Homework - Taylor High School
advertisement

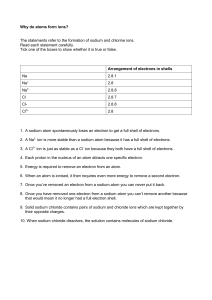
Taylor High School Chemical Changes and Structure Bonding Homework Exercises Atomic Structure and bonding related to properties of materials SCN 4-03a Covalent and Ionic Bonding 1. In which of the following compounds are the atoms held together by covalent bonds? Sodium chloride Water Carbon dioxide Sulphur dioxide Boron hydride Calcium carbonate Carbon tetrafluoride Lithium fluoride Aluminium oxide Magnesium bromide 2. The following diagram shows how the atoms are held together in a molecule of chlorine: a) What is the chemical formula of chlorine? b) What is the electron arrangement for each atom of chlorine before the covalent bond is formed? c) Explain why each atom of chlorine reacts and forms a covalent bond with another atom. 3. Copy and complete the diagram below to show what holds the atoms together in a covalent bond. Negative __________ Positive nucleus _________ force of attraction 4. Copy the sentence below and circle the correct words. 5. The table lists the names of some elements. (a) Identify the two elements which exist as diatomic molecules. (b) Explain the meaning of the word diatomic. 6. Write the names and chemical formula of the 7 diatomic elements. 7. Use the word bank below to answer the following questions Oxygen Carbon Nitrogen Fluorine Argon Magnesium Identify the element a) which forms 2 covalent bonds between its atoms. b) which forms 3 covalent bonds between its atoms. c) which does not form bonds because it has a stable electron arrangement. 8. The diagram below shows the arrangement of electrons in a molecule of hydrogen chloride. Draw similar diagrams to show how the outer electrons are arranged in the following molecules a) b) c) d) e) nitrogen hydride (NH3) carbon tetrafluoride (CF4) hydrogen sulphide (H2S) hydrogen oxide (H2O) carbon dioxide (CO2) 9. The chemical formula for a molecule of methane is CH4. a) Draw an outer electron diagram to show how these atoms combine to form the methane molecule. b)What is the term used to describe the shape of this molecule? 10. Draw and name the shape of each of the following molecules. a) CCl4 b) NH3 e) NCl3 f) HCl c) H 2O d) SiH4 11. Match the word to the statement Molecule the ratio of atoms of each element in the substance Covalent bond a group of atoms joined together Chemical formula attraction between the positive nuclei and shared electrons 12. Which of the following compounds are ionic? Aluminium chloride Silicon oxide Nitrogen dioxide Phosphorous chloride Magnesium iodide Calcium oxide 13. Copy and complete the table Atom symbol Na Atom electron arrangement 2)8)1 Ion symbol Na+ Ion electron arrangement 2)8 K 2)8)2 2)8)8)2 Al O ClN314. Explain why the noble gases do not form ions. 15. Identify the compound from the following list in which both ions have the same electron arrangement as argon. Strontium chloride Barium fluoride Lithium oxide Sodium fluoride Calcium oxide Potassium chloride 16. Magnesium has the electron arrangement 2, 8,2 It forms an ion as shown below + 2e- 2,8,2 2,8, The magnesium atom gets a more stable electron arrangement by giving away two electrons to form a magnesium 2+ ion a) Write the electron arrangements for i) a sodium atom ii) a chlorine atom b) copy and complete the diagram below to show how a chlorine atom forms an ion. + e- 2,8,8 2,8,7 c) Use target pictures and electron arrangements to show how a sodium atom forms an ion. d) What is meant by the term ionic lattice? 17. Use the following to answer the questions below… NaCl(aq) HCl (g) KF(s) CCl4(l) MgCl2(l) SiO2(s) Identify the substance(s) which a) do not conduct electricity b) always conducts electricity due to free moving ions 18. a) Why do ionic compounds like lead iodide not conduct electricity when solid? b) Explain what is meant by the term ionic bond. 19. Copy the passage and delete the incorrect phrases: Ionic substances conduct / do not conduct electricity in solid form because the ions are/ are not free to move. However ionic compounds conduct / do not conduct electricity when molten or in solution because the ions are/ are not free to move. 20. The table contains information about some substances. Substance A B C D E Melting point (0C) 639 2967 159 1402 27 Boiling Point (0C) 3228 3273 211 2497 677 Conducts as a solid Yes No No No Yes Conducts as a liquid No No No Yes Yes a) Identify the substance which exists as a covalent network. b) Identify the substance which could be calcium fluoride. c) Identify the substance which exists as covalent molecules. 21. The dead sea is a pool that was left behind after a sea had evaporated over many centuries. The following table gives average values of some ion concentrations in water samples from the open sea and the dead sea (In gl-1). Ion Na+ ClMg2+ SO42Ca2+ Concentration 10.5 19.0 1.5 2.5 0.5 30.0 160.0 40.0 0.5 10.0 of ion in Sea water (gl-1) Concentration of ion in Dead sea (gl-1) a) Use a suitable scale to draw a bar graph for the concentration of ions in water from the Dead sea. b) Which ion is more concentrated in sea water than in the Dead sea? 22. Peter tested the conductivity of molten sodium chloride, hexane (C6H14) and water. a) Draw the apparatus that Peter would have used to test the conductivity of the samples. b) Explain why hexane will not conduct electricity. c) Peter also tested solid sodium chloride and found that this did not conduct electricity. Explain why sodium chloride conducts electricity when molten but not when solid. 23. A student investigated how the concentration of sodium chloride in water affected the freezing point. (a) What type of bond is broken in sodium chloride when it dissolves in water? (b) The table shows information about the freezing point of different sodium chloride solutions. Concentration of sodium chloride solution (moll-1) Freezing point (oC) 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0 -0.2 -0.5 -0.8 -1.1 -1.5 i) Draw a graph of concentration of sodium chloride against freezing point. ii) Describe the relationship between the concentration and freezing point. iii) Predict the freezing point of a 0.6moll-1 solution of sodium chloride. 24. Write ionic formula for the following: a) sodium chloride c) potassium bromide e) barium carbonate g) aluminium sulphate b) magnesium oxide d) zinc (II) sulphide f) lithium hydroxide 25. The colour of some compounds is shown in the table below. Compound cobalt chloride iron (III) sulphate nickel (II) chloride sodium chloride sodium manganate (VII) sodium sulphate iron (III) chloride potassium chloride potassium manganate (VII) Colour red brown green colourless purple colourless brown colourless purple Using the information from the above list, suggest possible colours for the following ions. (a) Cobalt (II) ion, Co²+ (b) Iron (III) ion, Fe³+