1 - Oxford University Press
advertisement
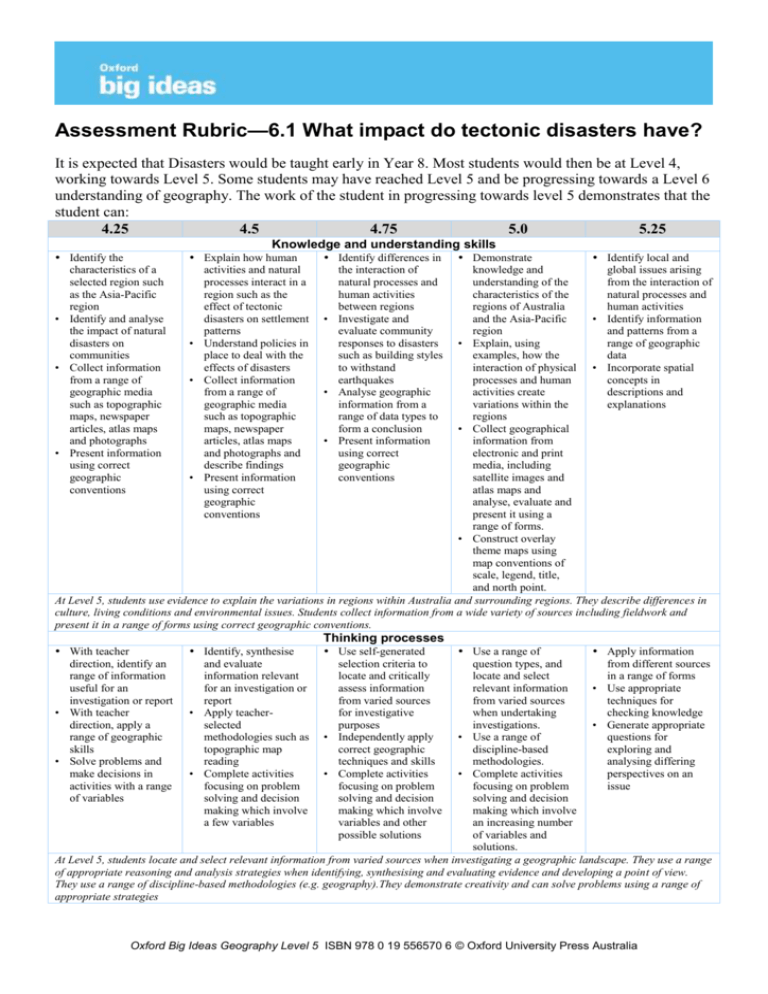
Assessment Rubric—6.1 What impact do tectonic disasters have? It is expected that Disasters would be taught early in Year 8. Most students would then be at Level 4, working towards Level 5. Some students may have reached Level 5 and be progressing towards a Level 6 understanding of geography. The work of the student in progressing towards level 5 demonstrates that the student can: 4.25 4.5 4.75 5.0 5.25 Knowledge and understanding skills Identify the characteristics of a selected region such as the Asia-Pacific region • Identify and analyse the impact of natural disasters on communities • Collect information from a range of geographic media such as topographic maps, newspaper articles, atlas maps and photographs • Present information using correct geographic conventions Explain how human activities and natural processes interact in a region such as the effect of tectonic disasters on settlement patterns • Understand policies in place to deal with the effects of disasters • Collect information from a range of geographic media such as topographic maps, newspaper articles, atlas maps and photographs and describe findings • Present information using correct geographic conventions With teacher direction, identify an range of information useful for an investigation or report • With teacher direction, apply a range of geographic skills • Solve problems and make decisions in activities with a range of variables Identify, synthesise and evaluate information relevant for an investigation or report • Apply teacherselected methodologies such as topographic map reading • Complete activities focusing on problem solving and decision making which involve a few variables Identify differences in the interaction of natural processes and human activities between regions • Investigate and evaluate community responses to disasters such as building styles to withstand earthquakes • Analyse geographic information from a range of data types to form a conclusion • Present information using correct geographic conventions Demonstrate Identify local and knowledge and global issues arising understanding of the from the interaction of characteristics of the natural processes and regions of Australia human activities and the Asia-Pacific • Identify information region and patterns from a • Explain, using range of geographic examples, how the data interaction of physical • Incorporate spatial processes and human concepts in activities create descriptions and variations within the explanations regions • Collect geographical information from electronic and print media, including satellite images and atlas maps and analyse, evaluate and present it using a range of forms. • Construct overlay theme maps using map conventions of scale, legend, title, and north point. At Level 5, students use evidence to explain the variations in regions within Australia and surrounding regions. They describe differences in culture, living conditions and environmental issues. Students collect information from a wide variety of sources including fieldwork and present it in a range of forms using correct geographic conventions. Thinking processes Use self-generated selection criteria to locate and critically assess information from varied sources for investigative purposes • Independently apply correct geographic techniques and skills • Complete activities focusing on problem solving and decision making which involve variables and other possible solutions Use a range of Apply information question types, and from different sources locate and select in a range of forms relevant information • Use appropriate from varied sources techniques for when undertaking checking knowledge investigations. • Generate appropriate • Use a range of questions for discipline-based exploring and methodologies. analysing differing • Complete activities perspectives on an focusing on problem issue solving and decision making which involve an increasing number of variables and solutions. At Level 5, students locate and select relevant information from varied sources when investigating a geographic landscape. They use a range of appropriate reasoning and analysis strategies when identifying, synthesising and evaluating evidence and developing a point of view. They use a range of discipline-based methodologies (e.g. geography).They demonstrate creativity and can solve problems using a range of appropriate strategies Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia Communication • Understand how Use specialised geographic language and symbols conventions such as as appropriate to the BOLTSS lead to study of tectonic precision in mapping disasters • Apply prior knowledge to new situations, challenge assumptions and justify their own interpretations At Level 5, students interpret complex information and evaluate the effectiveness of its presentation. When responding, they use specialised language appropriate to the context and purpose. They provide and use constructive feedback to develop effective communication skills Use appropriate key terms such as ‘tectonic plates’ and ‘subduction’ when describing tectonic disasters Use key terms to clarify meaning when presenting information Widely use and understand geography specific terms and conventions Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia Assessment Rubric—6.2 How do weather disasters affect communities? It is expected that disasters would be taught early in Year 8. Most students would then be at Level 4, working towards Level 5. Some students may have reached Level 5 and be progressing towards a Level 6 understanding of geography. The work of the student in progressing towards Level 5 demonstrates that the student can: 4.25 4.5 4.75 5.0 5.25 Geographic knowledge, understanding and skills Identify the geographic characteristics of a region such as the Huang He river basin, Bangladesh and south eastern Australia. • Identify and analyse the impact of weather disasters on communities • Collect geographic information from a range of media including choropleth maps, photographs and field sketches • Present information using correct geographic techniques Explain how disasters Identify the Demonstrate Identify issue arising are the result of the differences that occur knowledge of the from the interaction of interaction between between different geographic natural processes and natural processes and regions and the characteristics of human activities human activities reasons for these regions of Victoria • Identify the ways in • Understand policies in differences and in the Asiawhich a community’s place to manage the • Investigate and Pacific level of development effects of weather evaluate the • Explain the interaction can affect the way in disasters such as those sustainability of of human activities which they prepare for designed to mitigate policies designed to and natural processes and recover from a the effects of manage natural that lead to natural natural disaster. bushfires in Victoria disasters disasters • Identify information • Collect geographic • Analyse information • Collect geographical and patterns from a information from a from a range of information from range of geographic range of media geographic electronic and print data including choropleth information in order media, including • Incorporate spatial maps, photographs to form a conclusion, satellite images and concepts in and field sketches such as the underlying atlas maps and explanations and • Describe their reasons for analyse, evaluate and descriptions findings using correct devastating mudslides present it using a geographic language in Venezuela range of forms At Level 5, students use evidence to explain the variations in regions within Australia and surrounding regions. They describe differences in culture, living conditions and environmental issues. Students collect information from a wide variety of sources including fieldwork and present it in a range of forms using correct geographic conventions. Thinking processes With teacher direction, identify an range of information useful for an investigation or report • With teacher direction, apply a range of geographic skills • Solve problems and make decisions in activities with a range of variables Identify, synthesise and evaluate information relevant for an investigation or report • Apply teacherselected methodologies such as topographic map reading • Complete activities focusing on problem solving and decision making which involve a few variables Use self-generated selection criteria to locate and critically assess information from varied sources for investigative purposes • Independently apply correct geographic techniques and skills • Complete activities focusing on problem solving and decision making which involve variables and other possible solutions Use a range of Apply information question types, and from different sources locate and select in a range of forms relevant information • Use appropriate from varied sources techniques for when undertaking checking knowledge investigations. • Generate appropriate • Use a range of questions for discipline-based exploring and methodologies. analysing differing • Complete activities perspectives on an focusing on problem issue solving and decision making which involve an increasing number of variables and solutions. At Level 5, students locate and select relevant information from varied sources when investigating a geographic landscape. They use a range of appropriate reasoning and analysis strategies when identifying, synthesising and evaluating evidence and developing a point of view. They use a range of discipline-based methodologies (e.g. geography).They demonstrate creativity and can solve problems using a range of appropriate strategies Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia Communication Use appropriate key terms such as ‘river basin’ and ‘floodplain’ when describing weather disasters Use key terms to clarify meaning when presenting information Widely use and understand geography specific terms and conventions Use specialised Understand how language and symbols specialised as appropriate to the conventions study of tectonic contribute to precise disasters meaning; for example, • Apply prior use of conventions knowledge to new such as scale, legend, situations, challenge title and north point in assumptions and maps. justify their own interpretations At Level 5, students interpret complex information and evaluate the effectiveness of its presentation. When responding, they use specialised language appropriate to the context and purpose. They provide and use constructive feedback to develop effective communication skills Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia Assessment Rubric—6.3 What problems do man-made disasters cause? It is expected that disasters would be taught early in Year 8. Most students would then be at Level 4, working towards Level 5. Some students may have reached Level 5 and be progressing towards a Level 6 understanding of geography. The work of the student in progressing towards Level 5 demonstrates that the student can: 4.25 4.5 4.75 5.0 5.25 Geographic knowledge, understanding and skills Identify the geographic characteristics of a chosen region • Identify and analyse an environmental issue and its impact on a community • Collect information from a range of geographic media such as photographs and atlas maps including a choropleth map • Present information using correct geographic conventions Explain how natural Identify the Demonstrate Identify local and processes and human differences between knowledge and global issue resulting activities interact in a regions in terms of the understanding of the from the interaction of region such as the interaction between regions of countries natural processes and impact of wind natural processes and surrounding Australia human activities direction on air human activities • Explain how the • Identify information pollution • Investigate and interaction of natural and patterns from a • Understand policies in evaluate the processes and human range of geographic place to manage sustainability of activities create data environmental issues proposals to manage differences between • Incorporate spatial • Collect information an environmental regions concepts in written from a range of issue • Demonstrate an descriptions geographic media • Analyse information understanding of such as photographs from a range of environmental issues and atlas maps geographic data in and community including a choropleth order to form a responses to them map conclusion • Present information using correct geographic conventions At Level 5, students use evidence to explain the variations in regions within Australia and surrounding regions. They describe differences in culture, living conditions and environmental issues. Students collect information from a wide variety of sources including fieldwork and present it in a range of forms using correct geographic conventions. Thinking processes With teacher direction and self-formulated questions identify information suitable for an investigation or report • With teacher support, apply a range of geographic techniques such as map interpretation and drawing • Solve problems and make decisions in activities that involve a few variables Identify and synthesise information from a range of sources • Use appropriate strategies to analyse information for reliability • Apply teacher selected methodologies • Solve problems and make decisions in activities that involve a few variables Use of self-generated criteria to locate and analyse information suitable for an investigation or report • Independent application of appropriate geographic methodologies • Solve problems and make decisions in activities that involve a few variables and a range of possible solutions Use a range of Apply information question types and from a range of locate and analyse different sources in information from a different forms range of sources • Employ a range of • Use a range of methodologies in appropriate strategies checking information when analysing • Generate appropriate information questions for • Use a range of exploring and geographic analysing differing methodologies perspectives on an • Solve problems and issue make decisions in activities that involve a few variables and range of possible solutions At Level 5, students locate and select relevant information from varied sources when investigating a geographic landscape. They use a range of appropriate reasoning and analysis strategies when identifying, synthesising and evaluating evidence and developing a point of view. They use a range of discipline-based methodologies (e.g. geography).They demonstrate creativity and can solve problems using a range of appropriate strategies Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia Civics and citizenship Identify viewpoints in a particular contemporary issue such as nuclear power generation Develop a viewpoint on an issue, recognise others’ points of view and generate a possible solution Develop a viewpoint on issues, presented with supporting evidence, recognition of a range of perspectives, and plans for a solution Present points of view Develop a point of on contemporary view about an issue, issues and events and present it with using appropriate reference to a range of supporting evidence resources, including • Explain the different the mass media perspectives on some • Identify strategies for contemporary issues addressing a social or • Propose possible environmental issue solutions to problems At Level 5, students present points of view on contemporary issues and events using appropriate supporting evidence. They explain the different perspectives on some contemporary issues and propose possible solutions to problems. Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia Assessment Rubric—Transferring Ideas: The Aeta People It is expected that disasters would be taught early in Year 8. Most students would then be at Level 4, working towards Level 5. Some students may have reached Level 5 and be progressing towards a Level 6 understanding of geography. The work of the student in progressing towards Level 5 demonstrates that the student can: 4.25 4.5 4.75 Identify the geographic characteristics of a region in Asia • Identify and analyse an environmental issue and its impact on a community; for example, forest use • Collect information from a range of geographic media Explain how natural processes and human activities interact in a region • Understand policies currently in place to manage an environmental issue such as resettlement • Collect information from a range of geographic media and describe findings Identify differences in the interaction of human activities and physical processes between regions • Analyse information from a range of geographic data to form a conclusion With teacher direction and self-formulated questions identify information suitable for an investigation or report • With teacher support, apply a range of geographic techniques • Solve problems and make decisions in activities that involve a few variables Identify and synthesise information from a range of sources • Use appropriate strategies to analyse information for reliability • Apply teacher selected methodologies • Solve problems and make decisions in activities that involve a few variables 5.0 5.25 Geography skills Demonstrate Identify local issues knowledge and arising from the understanding of an interaction of natural Asian region processes and human • Explain how the activities interaction of natural • Identify information processes and human and patterns from a activities create range of geographic variations data • Describe differences • Incorporate spatial in culture, living concepts in conditions and descriptions and outlook, including explanations attitudes to environmental issues • Collect geographical information from electronic and print media At Level 5, students use evidence to explain the variations in regions within Australia and surrounding regions. They describe differences in culture, living conditions and environmental issues. Students collect information from a wide variety of sources including fieldwork and present it in a range of forms using correct geographic conventions. Thinking processes Use of self-generated Use a range of Apply information criteria to locate question types and from a range of information suitable locate information different sources in for an investigation or from a range of different forms report sources • Generate appropriate • Independent • Use a range of questions for application of geographic exploring and appropriate methodologies analysing differing geographic • Solve problems and perspectives on an methodologies make decisions in issue • Solve problems and activities that involve make decisions in a few variables and activities that involve range of possible a few variables and a solutions range of possible solutions At Level 5, students locate and select relevant information from varied sources when investigating a geographic landscape. They use a range of appropriate reasoning and analysis strategies when identifying, synthesising and evaluating evidence and developing a point of view. They use a range of discipline-based methodologies (e.g. geography).They demonstrate creativity and can solve problems using a range of appropriate strategies Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia Civics and citizenship Identify viewpoints in a particular contemporary issue such as deforestation Develop a viewpoint on an issue and recognise others’ points of view Develop a viewpoint on issues, presented with supporting evidence and recognize a range of perspectives. Present points of view Develop a point of on contemporary view about an issue, issues and events and present it with using appropriate reference to a range of supporting evidence resources. • Explain the different • Identify strategies for perspectives on some addressing a social or contemporary issues environmental issue At Level 5, students present points of view on contemporary issues and events using appropriate supporting evidence. They explain the different perspectives on some contemporary issues and propose possible solutions to problems Oxford Big Ideas Geography Level 5 ISBN 978 0 19 556570 6 © Oxford University Press Australia