Unit 3 – HD1 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
advertisement
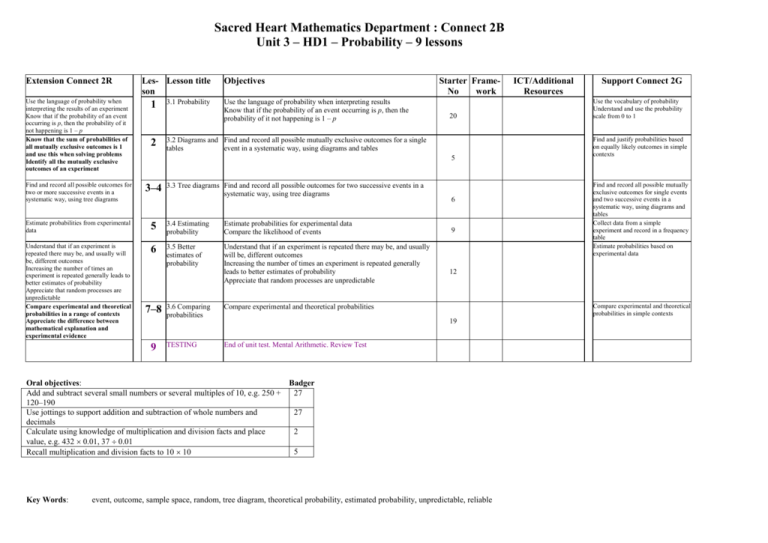
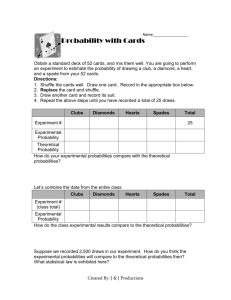
Sacred Heart Mathematics Department : Connect 2B Unit 3 – HD1 – Probability – 9 lessons Extension Connect 2R Les- Lesson title son Objectives Use the language of probability when interpreting the results of an experiment Know that if the probability of an event occurring is p, then the probability of it not happening is 1 – p Know that the sum of probabilities of all mutually exclusive outcomes is 1 and use this when solving problems Identify all the mutually exclusive outcomes of an experiment 1 Find and record all possible outcomes for two or more successive events in a systematic way, using tree diagrams 3–4 Estimate probabilities from experimental data 5 3.4 Estimating probability Estimate probabilities for experimental data Compare the likelihood of events Understand that if an experiment is repeated there may be, and usually will be, different outcomes Increasing the number of times an experiment is repeated generally leads to better estimates of probability Appreciate that random processes are unpredictable Compare experimental and theoretical probabilities in a range of contexts Appreciate the difference between mathematical explanation and experimental evidence 6 3.5 Better estimates of probability Understand that if an experiment is repeated there may be, and usually will be, different outcomes Increasing the number of times an experiment is repeated generally leads to better estimates of probability Appreciate that random processes are unpredictable 2 3.1 Probability Use the language of probability when interpreting results Know that if the probability of an event occurring is p, then the probability of it not happening is 1 – p Starter FrameNo work 20 3.2 Diagrams and Find and record all possible mutually exclusive outcomes for a single tables event in a systematic way, using diagrams and tables 5 7–8 9 3.3 Tree diagrams Find and record all possible outcomes for two successive events in a systematic way, using tree diagrams 3.6 Comparing probabilities Compare experimental and theoretical probabilities TESTING End of unit test. Mental Arithmetic. Review Test 6 9 Support Connect 2G Use the vocabulary of probability Understand and use the probability scale from 0 to 1 Find and justify probabilities based on equally likely outcomes in simple contexts Find and record all possible mutually exclusive outcomes for single events and two successive events in a systematic way, using diagrams and tables Collect data from a simple experiment and record in a frequency table Estimate probabilities based on experimental data 12 Compare experimental and theoretical probabilities in simple contexts 19 Oral objectives: Badger Add and subtract several small numbers or several multiples of 10, e.g. 250 + 27 120–190 Use jottings to support addition and subtraction of whole numbers and 27 decimals Calculate using knowledge of multiplication and division facts and place 2 value, e.g. 432 0.01, 37 0.01 5 Recall multiplication and division facts to 10 10 Key Words: ICT/Additional Resources event, outcome, sample space, random, tree diagram, theoretical probability, estimated probability, unpredictable, reliable