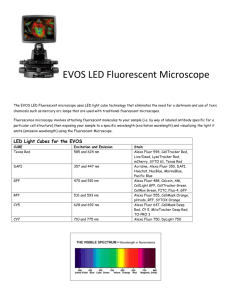
NanoDrop® ND-3300 Fluorospectrometer
advertisement

Thermo Scientific Confidential Thermo Scientific NanoDrop™ 3300 Positioning Versatile, small sample-size fluorometer featuring the following benefits: • Small sample volume (1-2 ul) – With assays in microgenomics, proteomics and drug discovery requiring progressively smaller samples, there is a clear need to measure minute amounts of biomolecules. The NanoDrop 3300 achieves this by measuring low concentrations in very small volumes. For example, as few as two picograms or one pg/µl of dsDNA can be measured using a three microliter PicoGreen assay volume. Sensitivity of Alexa 647 is five femtomoles or 2.5nM. (This lowers the detection limit of nucleic acids [more than 1000-fold] and dyes commonly used for microarray probes [~100-fold] below that of the NanoDrop 1000 Spectrophotometer.) • Broad spectrum analysis (400nm-750nm) – Allows the measurement of up to four fluorophores in a single sample and visualization of even more. – Software utility in FRET (fluorescent resonant energy transfer) analysis in which the emission of one fluorophore provides the excitation for a second fluorophore. – Ability to visually inspect the emission spectrum gives more confidence in the final RFU determination. • Broad excitation range (365-650nm) – NanoDrop 3300 enables a broad excitation range without the complexity associated with high end spectrofluorometers, but rather with the simplicity of low end, less versatile fluorometers. Both the monochromator (complex and expensive) and filter changes are effectively eliminated through the unconventional use of a white LED in addition to filtered UV and blue LED sources. The unconventional use of the broad spectrum, longer wavelength white LED is enabled by the combination of uniquely clean optics of the retention system and proprietary signal processing. Simply put, the software applies a virtual filter to remove the excitation source light from the emission signal. – As a point of comparison, sophisticated high end fluorometers or spectrofluorometers are most commonly found in research laboratories. They utilize a monochromator at the source (with broad range from a xenon or less powerful halogen lamp) and variable slit width to enable selection of the excitation wavelength and bandpass. Alternatively, some high end fluorometers rely on a wide variety of filters to select amongst common excitation wavelengths. – For comparison from the other side, low-priced fluorometers frequently use single or multiple sources, each providing excitation over a narrow range. Common sources include light emitting diodes (LEDs) in the UV, blue, green or red range as well as mercury lamps to obtain the common 460nm emission wavelength. Others use filters. • No cuvettes, capillaries, filters or specialized 96-well fluorescent plates • Easy to use – Preprogrammed methods – User-defined methods • Sample applications – Micro volume quantitation using common nucleic acid assays (PicoGreen, RiboGreen, SYBR Green, and Hoechst 33258) and protein assays (Quant-iT Protein). Thermo Scientific Confidential – – • Common probe dyes including Cy3 and Cy5, their Alexa Fluor counterparts (Alexa 555 and Alexa 647 respectively), Alexa 488, Alexa 546, and Alexa 568 have been excited with a single source (white LED). FRET reactions including: o FITC – Cy5 o FAM – 3’-Dabcyl o TET – 3’-Dabcyl o HEX – 3’-Dabcyl o Alexa 546 – 3’BHQ-2 o Alexa 594 – 3’BHQ-2 Small instrument size – 20cm X 15cm X 12 cm Competitive Products Low-Priced Fluorometers • Inexpensive RFU measurements • Disadvantages – No spectral analysis – Limited excitation sources – Larger sample volumes – Cuvettes needed – Some require filters – Cost of disposables • Examples – Turner TBS380 & Modulus – GE (Amersham) DynaQuant – BioRad-Versafluor – Turner Barnsted Quantech – Farrand Optical A-1 High-Priced Fluorometers • Full spectrum analysis for versatility • Disadvantages – Expensive (purchase, maintenance) – Large footprints – Larger sample volumes – Cuvettes needed – Many require filters – Cost of disposables – Light source stabilization period and longevity • Examples – Hitachi F-2500 – Horiba Jobin Yvon FluoroMax-3 – Jasco FP-6200 – Shimadzu RF1501 & RF5301PC – Varian Cary Eclipse Thermo Scientific Confidential Plate Readers • Fluorescent readings (simple to sophisticated) of microtiter plates for higher throughput • Disadvantages – Relatively expensive instrumentation – Large sample volume – Costly disposables (e.g., specialized 96-well fluorescent plates) – Not conducive for single sample or very limited sample analysis • Examples – BioScan Chameleon – BioTek FLx800 – Perkin Elmer Victor2 D – Tecan Genios-FL – Thermo Electron Fluoroskan – Molecular Devices Gemini EM , XPS