Answer Key for activities
advertisement

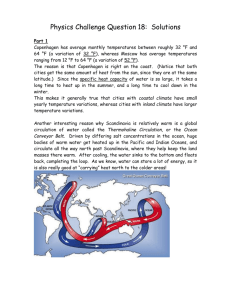
SEA LEVEL: ICE VOLUME CHANGES Answer Key for Exercises 1-3 To the Teacher: Use your discretion to fully and accurately evaluate student work. The answers on this page are meant to provide an outline of concepts that students may include in their responses and are not detailed. Students may have more or less information in their answers, depending on their interaction with the information on the web pages. Exercise 1: 1. What different environmental factors could be causing the melting of the ice in the two tanks? -The room temperature is above 32, so this will cause the solid ice to melt into a liquid (water). -The water around the ice in the tank is warmer than the ice and causing it to melt. -In the tank where the ice is sitting on the slanted platform, gravity could be helping the ice to melt into the water as the room temperature turns the ice into liquid. 2. How has the melting of the ice affected the water level in both tanks? -The melting of ice in the tank where there is no platform has had little effect on the level of the water in the tank. In the tank where the ice is raised on a platform, the water level has visibly risen as the ice has melted into the water. 3. By how many centimeters has the water level in the tanks changed? -There has been no change in the tank where the ice melted in the water. In the tank where the ice has melted from the platform, the level of the water risen by 23 centimeters (assuming that the measuring stuck on the side of the tank is marked off in centimeters). 2-Ice Volume Activity Answer Key Exercise 2: 1. Has the coastline of Antarctica advanced or retreated since the peak of the last ice age? Why? - The coastline of Antarctica has retreated since the peak of the last ice age because as the world has gotten warmer, the ice that forms the coast of Antarctica has melted in to the oceans. 2. How has the shrinking of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet since the last glacial maximum affected sea level (has sea level dropped or risen)? By how much (in meters)? -Sea level has increased. The Earth’s climate has warmed causing the ice sheet to melt. The water that has melted away was deposited in the ocean, causing a rise in sea level of approximately 10 meters. 3-Ice Volume Activity Answer Key Exercise 3: 1. What does breaking of ice shelves mean? -The breaking of the ice shelves means that the climate is warming. As the climate warms, the ice shelves become less stable and break off into the ocean. The breaking of land-based ice will eventually lead to a rise in sea level. The breaking of sea-based ice will have little effect on the sea levels of the Earth, since it is already displacing water by sitting in the sea. 2. Is Antarctica melting? How can we tell? -Yes, Antarctica is melting. We can tell because more of the ice from its ice sheets is in contact with the ocean and is melting. In addition, the land-based ice sheets are melting and the sea level of the oceans is slowly rising. More and more parts of Antarctica’s ice shelves are breaking apart and coming in contact with the sea. 3. What would happen to Washington D.C., Baltimore, Miami and other coastal cities around the world if sea level was to rise 170 feet? -They would be flooded and underwater. This would cause damage to buildings roadways and other human structures. People would be forced to move inland and cities that are 50 miles or more away from the oceans currently, would become coastal cities with the rise in sea levels. 4-Ice Volume Activity Answer Key 4. Can we expect complete melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet in the next 50 years? Why or why not? -Complete melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is unlikely (although students may provide evidence that it can happen, evaluating this response will depend on the discretion of the teacher and the argument presented by the student). Although the climate of Earth seems to be warming, the sheer size of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet will likely prevent it from completely melting away. Large parts of the sheet will likely break off and melt into the sea within in the next 50 years. The ultimate fate of this ice sheet will depend on human endeavors and global warming trends.