Problems
advertisement

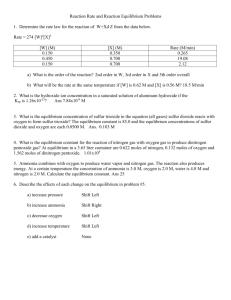
CONCENTRATION OF SOLUTIONS Molarity (M) = moles of solute Liters of solution Molalilty (m) = moles of solute kg of solution Grams of solute = M x L x gfm Grams of solute = m x kg x gfm Dilutions: M1 V1 = M2 V2 m1 V1 = m2 V2 1. What is the molarity of a solution that contains 49 g of NH4Br in 200 ml of solution? (2.5 M) 2. What is the molality of a solution that contains 10 g of sodium chloride in 125 ml of water? (1.38 m) 3. How many grams of sucrose (C12H22O11) is needed to make 500 ml of a .60 M solution? 3. What volume of a 2.5 M MgSO4 solution contains .40 moles of MgSO4? (102.6 g) (.16 L) 4. What volume of 2.0 M NaBr solution must be used to prepare 300 ml of a .75 M NaBr solution? (112.5 ml) 6. How many grams of NH4Cl needs to be dissolved in 100 g of water to produce a 1.10 m solution? (5.83 g) 7. What is the final molality of a solution prepared by diluting 200 ml of 8.0 m LiF to 727 ml? (2.2 m) WATER & SOLUTION REVIEW PROBLEMS 1. Calculate the % water in sodium sulfate decahydrate. 2. How many grams of water will be given off by the heating of 21.0 g of Ba(OH)2*8H2O? (55.9%) (9.6 g) 3. The molality of a solution of ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) in water is 1.54 m. How many grams of alcohol are dissolved in 2.50 kg of water? (177 g) 4. What is the molarity of an NaOH solution that contains 24.0 g of NaOH in 300 ml of solution?(2.00 M) 5. What volume of 1.71 M NaCl solution contains 1.20 moles of NaCl? (.7 ml) 6. What is the molality of a solution containing 10.0 g of Acetic Acid (CH3COOH) in 125 g of water? (1.33 m) 7. What volume of 18 M H2SO4 solution is needed to prepare 90 ml of 2.0 M H2SO4? (10 ml) 8. Determine the freezing point of a solution made by dissolving 27.5 g of methyl alcohol (CH3OH) in 250 g of water? (Kf = -1.86oC/m) (-6.39 oC) 9. What is the new boiling point of an aqueous solution that contains 191 g of Potassium Phosphate dissolved in 2.75 kg of water? (Kb = .512oC/m) (100.68 oC) 10. Calculate the GFM of a solution of 10.7 g of a nonvolatile molecular compound in 55 g of water that freezes at –3.26oC. ? (Kf = -1.86oC/m) (110.56 g/mol) CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM 1. One liter of a gas mixture at 100oC at equilibrium contains .0045 moles of dinitrogen tetroxide and .030 moles of nitrogen dioxide. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the formation of nitrogen dioxide from dinitrogen tetroxide. Are the products or reactants favored at equilibrium? (.20) 2. One mole of hydrogen and one mole of iodine are sealed in a 1 L flask and allowed to react at 450oC. At equilibrium 1.56 mol of Hydrogen Iodide is present. Calculate the Keq for the reaction. Are the products or reactants favored at equilibrium? (48.6) 3. The equilibrium constant for the decomposition of Bromine Monochloride gas into its elements is 11.1 and the equilibrium mixture contains 4.00 mol Chlorine gas. How many moles of Bromine gas and Bromine Monochloride gas are present in the equilibrium mixture? (4.00 mol, 1.20 mol) LeCHATLIER’S PRINCIPLE For the reaction: 2 SO3 (g) + CO2 (g) + heat 1. addition of CO2 or 2. addition of heat or 3. decrease in pressure or 4. removal of O2 or 5. addition of a catalyst or For the reaction: H2 (g) + F2 (g) 2HF (g) + heat 1. decrease in temp. or 2. increase in pressure or 3. removal of H2 or 4. addition of HF or For the reaction: CS2 (g) + 4 O2 (g) NaNO3 (s) + H2O (l) + heat solution 5. if the equilibrium shift causes heat to be released or 6. if the equilibrium shift causes the solubility to increase or 7. if the equilibrium shift favors re-crystallization or 8. if the equilibrium shift favors dissolving or 9. if the equilibrium shift favors the exothermic reaction or For the reaction: CO2 (g) + H2O (l) solution + heat 10. if the equilibrium shift causes heat to be absorbed or 11. if the equilibrium shift causes the solubility to decrease or 12. if the equilibrium shift favors the endothermic reaction or 13. if the equilibrium shift favors dissolving or 14. if the equilibrium shift favors effervescence or Calculating Boiling Point and Freezing Point Changes (Note: 1 L H2O = 1 kg H2O) 1. What is the boiling point of a solution that contains 15.0 g of sucrose (C12H22O11) in 150 g of water? (100.15 oC) 2. What is the freezing point of a solution that contains 10.0 g of sucrose (C12H22O11) in 85 g of water? (-6.40oC) 3. If 35.0 g of a molecular compound dissolved in 500 g of water results in a freezing point of –3.72oC, what is the GFM of the compound? (35 g/mol) 4. If the radiator of an automobile contains 12 L of water, how much would the freezing point be lowered by the addition of 5.0 kg of Prestone (glycol, (C2H4(OH)2)? How much Zerone (methyl alcohol, CH3OH) must be added to achieve the same result? (-12.5oC; 2.58 kg) 5. What is the boiling point of a solution that contains 137.5 g of Calcium Chloride in 1400 g of water? (101.35oC) 6. What is the freezing point of a solution that contains 72 g of Magnesium Sulfate in 1300 g of water? (-1.71oC) 7. One mole of a compound of Iron and Chlorine is dissolved in 1 kg of water. The boiling point of the solution is 102.05oC; the freezing point is –7.44oC. What is the formula of this compound? (FeCl3)