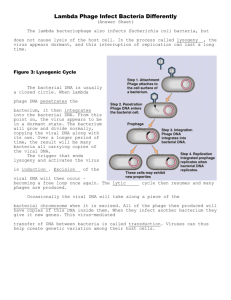
Chapter 5 Genetics and Variation
advertisement

Teaching plan of bilingual teaching 双语教学教案 Gannan Medical College Department of pathogenic Biology Teacher (教师) Date (日期) Grade (年级) Speciality 专业 Lecture type (授课类型) Clinical medical (临床医学) Subject (课程) chapters and sections (授课章节) Chapter 5 Genetics and Variation Objective and request 教学目的和要求 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Emphasis and difficulty 授课重点、难点 Reference teaching material 参考教材 Teaching aid 媒体与教具 Theory Course (理论课) Class hour (学时) Medical Microbiology 医学微生物学 Master the characteisticrs of plasmid. Master the mechanism of mutation and gene transfer of bacteria Master the interrelation between phage and bacteria Understand the.size, shape and structure of phage Understand the characteristics of Viral Genetics. 1. The interrelation between phage and bacteria 2. The mechanism of mutation and gene transfer of bacteria 1.周正任主编.《医学微生物学》第 6 版 2.Medical microbiology(21 edition, Jawetz, Melnick, and Adelberg) Powerpoint Teach contents(教学内容) Chapter 5 Genetics and Variation Section I Bacterial inheritance and variation Concept: (1) heredity : general stability on “likeness” in the characteristics of progeny and parent. (2) variation: the difference between progeny and parent Heritable variation: genetic substance changes . nonberitable variation : enviroment changes I. variation examples. 1.shape and structure variation 2.colony variation smooth colony rough colony 3. virulence variation, vaccine BCG: Bacilli of calmetter-Gueria ;230 passages, 13 years. 4. Resistance variation 1 2 hours II. Genetic substance 1. chromosome consists of a circular double strand DNA molecular, control bacterial life without introne. 2. Plasmid Extrochromosomal genetic substance. Circle double strand DNA (1)autonomous replication binding to chromosome —episome (2)contral most of auxiliary functions of bacterial cell Antibiotic resistance——R plasmid . production of fimbriae ——F plasmid bacteriocin——E. coli col. plasmid. (3)dispensable, it can be lost . (4)tranfer from a bacteria to another (5)Incompatibility and compatibility. 3. bacteriophage. Bacteriophage Infecting bacterial virus (1) viral common properties smallest ,simple structure , DNA/RNA, parasite in living cell (2) widespread existence (3) high host –specific parasitism (I.) biological properties 1. Shape and structure Seen by EM: Tadpol , microsphere slim rod Structure: head core: DNA/RNA Capsid: protein coat Tail: pipe-like, collar, base plate, tail fib (II). Interrelation between phage and bacteria 1. Virulent phage. Reproduction and lyzing Bacteria, which can replicate in cell and released in lysis of B . 2. lysogenic phage. infected bacterial phage doesn’t replicate it’s gene ,integrated with bacterial DNA, its replication is associated with bacterial DNA lysogenic phage (temperate phage) lysogenec bacteria prophage : The DNA of temperate phage integrated into bacterial DNA. 4.transposon: transposable elements insertion sequence transposon III. Mechanism of bacterial variation: 1. Mutation (1) concept: a stable heritable change of acterial gene , (2) type of mutation 2 2. genetic transfer and recombination 1) transformation recipient B. takes up exogenous DNA of donor B. 2) transduction . donor bacterial DNA is transfered to recipient bacterial by phage . 3) conjuqation bacterial DNA is transferred from donor bacteria to recipient bacteria by F pilus. 4) lysogenic conversion 5) protoplast fusion III. Medical application 1. Bacterial indentification 2. prevention treatment of diseases. Eg . vaccine 3. screening potential carcinogen . Ames test 4. genetic engineering Section II Viral Genetics The nature of the viral genome (RNA or DNA; segmented or nonsegmented) plays an important role in the genetics of the virus. 1. Mutations: ----permanent changes in sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acid. ----types of utation: Mutants can be point mutants (one base replaced by another) or insertion/deletion mutants. ---- origion (1) Spontaneous mutations (2) Mutations that are induced by physical or chemical means ----examples of Mutant 2. Recombination and reassortment: 3. Integration: viral genome insert into host cell genome . 4. Complementation: 5. Phenotypic mixing: question 思考题 What are the mechanisms of transformation, conjugation, transduction, and lysogenic conversion? 3