Modular Electronic Systems (part 1)
advertisement

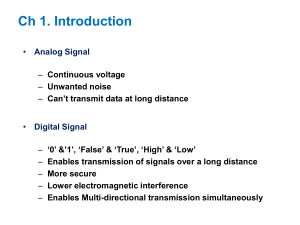
Modular Electronic Systems Introduction: Electronics A systematic approach The systems represented in this section make use of E&L systems boards. Centres using Alpha systems will be able to adapt the materials as appropriate. In all areas of technology, including electronics it is useful to have a systems approach to problem solving. This makes it easier to understand problems and enables you to solve these electronic problems in a structured manner. All electronic circuits and systems have an input, a process and an output. Identifying these basic parts is the first step in solving electronic circuit/system problems. Input Process Output Modular boards Modular circuit boards provide a simple means of solving both simple and complex electronics problems. It is easy to identify the input, process and output stages. The boards are, however, bulky and expensive. Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes 1 Analogue and digital signals All components in electrical and electronic circuits are either receiving or transmitting electrical signals. These signals can be either analogue or digital. Analogue devices An analogue signal varies according to the physical surroundings. For example, the E&L light-sensing unit will send out a voltage that is proportional to the amount of light falling on the LDR. TP Light sensor (ORP 12) + + S 0V S 0V - - 0v E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd This E&L unit is called an input transducer because it converts the change in light to a change in voltage. Light Intensity LDR Varying Voltage The graphs of analogue input transducers are typically a sloping line or a curve. Typical analogue input transducers are: input voltage units light-sensing units temperate-sensing units moisture/rain sensor units sound-sensing units. 2 Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes Digital devices A digital signal is one which has only two settings, on or off. In electronic terms it has only two levels, high or low. The push switch unit below is a typical simple digital transducer. O/P IND + + S 0V S 0V TP - - 0v ACTIVE HIGH E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd This E&L unit is called an input transducer because it converts the change in physical movement to a change in voltage. Mechanical Movement Switch High or Low Voltage The graph of typical digital input transducers is shown below. Time Typical digital input transducers are: switch units magnetic switch units pulse generator units. Logic In digital terms: on or high is Logic 1 off or low is Logic 0. This is why modern appliances have switches marked in this way. 1 0 Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes 3 Transducer driver board All systems require a transducer driver. This will normally be the second last board in the system, that is the board before the output board. COLLECTOR +V EMITTER + TP S 0V - BASE + S 0V - 0v 0v E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd The transducer driver is a small transistor amplifier that provides the output devices with enough power for them to operate. The signal (current and voltage) from the input is otherwise too weak to power the output. The terms in the above diagram are explained in the ‘Component Electronic Systems’ section. Output transducers Output transducers take an electrical signal and change it into a physical output. They include the output boards in modular systems or output components in any electronic system. The main output transducers are shown below. ACTIVE LOW + + S 0V S 0V - + - - S 0V + + S 0V - S 0V - E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd + S 0V - - E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd 4 + + S 0V S 0V - E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd + + S 0V - S 0V - E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes The Inverter The inverter is often referred to as a NOT gate. This is because the output from the inverter is NOT equal to its input. If the input signal is high (or logic 1) then the output signal is low (or logic 0). 1 0 Inverter If the input signal is low (or logic 0) then the output signal is high (or logic 1). 0 1 Inverter From the diagrams above, you can work out that there are two input combinations. These can be represented in a table called a truth table. Copy the symbol and table and then complete the table. A 0 1 Symbol for NOT gate Z 1 0 Truth table Switches Switches are the most common types of input device. Most electronic systems use switches. As shown earlier in this area of work, switches are digital devices. Off (Logic 0) On (Logic 1) The switch used in task 6 above is a normally open switch. This means it is normally off, that is at logic 0 state. You have to press the switch to turn it on and its spring will return it to its normal position when the pressure is removed. Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes 5 AND gate logic It can be worked out that there are four input combinations. These can be represented in a truth table. Copy the symbol and table and complete the table. A Z B Symbol for AND gate A 0 0 1 1 B 0 1 0 1 Z 0 0 0 1 Truth table OR gate logic It can be seen that there are four input combinations. These can be represented in a truth table. Copy the symbol and table and complete the table. A Z B Symbol for OR gate A 0 0 1 1 B 0 1 0 1 Z 0 1 1 1 Truth table 6 Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes Pulse Generator +V INC FREQ ACTIVE LOW + POS SIG + S PULSE 0V GEN. - 0V TP + S 0V S 0V - - NEG TP + + + S 0V S 0V S 0V - - - 0v + 0V RANGE +5V DC TO +8V DC + EXT.C 0v PULSE IND E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd The pulse generator is used to give a signal which constantly switches off then on. The speed of this switching is controlled by the potentiometer on the board. The pulse generator is most commonly used with an AND gate as shown below. This means that the bulb here will only flash when the pulse generator is pulsing AND the switch is pressed. Push Switch Pulse Generato r Power Connectio n And Gate Transduce r driver Bulb Unit Latch Unit INPUT IND OUTPUT IND + TP S 0V - + S 0V LATCH A latched system is one that remains on until it is reset. It is often called a memory system as it ‘remembers’ that the switch has been pressed until the reset on the latch is pressed. - TC4011BP 864BHB EXT RST E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd Note: the inverter is needed because the latch unit only works as the voltage signal is dropping – this is called negative-edge triggering. The inverter allows the system to work when the voltage signal is rising, as happens with a normal switch unit. This converts the overall system to positive-edge triggering. In any exam question you will use positive edged triggered latches. YOU DO NOT NEED TO PUT AN INVERTER IN FRONT OF A LATCH IN AN EXAM QUESTION Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes 7 Relay Unit The relay unit is used to switch on a separate circuit, usually one which has a higher voltage. + + S 0V S 0V - The ‘clicking’ sound at the output is caused by the contacts of a switch inside the relay closing. The contacts are moved by the electromagnet energising. - SOFT IRON ARMATURE PIVOT SOFT IRON CORE E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd COIL SPRING TERMINALS CONTACT TERMINALS COIL TERMINALS Delay Unit INC. DELAY + TP SA 0V + S 0V - - DELAY NEC556 0862 B 2 + 0v + E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd This task uses a delay unit. The delay unit reacts to an input signal by waiting a few seconds before it sends out a high (logic 1) signal to the next sub-system. In any exam question you will use positive edged triggered delay units. YOU DO NOT NEED TO PUT AN INVERTER IN FRONT OF A DELAY UNIT IN AN EXAM QUESTION 8 Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes The comparator The comparator board receives an input voltage from a sensor and compares it with another voltage called the reference voltage. If the input voltage is smaller than the reference voltage the comparator gives out a ‘low’ signal (logic 0). If the input voltage is greater than the reference voltage the comparator gives out a ‘high’ signal (logic 1). The comparator may be used as an error detector in closed loop systems, where it compares a feedback voltage to a reference voltage. COMPARATOR REQUIRED TEMP OUTPUT DRIVER OUTPUT TEMP MOTOR TEMP SENSOR VREF INC REF VOLTS + + S 0V S 0V - REF - FEEDBACK LOOP The output signal from a comparator is digital, that is, it is logic 0 or logic 1. The feedback signal that is fed into the comparator is usually analogue. Therefore the comparator can be thought of as an analogue-to-digital converter. TP MAGIC THINGY 0V The potentiometer on the comparator board sets the reference voltage. WITH REF VOLTS E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd VREF +V + POS SIG TP S 0V - 0V NEG INC REF VOLTS +V + + + + + S 0V S 0V S 0V S 0V - - REF - - TP 0V TP + + S 0V S 0V I N 0V TP - - TP + S 0V - 0v 0V RANGE +5V DC TO +8V DC O U T 0v 0v MAGIC THINGY 0V WITH REF VOLTS E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd The temperature sensor sets the input voltage signal (feedback) to the comparator. The comparator takes the analogue signal and gives a digital output. COMPARATOR Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes 9 NAND and NOR gate boards There are two modular logic boards that are very useful in building systems. These are the NAND gate and the NOR gate. + SB 0V - + TP O/P IND SA 0V - Inverter + S 0V - NAND GATE And Gate THIS IS A CHIP BUTTY 0v E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd NAND gate This board is like a combination of AND gate and inverter (NOT gate) boards. This may simplify some problems or give alternative solutions. NOR gate This board is like a combination of OR gate and inverter (NOT gate) boards. Again, this may simplify some problems or give alternative solutions. O/P IND SA 0V - Inverter + SB 0V - + TP + S 0V - NOR GATE Or Gate THIS IS A CHIP BUTTY 0v NOR E & L INSTRUMENTS Ltd 10 Standard Grade Technological Studies: Electronic Systems Revision Notes