Rational use of antibiotics
advertisement

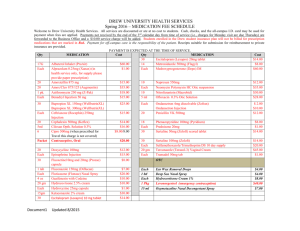
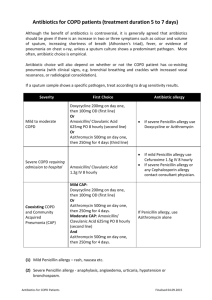
Antibiotic guidelines Department of Internal Medicine PMHC The guidelines suggested below are aimed to encourage rational, safe, effective and economic use of the limited number of anti-infective drugs we have available to us. Where possible these guidelines follow the South African essential drug list guidelines. The choice of antibiotic in each guideline is based on the best available evidence from international and existing South African guidelines. The guidelines suggest empirical treatment of common conditions and syndromes. It must be stressed that taking appropriate samples for culture is of paramount importance both for the individual patient and for monitoring of resistance. If a patient has a positive culture result their treatment should be rationalised to the narrowest spectrum of antibiotic possible to prevent resistance occurring. If you are in doubt about what antibiotic to use please call one of the medical consultants for advice. The department of internal medicine is currently in the process of auditing microbial isolates from the medical wards. The sensitivity patterns will be analysed and this may lead to changes in the antibiotic guidelines. Currently the most common infecting organism is given for each infection. These guidelines are not compulsory but if you wish to deviate from the guidelines you must be prepared to justify your decision. These guidelines only apply to adult patients under the care of the department of medicine. The guidelines outline antibiotic choices only, other aspects of management will be covered in the department of internal medicine management protocols. 1. Upper respiratory tract infections a. Tonsillitis / pharnygitis – (Streptococcus pyogenes) i. First line – Pencillin V 500mg 6hrly p.o. for 10 days ii. If unable to swallow – benzyl penicillin 1.2 g 6 hrly i.v. – until able to swallow then switch to penicillin V iii. Penicillin allergry – erythromycin 500mg 6 hrly p.o. for 5 days (can be given i.v. in necessary) b. Otitis externa – clean and dry ear with acetic acid – use flucloxacillin 500mg 6 hrly p.o. for 5 days if evidence of bacterial infection ( for severe infection in diabetic patients use ciprofloxacin 500mg 12hrly p.o. and gentamicin 5mg/kg daily i.v.i.) c. Otitis media- (S.pneumoniae) i. Acute – amoxicillin 500mg 8 hrly p.o. for 5 days 1. Pencillin allergy – erythromycin 500mg 6 hrly p.o. for 5 days ii. Chronic – dry mopping and refer to ENT d. Oropharnygeal candadiasis – (Candida albicans) i. First line – nystatin 100,000 iu 6 hourly p.o. for 7 days ii. Alternative – fluconazole 750mg stat po. 2. Lower respiratory tract infections a. LRTI / Pneumonia – (S.pneumoniae, Heamophilus influenzae) i. Mild – amoxicillin 500mg 8 hourly p.o. for 5 days 1. Penicillin allergy – use erythromycin 500mg 6 hourly orally. ii. Severe – Benzyl Penicillin 1.2g 6 hrly i.v.i. until patient improves and can be changed to oral therapy iii. In severe pneumonia add gentamicin 5mg/Kg daily.. iv. If atypical pneumonia is suspected add erythromycin 500mg 6 hrly p.o. or 1g 6hrly ivi. b. Infective exacerbation of chronic obstructive airways disease – (S.pneumoniae, H.influenzae, Moraxella cattarhalis) i. Amoxicillin 500mg 8 hrly p.o. for 5 days 1. Penicillin allergic patients use either erythromycin 500mg 6 hrly p.o. or doxicyclin 100mg daily p.o. c. Tuberculosis – (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) d. i. See EDL – RHZE – remember to choose dose according to weight and also to prescribe pyridoxine Pneumocystis pneumonia – Cotrimoxazole 4 tabs 8 hrly p.o or 4 vials 8 hrly ivi. for 21 days then 2 tabs daily for life. Note if oxygen saturation is <93% or PaO2 <8 kPa add prednisolone 0.5mg/kg 12 hrly p.o. for 7 days then reduce dose over next 2 weeks. 3. Gastrointestinal tract infections a. Oesophageal candadiasis – (C. albicans) i. Fluconazole 200mg daily p.o. for 2 weeks b. Helicobacter pylori infection – Omeprazole 20mg daily po, amoxicillin 1g 12 hrly p.o. and metronidazole 400mg 8 hourly p.o. for 7 days c. Gastroenteritis – (many enteric viruses, Campylobacter jejuni, Esherichia coli, Salmonella species ) mainstay of treatment is fluid replacement – patients who are systemically unwell with fever use ciprofloxacin 500mg 12hrly p.o. for 5 days d. Cholera – (Vibrio cholera) fluid replacement essential – use ciprofloxacin 500mg stat p.o. to reduce duration of illness and carriage e. Dysentery i. Bacterial dysentery – (Shigella species) ciprofloxacin 500mg 12 hrly p.o. 5 days ii. Amoebic dysentery – (Amoeba histolitica) metronidazole 400mg 8 hrly p.o. 5days f. Typhoid – Ciprofloxacin 500mg 12 hrly po 10 days, use ceftriaxone 2g daily in severely ill patients g. Liver abscess i. Amoebic – metronidazole 800mg 8 hrly p.o. 7-10 days ii. Polymicrobial – co-amoxiclav 1.2g 8 hrly i.v.i and metronidazole 500mg 8 hrly i.v.i. .until improvement seen (will need aspiration) 4. Cardiac infections a. Rheumatic fever – (S.pyogenes) i. Acute attack – benzyl penicillin 1.2 g 6 hourly i.v.i. can change to oral penicillin v or amoxicillin as soon as patient is well enough – treat for 5 days ii. Prophylaxis – benzathine penicillin 1.2g monthly i.m.i. or pen VK 250mg 12 hourly b. Infective endocarditis – (various organisms including S.viridans, Staphlococcus areus, HACEK etc) initial treatment – benzyl penicillin 1.2g 6 hrly i.v.i. and gentamicin 40mg 12 hrly i.v.i.. Adjust treatment according to blood culture results. (Penicillin allergy use vancomycin 500mg 12 hrly i.v.i.) c. Pericarditis – usually tuberculosis – treat with standard antituberculosis treatment and add prednisolone 60mg daily for one month then taper – see guideline 5. Central nervous system infections a. Viral meningitis – no specific antiviral therapy indicated b. Bacterial meningitis – (Nessiria meningitides, S.pneumoniae, H.influenzae, Listeria monocytogenes) i. First line – ceftriaxone 2g 12 hrly i.v.i. – give as soon as the diagnosis of meningitis is expected. Change therapy as soon as a specific diagnosis (e.g. benzyl penicillin for pneumococcal meningitis) is made or if meningitis is ruled out after lumber puncture. c. Tuberculous meningitis – (M.tuberculosis) see TB treatment guidelines and guideline for use of dexamethasone in TB meningitis d. Cryptococcal meningitis – (Cryptococcus neoformans) first line amphoteracin 1.0 mg/kg daily i.v.i. for 2 weeks followed by fluconazole 400mg daily p.o. for 8 weeks then fluconazole 200mg daily for life e. Cerebral toxoplasmosis – (Toxoplasma gondi) cotrimoxazole 4 tabs 12 hourly p.o. for 30 days then 2 tabs daily for life. (or until CD4 count >200 for 6 months) f. Viral encephalitis –(H.simplex) if HSV encephalitis suspected use acyclovir 10mg/kg 8 hrly i.v.i. for 21 days (can change to oral acyclovir once the patient responds) 6. Urinary and genital tract infections a. Urinary tract infection –(E.coli, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella sp, Pseudomonas auerigenosa) b. ciprofloxacin 250mg 12 hrly p.o. for 5 days i. Can give ciprofloxacin 500mg single p.o. dose to non pregnant women ii. Pregnant women – nitrofurantoin 100mg 6 hrly p.o. for 5 days c. Pyelonephritis – (E.coli, P. mirabiliss, K. areogenes, P. auerigenosa) i. First line – ciprofloxacin 500mg 12 hrly p.o.for 5 days ii. Second line (or in severely ill patients with signs of SIRS or vomiting) – cefuroxime 1.5g 8 hrly i.v.i. for 5 days or until able to take oral medication then change to ciprofloxacin 500mg 12 hrly p.o. d. STI’s – refer to DOH protocols i. Male discharge – (N. gonorrhoeae, C.trachomatis) cefixime 400mg po. stat, doxicycline 100mg 12 hrly p.o. for 7 days ii. Female discharge –(N. gonorrhoeae, C.trachomatis, G.vaginalis, Trichomonas) ceftriaxone 250mg i.m.i. stat, doxicycline 100mg 12 hrly p.o. for 7 days and metronidazole 2g stat p.o. iii. Pelvic inflammatory disease –mild treat as for female discharge severe – admit and give- cefuroxime 750mg 8 hrly i.v., gentamicin 5mg i.v. daily for 5 days and doxicycline 100mg 12 hrly p.o. for 7 days. iv. Genital ulcers – (Treponema pallidum, Cl.trachomatis, H.ducreyi, C.granulomatis) benzathine penicillin 2.4 mu i.m.i. stat, erythromycin 500mg 6 hrly p.o. for 7 days. ( also consider acyclovir 400mg 8hrly p.o. for 5 days if has herpes simplex) 7. Skin infections a. Impetigo – (S.aureus) i. flucloxacillin 250mg 6 hrly p.o. 5 days ii. Penicillin allergy – erythromycin 250mg 6hrly p.o. 5 days b. Erysipelas – (S.pyogenes / S.aureus) i. Flucloxacillin 500mg 8 hrly p.o. 5 days ii. Penicillin allergy – erythromycin 250mg 6 hrly p.o. for 5 days c. Cellulitis – (S.pyogenes, S.aureus) i. Mild – flucloxacillin 500mg 6 hourly p.o. for 5 days 1. Penicillin allergy – use erythromycin 500mg 6 hrly p.o. for 5 days ii. Severe – benzyl pencillin 1.2g 6 hrly i.v. and flucloxacillin 1g 6hrly i.v. until improved (swap to oral flucloxacillin as soon as improving) iii. Faliure to improve – consider another diagnosis – use cefuroxime 1.5 8 hrly i.v. and gentamicin 5mg/kg daily i.v. iv. MRSA – be guided by sensitivities – use two antibiotics to which organism is sensitive – ask advice of medical consultant d. Deep seated skin infection (various Streptococci and other gram negative and positive organisms) – benzyl penicillin 1.2g 6 hrly,i.v.i. flucloxacillin 1g 6 hrly i.v.i. and gentamicin 5mg/kg daily i.v. (can also add clindamycin) e. Herpes simplex – (Herpes simpex virus 1 and 2) i. Acute attack – try to start during prodrome – acyclovir 200mg 5 times a day p.o. for 7 days f. Herpes zoster – (Varicella zoster) i. Zoster - if diagnosed early with fresh blisters use – acyclovir 800mg 6 hrly p.o. for 7 days ii. Chickenpox in adults – use acyclovir 800mg 6 hrly p.o. for 7 days. If patient severly ill especially with lung involvement use –aciclovir 10mg/kg 8 hrly i.v.i. until improvement occurs g. 8. 9. Scabies – (Sarcoptes scabiii) i. Use benzyl benzoate one application – remember to treat all family members Sepsis a. General principles of management i. Try and determine the source of sepsis and use antibiotics appropriate to the source of infection. Remember malaria can prevent with sepis. ii. Sepsis source unknown – use ceftriaxone 2g daily i.v. add gentamicin 5 mg/kg daily i.v. and metronidazole 500mg 8hrly i.v. for intra-abdominal infections. Check renal function and adjust gentamicin dose as appropriate. Malaria – (Plasmodium falciparum and other Plasmodium sp.) i. Co-artem is the treatment of choice for non severe uncomplicated malaria. The dose regimen is based on weight as shown below. The patient should take a stat dose then take the next dose after 8 hours then take a dose 12 hourly for the next two days (i.e. a total of 6 doses are taken). Weight of patient Dose (6 doses in total as shown above) 10 – 15 Kg 1tab 15 – 25 Kg 2 tabs 25 – 35 Kg 3 tabs 35 – 65 Kg 4 tabs >65 Kg 4 tabs as above given with a fatty meal of milk to ensure absorption ii. Complicated malaria – Quinine 600mg 8 hrly for 7 days 1. If intravenous quinine used give 20mg/kg over 4 hours then after 8 hours give quinine 10mg/kg over 4 hours every 8 hours until the patient can take oral quinine. Monitor closely for hypoglycaemia 2. In complicated malaria also give oral doxicycline 100mg 12 hourly for 7 days. In children, pregnant women, and patients who are unconscious use clindamycin iv 10mg/kg 12 hourly until able to take oral doxicycline. 10. Surgical and orthopaedic infections a. Please refer to protocols from the relevant departments 11. HIV infection a. Please refer to Department of health antiretroviral treatment guidelines b. Patients admitted to hospital who are taking antiretrovirals should generally have their treatment continued unless interruption is specifically indicated. If unsure ask advice from senior medical staff. Please make sure you write up their treatment correctly. There are many potential interactions between antiretrovirals and other medication. Before starting new medication in patients on antiretrovirals consider possible drug interactions and if unsure ask advice. 12. Reserve antibiotics a. The following antibiotics should be kept in pharmacy for use in specific indications under consultant physician only direction Piperacillin, piptazobactam, co-amoxiclav, vancomycin, amikacin meropenem, valaciclovir, ganciclovir and valganciclovir Date of guideline December 2008 Date of review December 2009 Signed