Question 1
advertisement

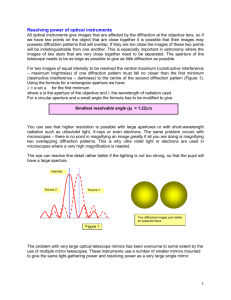
HW 1 Question 1. The plots show a diffraction pattern from a diffraction grating. The horizontal axis is angle (radians, assume small angle approximation). One of the plots is on an expanded scale. Find three quantities and explain briefly (in one sentence, each) how you found these. The quantities to be determined are: a) Number of slits, N. b) Spacing between slits, d. c) width of each slit, w. Assume that the wavelength of the light is 1 length unit HW 2. When you observe Fresnel Diffraction with a "narrow" slit the diffraction pattern resembles Fraunhofer Diffraction. a) What does "narrow" mean; "narrow" compared to what? b) Explain in a sentence or two why the pattern resembles Fraunhofer Diffraction Question 2. You take data at three values of x and obtain three values of y. For each point the uncertainty in y is 2.0 The data points are x y 1 10 2 17 3 32 ------------------------------------The data should be fit to a line through the origin. a) What is the slope of the best fit line? b) What is Chi-squared for this fit? c) explain in one sentence how you solved this problem HW 3 The ideal setup for observing Fraunhofer Diffraction involves a parallel beam incident on a grating. One views the diffraction pattern at an infinite distance where the ourtgoing parallel rays interfere. Since it is not convenient to go to infinity to observe the pattern we place a converging lens after the grating and focus on a screen. (in the lab we focused the pinhole source on a screen). Why do these techniques using a lens to observe Fraunhofer Diffraction work? Explain in a couple of sentences. Question 2. Near the forward direction of a multiple slit diffraction pattern the intensity distribution resembles the diffraction pattern of a single wide slit. How come? Question 3. The aperture function is the sum of a positive and a negative delta function: f(x)=δ(x-a)-δ(x+a) What is the Fourier transform g(k)? Give the answer in a simple form. HW 4 Question 1. The central circle of a zone plate is opaque. Alternate rings at larger radii are also opaque. In between rings are transparent. When a parallel beam hits the zone plate a bright spot is seen on the axis at some distance beyond the zone plate. a) Explain why this happens (in a couple of sentences). b) If you made a hologram using as an object a single point source would the hologram look exactly like this zone plate? Explain why or why not. Question 2. An aperture is opaque for x>a and for x<-a. Between -a and +a the transmission of the aperture has the form 0.5 ( 1 + cos(p x) ). p is a number which is related to the spatial frequency. a) What is the Fourier transform of this aperture function? b) This aperture is used as a diffraction grating in a laser beam. Describe in a couple of sentences what the diffraction pattern will look like