent to participate e.g., writing, face-to-face explanations etc. And how is it made clear to subjects that they can end their participation in the study at any time? 3.3 describe how you will obtain consent in cases where subjects who are minors (under 18), mentally infirm, or otherwise not legally competent to consent to their participation. How is their assent obtained and from whom is proxy consent obtained? 3.4 describe how you will ensure full consent and participation in cases where the research is not conducted in the mother-tongue of the subjects or in a language in which the subjects feel competent? 4. QUALIFICATIONS AND EXPERTISE OF THE RESEARCHER 57 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 4.1 describe your experience with this kind of research. 4.2 do you as researcher require registration for any specific techniques or treatment that you will administer in this study? 4.3 list any assistants who might be working with you, describe what they will do, and their competence and preparation to do such tasks 5. RISKS AND DISADVANTAGES TO HUMAN RESPONDENTS OR PARTICIPANTS 5.1 Do respondents risk any harm—physical, psychological, legal, social—by participating in the research. What safeguards do you take to minimize the risks? 6. BENEFITS AND ADVANTAGES TO HUMAN RESPONDENTS OR PARTICIPANTS 6.1 In what ways—if at all—will this research benefit the participants? 7. CONFIDENTIALITY, ANONYMITY AND TRUST 7.1 Were the respondents offered confidentiality and anonymity for their involvement in the research? How did you go about ensuring confidentiality and anonymity to respondents? 7.2 Will participants receive feedback on the research process and its conclusions? Will participants be asked to comment on drafts e.g., transcripts of interviews? If so, how will you use such comments from respondents in your research report? 7.3 Will research data be destroyed at the end of the study? If not, where and in what form, and for how long, will the data be stored 58 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES FACULTY OF EDUCATION UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA FACULTY RESEARCH ETHICS COMMITTEE STUDENT APPLICATION FOR ETHICS APPROVAL OF RESEARCH INVOLVING HUMAN RESPONDENTS COVER SHEET STUDENT DETAILS: _________________________ (Name and Surname, printed) _________________________ (Student ID Number) _________________________ (Year of first registration) QUALIFICATION BEING PURSUED: _________________________ (e.g., PhD Policy Studies) TITLE OF PROPOSED RESEARCH ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ STATUS OF SUBMISSION TO ETHICS COMMITTEE First Submission Second Submission INDICATE WHETHER FUNDED: _____ _____ Yes _____ No _____ Agency _____ (e.g., the NRF) INDICATE WHETHER THE RESEARCH WILL INVOLVE: Yes ___ ___ ___ Subjects under 18 Mentally Disabled Mentally Retarded No ___ ___ ___ Signature indicates that the signing party has approved this proposal for submission to the Faculty Ethics Committee STUDENT’S SIGNATURE: ____________________ ___________ (date) SUPERVISOR’S SIGNATURE: ____________________ ___________ (date) HEAD OF DEPARTMENT’S SIGNATURE: ____________________ ___________ (date) BELOW THIS LINE: FOR RESEARCH ADMINISTRATION OFFICE ONLY APPLICATION NUMBER: DATE RECEIVED: _________________________ _________________________ DATE APPROVED: _________________________ 59 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES ANNEXURE B UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA FACULTY OF EDUCATION SHORTENED GUIDELINES FOR THE SUBMISSION OF THESES/DISSERTATIONS/DISSERTATIONS OF LIMITED SCOPE: 2004 1. SUBMISSION DATES (a) (b) 30 March 29 October GRADUATION CEREMONY for for September April 2. DOCTORAL CANDIDATES: THESIS 2.1 Copies required: 2.2 Bound: (Spring) (Autumn) Ring bound copies for examining: One copy each for dean, supervisor and examiners – must be followed up by bound copies (hard cover) to examiners after examination Copies for Academic Information Service (final copies after examination: Students who are registered since earlier than 2002, submit one bound paper copy (hard cover) and are advised to, in addition, submit one electronic copy (format not specified), as prescribed for students of 2002 and 2003. One bound paper copy (hard cover) and one electronic copy (format not specified) for students who registered since 2002 and 2003. Students who registered since 2004 must submit one bound paper copy (hard cover) as well as two electronic copies, one in PDF and the other in Word or WordPerfect. Electronic copies may be on CD or diskette, or students can do the submission on the UPeTD web site themselves in which case their documents will receive preferential treatment. More information available at www.upetd.up.ac.za Final copies must reach the Student Administration not later than four weeks prior to the graduation ceremony. Electronic copies must be accompanied by the prescribed UPeTD form which must be completed by the student as well as the supervisor. Form and UPeTD instructions obtainable from the Student Administration. (a) (b) 2.3 Title page in front. A summary of not more than 500 words in English (in front or at the back) with a list of 10 key words. Unbound: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Title page in English An abstract in English of not more than 350 words (together with a list of 10 key words). Submission form - signed by supervisor. (Obtainable from the Student Administration). R50 administration fee (payable to the cashier before submission). A completed "Abstract" form (obtainable from Student Administration). Curriculum Vitae, in consultation with supervisor - maximum 170 words. Last paragraph 60 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES (g) 100 words. Typed in double spacing. Signature of supervisor required. (Example obtainable from Student Administration). Draft article for publication – 2 hard copies as well as a CD or diskette in consultation with supervisor. 3. MASTER’S DEGREE CANDIDATES 3.1 DISSERTATION 3.1.1 Copies required: As for doctoral thesis, but extra copy for dean not required. 3.1.2 Bound: As for doctoral thesis. 3.1.3 Unbound: (a) (b) (c) 3.2 Submission form signed by supervisor (obtainable from Student Administration). R50 administration fee. (Payable to cashier before submission). Draft article for publication - 2 hard copies as well as a CD or diskette in consultation with supervisor. DISSERTATION OF LIMITED SCOPE 3.2.1 Copies required: 3.2.2 Bound: As for doctoral thesis, but extra copy for dean not required. (a) (b) 3.2.3 Title page in front. A summary of 150 - 200 words in English (after the table of contents), together with a list of 10 key words. Unbound: (a) 4. Submission form - signed by supervisor (obtainable from the Student Administration Office). (b) R50 administration fee (payable to the cashier before submission). (c) Draft article for publication – 2 hard copies as well as a CD or diskette in consultation with supervisor. TECHNICAL DETAILS 4.1 Final copies must be bound in a hard cover with: (a) 4.2 the title of the thesis/dissertation/dissertation of limited scope and initials and surname of the candidate on the front cover; and (b) Year, surname and initials on the spine. Copies must be printed on good quality paper and in letter quality. 4.3 A4 or A5 paper size may be used and printing may be done on both sides of the page. Students should inform the Student Administration, in writing, of their intention to submit the thesis/dissertation/dissertation of limited scope at least three months prior to submission and are requested to set an appointment at least a week prior to submission. For further details consult the General Regulations of the University. 61 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES ANNEXURE C FORM A UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA FACULTY ____________________________________ DEPARTMENT ________________________________ The Department _________________________ places specific emphasis on integrity and ethical behaviour with regard to the preparation of all written work to be submitted for academic evaluation. Although academic personnel will provide you with information regarding reference techniques as well as ways to avoid plagiarism, you also have a responsibility to fulfil in this regard. Should you at any time feel unsure about the requirements, you must consult the lecturer concerned before you submit any written work. You are guilty of plagiarism when you extract information from a book, article or web page without acknowledging the source and pretend that it is your own work. In truth, you are stealing someone else’s property. This doesn’t only apply to cases where you quote verbatim, but also when you present someone else’s work in a somewhat amended format (paraphrase), or even when you use someone else’s deliberation without the necessary acknowledgement. You are not allowed to use another student’s previous work. You are furthermore not allowed to let anyone copy or use your work with the intention of presenting it as his/her own. Students who are guilty of plagiarism will forfeit all credit for the work concerned. In addition, the matter can also be referred to the Committee for Discipline (Students) for a ruling to be made. Plagiarism is considered a serious violation of the University’s regulations and may lead to suspension from the University. For the period that you are a student at the Department ______________________ , the under-mentioned declaration must accompany all written work to be submitted. No written work will be accepted unless the declaration has been completed and attached. I (full names) Student number Subject of the work __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ 62 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES Declaration 1. I understand what plagiarism entails and am aware of the University’s policy in this regard. 2. I declare that this ______________________ (e.g. essay, report, project, assignment, dissertation, thesis etc) is my own, original work. Where someone else’s work was used (whether from a printed source, the internet or any other source) due acknowledgement was given and reference was made according to departmental requirements. 3. I did not make use of another student’s previous work and submitted it as my own. 4. I did not allow and will not allow anyone to copy my work with the intention of presenting it as his or her own work. Signature __________________________________ 63 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES ANNEXURE D UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA FACULTY OF EDUCATION CONFIDENTIAL EXTERNAL REPORT ON POTENTIAL OF CANDIDATE TO UNDERTAKE RESEARCH AT POSTGRADUATE LEVEL NB: DIE BESONDERHEDE OF HIERDIE VORM MOET GETIK OF MET SWART INK VOLTOOI WORD / THE INFORMATION SUPPLIED ON THIS FORM SHOULD BE TYPED OR COMPLETED IN BLACK INK. 1. KANDIDAAT/ CANDIDATE 2. Hoe lank ken u die kandidaat? / How long have you known the candidate? Baie goed/Very well 3. In watter mate ken u die kandidaat? / To what degree do you know the candidate? Goed/Well Nie goed nie/Not well Dosent/Lecturer 4. In watter hoedanigheid ken u die kandidaat? / In which capacity do you know the candidate? Werkgewer/Employer Studieleier/Supervisor Ander:/Other: 5. In watter mate sou u die kandidaat se academiese vermoë beoordeel? / To which degree would you evaluate the candidate’s academic potential? 6. Swak/Poor 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Uitstekend/Excellent Indien u die kandidaat se studieleier vir sy/haar Magisterverhandeling was, beoordeel asseblief die kandidaat ten opsigte van die volgende vaardighede: / If you had been the candidate’s supervisor for his/her Master’s dissertation, please evaluate the candidate on the grounds of the following: (1 = swak/poor; 5 = uitstekend/excellent) Formuleringsvermoë /Ability to formulate 1 2 3 4 5 Gefokusheid/Clarity of focus 1 2 3 4 5 Vermoë om teorie te integreer/Theoretical 1 2 3 4 5 integration Analitiese vermoe/Analytical ability 1 2 3 4 5 Akademiese skryfvermoë/Academic writing skills 1 2 3 4 5 Logiese redeneringsvermoë /Logical reasoning 1 2 3 4 5 ability Vermoë om navorsing uit te voer /Knowledge of 1 2 3 4 5 research methodology Vermoë tot selfstandige werk /Ability to work 1 2 3 4 5 independently Vakkennis /Subject knowledge 1 2 3 4 5 Bykomende inligting in hierdie verband wat us as belangrik beskou: / Additional information in this regard which you might regard as important: 64 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 7. Evalueer asseblief die kandidaat op grond van die volgende persoonlikheids-eienskappe / Please evaluate the candidate regarding the following personality traits (1 = swak/poor; 5 = uitstekend/excellent; 0 = kan nie ‘n oordeel fel nie/unable to give an option) Gedissiplineerd / Disciplined Deursettingsvermoë / Perseverance Selfstandigheid / Independence Verantwoordelikheid / Responsibility Netheid / Neatness Stiptelikheid / Punctuality Interpersoonlike sensitiwiteit / Interpersonal sensitivity Emosionele stabiliteit / Emotional stability Buigsaamheid / Flexibility Hantering van spanning / Coping with stress Etiese gedrag / Ethical Behaviour Motivering / motivation Persoonlike insig / Personal insight Reaksie op terugvoer/Response to feedbvack Verbale vermoë/Verbal abilities 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Bykomende inligting in die verband wat u as belangrik beskou: / Additional information which might be important in this regard: 8. 9. In watter mate dink u behoort die kandidaat tot ‘n PhD graad in Opvoedkundige Sielkunde of Leerondersteuning, Voorligting en berading, toegelaat te word? /To which degree do you think the candidate should be admitted to a PhD in Educational Psychology or Learning support, Guidance and counselling? Glad nie / Not at 1 2 all REFERENT / REFEREE 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 Beslis / Definitely Naam/Name:___________________________________________________________ Beroep/Occupation:_____________________________________________________ Adres/Address:_________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Tel:___________________________ (w) ______________________________(h) Sel/Cell:_______________________________________________________________ Epos/E-mail:___________________________________________________________ Handtekening/Signature:_________________________________________________ Datum/Date:___________________________________________________________ Baie dankie vir u samewerking / Thank you for your cooperation. 65 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES ANNEXURE E DWARSVORM UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA DEPARTMENT: EDUCATION MANAGEMENT, LAW AND POLICY M&D COMMITTEE DATE: ESS VERDELING DEPT FOR OFFICE USE: Enrolled: % Letter sent on: STUDENT DETAILS TITLE Yes No EXTERNAL EXAMINERS RECOMMENDED Name: Name and initials Stud no. Address Name: Position: Address Position: Address Tel Fax e-mail First year of registration Tel Fax Cell: Academic qualification e-mail Name: Tel Fax Cell: Academic qualification e-mail Name: Head of Department Position Address Position Address Date: Tel Fax Cell: Academic qualification e-mail Tel Fax Cell: Academic qualification e-mail FIELD OF STUDY SUPERVISOR Name Personnel no. CO-SUPERVISOR Name Personnel no APPROVAL Dean Date 1 GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES ANNEXURE E PROGRESS REPORT FORM UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA FACULTY OF EDUCATION PROGRESS REPORT FORM DEPARTMENT: FOR OFFICE USE: Date of 1st registration Date last progress report DATE: y y STUDENT DETAILS Name and initials Student number Degree enrolled for: Contact details m m d d TITLE OF DISSERTATION Tel: Fax e-mail Comments on progress and recommendation APPROVAL Head of Department ADMINISTRATIVE PROCESSES Successfully defended proposal at departmental level Successfully defended proposal at Faculty level Date: CO-SUPERVISOR Name Personnel no Date: Title approved (Dwarsvorm) External examiners appointed Administration informed of submission date Completed chapters Date Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Date: Date: Date: Fieldwork Data analysis Chapter 4 Draft dissertation Final edited dissertation submitted Research Committee Date 2 Date: Ethics statement submitted SUPERVISOR Name Personnel no. Date: Comments: GUIDELINES AND PROCEDURES FOR POSTGRADUATE STUDIES 3