International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research (IJSETR)
Volume 1, Issue 1, July 2012
A Novel Non-Expandable Visual Cryptography
with Increased Capacity
Madhurendra Kumar, Dr.Cyril Prasanna Raj P, Vinod Kumar B. L
Abstract—Now a days serious matter is to send the
confidential message from one person to another person
who is separated from us, and sitting somewhere in the
different location of globe. In order to hide the
information from third person, the concept called
encryption and decryption has come in picture. And this
whole concept as a one is called cryptography. In past
data are hidden in image and the image size is increased
to two to four times as a return the secret information
pixel size is also increased at the transmitting end and at
the receiver end the message is decrypted. But the quality
of image which has been received at the receiver end is
not good. In order to overcome that problem, we come up
with the non-expandable visual cryptography.
Index Terms— Visual cryptography, Image sharing
I. INTRODUCTION
Due to tremendous increased in network communication and
use of computer in the network communication. It is easy to
transmit message in form of the text, image and video. It can
be used in personal, official purpose. So, it’s very important to
transmit the data in the hidden format. It’s very important to
prevent the detection of information. Visual cryptography
was bring out by Naor and Shamir. In this technology Secret
image is decrypted by overlapping the shared image. In past
image is expanded two to four times the original image and
then pixel of the expanded image is encoded. But when it is
decrypted the image which has been recovered is not good
quality. And this leads to blurriness in the image. In order to
avoid it concept called non expanded visual cryptography
discovered. Now a days it’s very important to hide the
information and it’s not been detected.
Manuscript received Oct 15, 2011.
Madhurendra kumar, Dept of ECE ,M..S Engineering College , Bangalore,
India, (madhu2kumar@gmail.com),9632099347
Dr.Cyril
Prassana Raj P, Dean(R&D),professor (ECE),M..S
Engineering College, Bangalore, India,(cyrilyahoo@gmail.com)
Mr.Vinod Kumar B. L (Asst.Professor) Dept of ECE , M..S Engineering
College, Bangalore, India,( vinodtaurus87@gmail.com)
,
II. PROPOSED METHOD
In proposed scheme the image which has to be hide is divided
into four parts. Share block is generated for each parts. The
share block is encoded. Each block will have two sharing.
Then the two Sharing will be overlapped and we will get the
one part of the image. And this process is repeated. So that we
will able to get whole of the image. In this method we can also
able to get the confidential data. For that we need to divide the
region as explained above. And one region will have two
share. Then one share will be reversed. If we will do this
process we will able to get the extra confidential data which
has to be hidden in the cover image. By this proposed method
we will be able to prevent the detection of information by the
unauthorized person. And only the authorized person will be
able to get the information safely. In this paper proposed
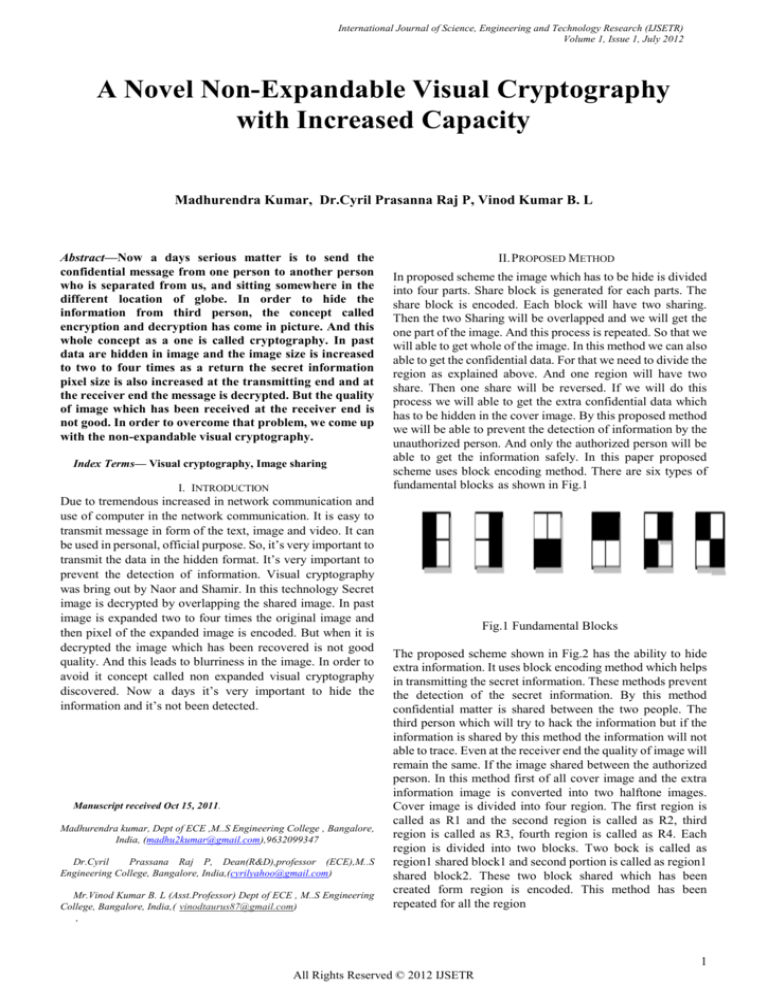
scheme uses block encoding method. There are six types of
fundamental blocks as shown in Fig.1
Fig.1 Fundamental Blocks
The proposed scheme shown in Fig.2 has the ability to hide
extra information. It uses block encoding method which helps
in transmitting the secret information. These methods prevent
the detection of the secret information. By this method
confidential matter is shared between the two people. The
third person which will try to hack the information but if the
information is shared by this method the information will not
able to trace. Even at the receiver end the quality of image will
remain the same. If the image shared between the authorized
person. In this method first of all cover image and the extra
information image is converted into two halftone images.
Cover image is divided into four region. The first region is
called as R1 and the second region is called as R2, third
region is called as R3, fourth region is called as R4. Each
region is divided into two blocks. Two bock is called as
region1 shared block1 and second portion is called as region1
shared block2. These two block shared which has been
created form region is encoded. This method has been
repeated for all the region
1
All Rights Reserved © 2012 IJSETR
International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research (IJSETR)
Volume 1, Issue 1, July 2012
Table.2 Generation of share blocks
Fig.2 Proposed Block Diagram
III. ENCRYPTION AND DECRYPTION
In the above table. 2 sequence of the matrix consider 0 as the
Steps which are needed to encrypt and decrypt the image is
as follows.
black pixel and 1 as the white pixel.
Finally we do the xor operation to get the cover
images. Let us consider that the cover image divided
into 4 regions. Let’s say region R1, region R2,
Region R3, Region R4. Region R1 is divided into
shared region as R1S1 and R1S2. This process is
repeated for Region 2 to get R2S1 and R2S2. Region
3 to get R3S1 and R3S2.But 4th location is obtained
by xor operation of R1S2 and the extra secret
information to get the R4S1 and again R4S2 is
obtained by the Xor operation of region 4 with
R4S1. Now to obtain the cover image we need to do
the xor operation between the obtained shared. In
order to obtain the extra information we need to
exchange the location of shared 1. In location 1 we
need to exchange the first shared location with the
fourth location. And after exchanging the location do
xor operation with the shared2 to get the extra
information. The whole of the above process is
shown in Fig.3.
we divide the cover region into number of shared
blocks with 2x2 pixels. In this case cover region,
say has MxN pixels. We need to have 2x2 Block.
So, in order to find the no. of blocks in cover
region we need to divide the total pixel in cover
region by 2x2 block pixels. The division will
gives us the no. of 2x2 block in the given cover
region. Consider 0 as the black pixel and 1as
white pixel. So in order to show the particular
block, we can use matrix format. Consider the
block has the combination of
can be written
in matrix format as
.
In step 2 we do sharing of region. Region are
divided into the blocks. The division of secret
block in two shares are explained in Table1.
There are certain pattern by which image can be
denoted in term of the matrix.
Table.1 16 types of blocks with 2*2 pixels in the
original secret image
Fig.3 Process of generating share for each region
IV. SIMULATION RESULTS
Non-Expanded Visual cryptography method
helps us to get the hidden information from the
cover image in a better quality. As pixel size
remain same as the original image. In order to
avoid the loss of information in the image
Non-Expanded Visual Cryptography has been
proposed, to maintain the quality of the image.
2
All Rights Reserved © 2012 IJSETR
International Journal of Science, Engineering and Technology Research (IJSETR)
Volume 1, Issue 1, July 2012
V. CONCLUSION
Fig.4 Cover image and extra information
Now a days the challenging work is to transmit the secret
information and avoid the detection of the information. In
Non-Expanded Visual Cryptography which has been
proposed in this paper. In this process first step is to divide the
secret image into four regions. Again each region is divided
into two shared blocks. The blocks are generated then we
encode each of the block. Blocks are divided in such a way
that each block will be 2x2 pixels. Extra information is
detected by reversing the first share and superimposing with
the other image. In this way we can avoid the detection of the
secret information.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research work has been supported by my project
supervisors Dr. Cyril Prasanna Raj P, Dean (R&D), Mr.
Vinodkumar B.L (Asst.Prof) Dept. of ECE. I would like to
thank my supervisors, parents and friends for their support.
REFERENCES
Fig.5 Divide into four logical regions
[1] M. Naor and A. Shamir, “Visual cryptography,” Advance in Cryptology:
Eurpocrypt’94, Lecture Notes In Computer Science, Springer Verlag,
Germany, Vol. 950, pp. 1–12, 1995.
[2] O. Kafri and E. Keren, “Encryption of pictures and shapes by random
cipher-grids,” Optics Letters, Vol. 12, No. 6, pp. 377–379, 1987.
[3] W.P. Fang and J.C. Lin, “Visual cryptography with extra ability of hiding
confidential data,” Journal of Electronic Imaging , Vol. 15, No. 2,
pp.0230201–023020 7, 2006.
Fig.6 Encrypted Image
[4] C. C. Lin and W. H. Tsai, “Visual cryptography for gray-level images by
dithering techniques,” Pattern Recognit. Lett., Vol. 24, No. 1–3, pp.
349–358, 2003.
Fig.7 Decrypted cover image
Fig.8 Decrypted extra image
3
All Rights Reserved © 2012 IJSETR









