How to learn vocabulary quickly
advertisement

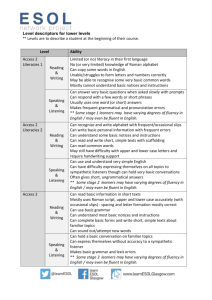
How to learn vocabulary quickly? 031066 Emi Takahashi Introduction We have learned English until junior high, after we can more communicate in English we need more wide vocabulary skill. We can’t learn so many words so quickly. How should we learn vocabulary quickly? 1. How many words we should learn? It is obvious that in order to learn a foreign language, one needs to learn many many words. But how many? Educated English native speakers have a vocabulary of about 20,000-25,000 word families (A 'word family' refers to a group of words that share the same basic meaning e.g. create, creation, creating, created, creative etc), foreign learners of English need far fewer[1].The speaking vocabulary is usually said to be half of the reading and writing vocabulary. Foreign learners of English only need about 3000-5000 word families to be quite competent in speaking and listening to English. This is great news for learners of English because their task is much easier than that of native speakers! 1 ◎How should we learn words each word families? 0-500 word families 500-1000 word families 1000-2000 word 2000-5000 word families 5000+ word families families Speaking Very difficult and often not Mostly incomplete Daily conversation Daily conversation with Can speak well on even attempted. Mostly one sentences and some with difficulty, mostly some most topics. Some word sentence of a maximum original constructions broken. A few ease. Unpredictable vocabulary problems of about 4 words. Some set but still a lot of non- complete sentences conversation is difficult in specialist areas. phrases and memorized verbal communication. but characterized by especially abstract topics. Able to mingle with chunks of language are use Communication is poor word choice. May feel lost especially natives with relative but in disconnected speech. broken while the learner Mostly transactional when listening in to a ease, but may on Gesture and reliance on searches for words. Some language is used. natives' conversation. occasions will lose visual support are main questions can be formed Beginnings of ability Constant need to ask for the thread or feel communication strategy. The but often after several to speak freely but clarifications or to check overawed. Need to speaker 'hopes' the listener attempts. Very poor word often hesitatingly one's understanding. occasionally ask for will understand by speaking choice. Most questions even on familiar Collocation and clarifications. in remembered words or are formulaic. Able to subjects. idiomaticity is a problem. phrases rather than respond to predictable Self-correction is sentences. Avoidance of direct questions often common. Questions partially known forms is a after being prompted. sometimes go beyond major strategy. Avoidance of verbs and a the formulaic and preference for pronouns predictable. Many and nouns to convey errors when meaning. Some producing capacity to correct lexical collocations. errors. Listening Very little of natural speech The language still seems Most words are Comprehension of Inference mostly is understood and most to be full of noise. Many recognized, but not predictable TV and radio understood. TV and 2 speech has to be slowed down words are recognized, comprehended is possible. Determining radio can be and enunciated clearly. Only but many can't be quickly. Native inference is possible. comprehended the most predictable recalled quickly enough discourse is still Many jokes are still a provided the topic is conversations are possible. to enable fluent mostly a blur. Top mystery. not specialized. Able The main listening strategy comprehension. More down listening to deal with abstract is to try to get a rhythm for often loses the thread strategies are mostly topics the language (a top-down than has it. Visual used. Comprehension strategy) and catch the odd stimulus still a major of highly structured word here and there. Visual assistance. Short term text possible (but not clues are often vital to memory technical or specialist understanding. Memory is overloaded. Often language). Limited constantly overload. guesses poorly at number of words with unknown words. Low multiple meanings chance of learning new are recognized. words from speech. Reading Pictures and illustrations Native speaker texts are The dictionary Most words are Most native text can have to contribute strongly still well beyond the remains a main understood but not be comprehended if to aid comprehension. A few learner. Dictionary use is reading strategy for fluently. A dictionary is the topic is not content words are recognized the main reading native texts except for regularly called upon. specialized. May be in native text. Can only strategy. Slow and highly predictable Able to deal with texts at willing to try more understand the most halting. Re-reading is text. May soon give up the discourse level. academic texts. 'babyish' of texts. Often not very common. Word by with native texts. able to identify letters or word reading. The Beginning to see letter strings thread is often lost. words in chunks of immediately. Reading Cannot understand text. Humour is not letter-by-letter, or word by inference. Difficulty in often spotted. Can word. Often forgets the retaining the message - deal with most texts 3 beginning of the sentence content soon forgotten. at the sentence level. when she gets to the end of Slow and predictable Not good at inference. it. Comprehension poor. plots in graded readers Complex plots Dictionary always open. can be read. Soon gets difficult to follow. tired. Writing Only the most basic of A few complex sentences Writing longer texts Predictable texts can be The dictionary is sentences can be made, are used and then only without a dictionary written without the need rarely used for characterized by extremely basic conjunctions. Tends is almost impossible. of the dictionary, but the predictable texts poor word choice. Mostly set to read as if it had been Word choice needs dictionary is always except for phrase or words strung 'translated'. Poor word work. Some nearby. Unpredictable discriminating together with strong choice. collocations are topics require constant between difficult elements of the mother known, but many are use of a dictionary. words or for finding tongue. Many phrases strange. Colligation is 'forgotten words'. appear translated straight still a problem. Extensive use of the from the dictionary. dictionary for specialist texts. Some fossilized errors apparent. Major weakness is still collocation. 'Grammar' Lack of ability to control Major distortions of basic Basic structure Grammar often sounds Generally cohesive many basic sentence sentence patterns often becoming more foreign but not serious for and coherent. patterns.. Inability to form accompanied by native-like, but errors getting the message Relatively few errors many questions, or control seemingly correct forms abound. Great across. Able to construct with a wide range of word order. Almost clueless that are later seen as not difficulty with many kinds of sentence structures used, but about the use of prepositions, properly developed. complex structures. patterns. complex structures 4 tenses and so on. Basic connectors can be Can experiment with used, but often get mixed less common up. Grammar use can be grammatical a kind of 'try and see if it elements. Some forms works' but more in hope are still not yet fully than from real developed. Still knowledge. having problems with still cause problems. tenses and prepositions. Vocabulary Very slight, so Severe lack of vocabulary May have an Sounds stilted and still Still nowhere near resources. communication is hardly make communication at adequate everyday finds it difficult to native-like. Choice of possible. Word selection is best difficult. Usually the vocabulary, but is converse freely even on vocabulary is often very poor and speaks or person has a store of limited in word non-specialty topics. Still adequate but sounds writes with great difficult.. 'ready to use' phrases choice. Often lost for may sound 'odd' to stilted and not Almost completely dictionary and may take the words. Can guess natives. Fluency still a idiomatic. Can dependent. Almost always at initiative in a meanings of some problem. control register or sea. conversation to control it unfamiliar words select appropriate to within the learner's from context. Many forms in many ability level. A lot of words with multiple situations. Still searching for words. Can meanings are noticed. distinctly foreign in handle predictable Messages can be lost many ways but not vocabulary situations due to the poor 'odd'. Fluency such as personal selection of the correct largely attained, but information. Some words sense of words with needs accuracy of with multiple meanings multiple meanings. expression rather are noticed. than fluency. 5 So, what is a Start-up vocabulary? A Start-up vocabulary would be a basic set of words that the learner needs in order to start to learn from books or by listening to the teacher. Learners with little or no vocabulary can do very little in the target language and as soon as they get a few hundred basic words, then they will be able to learn from their coursebooks and understand their teacher in the L2. As a complete beginner, we cannot of course just pick up a book and try to read from that as we do not know the spelling-sound combinations. How can we learn this startup vocabulary? Foreign language learners do not have the benefit of a huge listening or reading vocabulary to start reading with. Secondly, in the same way the foreign language learner does not already have a grammatical system in place to hang new words on, this also has to be learned. Thirdly, children do not learn in the same ways that adult foreign language learners do. Adult language learners have the benefit of analytical skills that children do not posses, but they also have lost the ability to learn freely and easily like children do. Therefore, it is probably more effective to teach the basic vocabulary first to enable learning from the reading (or listening) to take place. Fitting a Start-up vocabulary into a curriculum Initially in this schedule there is a very heavy emphasis on vocabulary learning and if the learning is done effectively this need not last more than a few weeks. Also important in this process is to see an early emphasis on building a study atmosphere, explaining why it is necessary to learn a lot of words quickly so they can quickly start to read and listen later, and explaining how to do it. Most of this learning is done out of class, and there would need to be constant need to ensure that the learning was being done effectively. Learners can test each other and competitive classes may have a reward / competitive element if desired. The aim at this stage is to build the Start-up vocabulary, so that learners can then move on to other things. As the ability level of the learner increases, different activities come to dominate. There will be more normal classwork which the learners will now be able to tackle faster and easier, and a LOT of work on simplified reading and listening to build fluency with the words learned and to consolidate them. The following table sets out the steps necessary to master the types of vocabulary one will need. 6 Conclusion We should learn by best way for each words family, and the balance is important of reading /listening /writing . Study in class room important but out class learning is important ,too. As an English course student, I must challenge more by these way . 0 - 600 word families Aim Build a recognition 600 - 1000 word families 1000 - 2000 word families 2000 + word families (sight Build recognition Start-up vocabulary. Consolidate Start-up vocabulary. Continue direct Learning from context as the main vocab vocabulary) Start-up vocabulary Reinforce direct learning with learning to feed the extensive reading and strategy (WordBank system still operates). quickly. extensive reading and listening to listening. Build chunking skills to aid fluency / Build accuracy / word distinctiveness Build class study atmosphere. increase lexical access speed. Speed comprehension / speed. Build 'deeper levels' of awareness. reading and quick reading exercises. Reading. Reading and word knowledge e.g. word partnerships, multiple Reading. meanings. semantic networks. Vocab Receptive vocabulary. Emphasis NOTE. The first 1000 words are the Emphasis on word distinctions and boundaries. Filling out word families. Low frequency type on words of wide range and most important as they are needed Work on common words from word families of words for special interest e.g. Academic / coverage. Very few functors the most often, and they hold the most words already known. Multiple meanings. medical etc. (tend to be grammatical and hard meaning senses. It is VITAL a LOT of Common collocations / associations. Word roots to acquire). Formulaic phrases. work is done on these. and affixes. Loan words. Receptive (and a few productive). Functors and content words with wide range. Less common meaning of already known word forms. Formulae. Loan words. Fixed and semi-fixed expressions. Sentence heads. Common collocations. Teacher - Compile word lists to hand out at Compile word lists to hand out at each Compile word lists to hand out at each class. Compile word lists of special needs out of each class. Write check tests. class. Set up extensive reading and Write check tests (this can be handed over for vocabulary. 7 class listening. Write check tests. each learner in turn to write the class test). task Learner - Create out WordBank and word Making word cards and learning them. Making word cards and learning them. Expand Continue with extensive reading / listening. of cards. Learn X words for every Introduce a lot of work on extensive work on graded reading and listening (e.g. at least Introduce some native speaker level video class class hour. task reading and listening (e.g. at least a a book a week at the learner's ability level). / reading as fluency work. Wide reading book a week at the learner's ability and listening - as much as possible. At this level) level to buld vocabulary the learner has to meet more text tomeet more unknown words, thus the volume of text that needs to be met will INCREASE a lot from now on - but hopefully they can read it faster now! In class Explain the need for a large early Monitor WordBank and SAC work. work Start work on word parts and word roots and on A lot of work on guessing from context / vocabulary. Agree with class on Check vocabulary targets are met - guessing from context of graded material only. word parts and roots. setting vocabulary targets (X start a wall chart (?). Start to use Eng - Eng dictionary. Monitor Monitor WordBank words for every class hour). Set Administer word check tests. WordBank work. Check vocabulary targets are up met. direct learning - explain Sight / sound correspondence work. mnemonics and WordBank / Work vocabulary notebook systems. Do vocab games/tests on reading strategies. and listening Administer word check tests. Build reading and listening strategies. Do vocab games/tests and and Do vocab games/tests and exercises exercises designed to build associations / and exercises designed to build the designed to build associations / and semantic networks. Speak about reading / number of words known. semantic networks. listening. Total Physical Response work will be good here. 8