American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology`s
advertisement

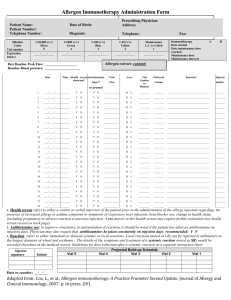
Allergen Immunotherapy Administration Form Recommended Documentation The purpose of the Allergen Immunotherapy Administration Form is to document the administration of the allergen immunotherapy extract to a patient. Its design should be clear enough so that the person administering an injection is unlikely to make an error in administration. It also should provide documentation in enough detail to determine what was done on each visit. The following recommendations on allergen immunotherapy are taken from The Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters. Patient information: Patient name, date of birth, telephone number, patient’s picture ( optional but helpful). Allergen immunotherapy extract information: Allergen immunotherapy extract name and dilution from maintenance in volume per volume bottle letter (e.g., A, B), bottle color or number if used Expiration date of all dilutions Administration information in separate columns Date of injection Arm administered injection may facilitate determination of exact cause of local reaction. Projected build-up schedule Delivered volume reported in milliliters Description of any reactions should be noted on the form. The details of any treatment given in response to a reaction would be documented elsewhere in the medical record and referenced on the administration form. Patient’s health prior to injection: An assessment of the patient’s current health status should be made before administration of the allergy immunotherapy injection to determine whether there were any recent health changes that might require modifying or withholding that patient’s immunotherapy treatment. This can be performed through a verbal or written interview of the patient prior to administering the immunotherapy injection. The patient should be questioned about increased asthma or allergy symptoms, betablocker use, change in health status (including pregnancy and recent infections), or an adverse reaction to previous injection (including delayed large local reactions persisting through the next day). Patients with significant systemic illness generally should not receive an injection. Antihistamine use: Antihistamines are frequently a component of an allergy medication regimen and it would be important to note if a patient is taking an antihistamine on the day they receive their immunotherapy injection. For consistency in interpretation of reactions, it may be desirable for a patient to either take or avoid antihistamines on a regular basis the days they receive immunotherapy. The physician should note on the form if he/she recommends the patient consistently take an antihistamine on immunotherapy treatment days. Peak flow reading: Consider obtaining a peak expiratory flow rate measurement prior to administering an immunotherapy injection to asthmatic patients. Poorly controlled asthma is considered a risk factor for immunotherapy. Obtaining a peak expiratory flow rate measurement prior to the immunotherapy injection may help identify patients with symptomatic asthma. The patient’s baseline peak expiratory flow rate should be provided on the form as a reference. Health care professionals administering immunotherapy injections should be provided with specific guidelines about the peak expiratory flow rate measurement for when an immunotherapy injection should be withheld and the patient referred for clinical evaluation. Baseline blood pressure: it may be useful to record the patient’s blood pressure as a baseline for future reference. Adapted from: Cox, L., et al., Allergen immunotherapy: A Practice Prameter Second Update. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 2007: p. In press. (IV).