Homework for Faults Folds Mtns from Intro Geology

Practice Questions for Faults Folds &Mtns Review
Homework used in Geology 1200
Use these questions to test your knowledge of Folds, Faults and Mountains.
A. Short answer:
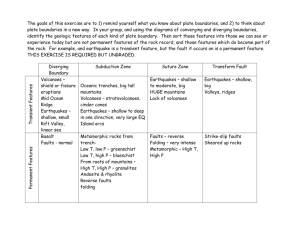
1. Normal faults are commonly found near ____________ plate boundaries
2. A __________ fault is caused by directed compressional stress, and the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
3. Strike-slip faults are caused by _________ stress.
4. Historically, the search for petroleum deposits focused on locating and drilling the crests of __________ structures.
5. Horsts and ________ are most commonly produced by tensional stress.
6. Strike-slip faults are characteristic of ___________ plate boundaries.
7. The Adirondacks of New York are __________ mountains. Such mountains are characterized by uplift with little deformation.
8. Deeply eroded cores of the Earth’s earliest mountains, forming flat interior regions of a continent, are called continental ___________
9. Alaska’s Aleutian islands are an example of ___________ mountains.
10. Fold-and-thrust mountains are most likely to occur in _________ plate collisions.
B. Match the Terms.
1. Appalachians _____ a. shallow reverse fault
2. Alaska’s Aleutian Islands ______ b. at divergent plate boundaries.
3. Eroded anticline ____ c. means mountain building
4. Hanging wall is up ____ d. fault-block mountains
5. Continental shields ____ e. tipped past vertical
6. Overturned rocks _____ f. fold-and-thrust mountains
7. Thrust fault _____ g. in reverse faults
8. Orogenesis ___ h. has oldest rocks in center
9. Basin and Range______ i. volcanic island arc
10. Normal faults _____ j. cores of earliest mountains
C. True or False? Circle the correct answer.
1. The general term for the change in shape of a rock when sufficient stress is applied is strain. True or False?
2. A rock that undergoes sufficient stress to change its original shape has exceeded its elastic limit. True or False?
3. Rocks in which plastic deformation occurs remain in their deformed shape when the stress is released. True or False?
4. Brittle failure is more likely to occur if stress is applied slowly rather than suddenly. True or False?
5. Plastic deformation is likely to occur in rocks under hightemperature and high-pressure conditions. True or False?
6.
The strike and dip of a rock refer to the orientation of a rock unit in relation to the surface of the Earth. True or False?
7. Mapping the strike and dip of rock units reveals the subsurface form of rock structures barely visible at the surface. True or False?
8.
Folds are typically associated with tension at divergent boundaries. True or False?
9.
Anticlines and synclines are caused by directed compressive stress.
True or False?
10.
In eroded anticlines, the oldest rocks are in the center; in eroded synclines, the youngest rocks are in the center. True or False?
11.
In plunging folds, the nose of the fold points in the direction of plunge in an anticline, and opposite the plunge direction in a syncline. True or False?
12.
When bedding planes cross streams, steeply dipping beds have larger V shapes than gently dipping beds. True or False?
D. Multiple choice:
1. A fold in which the axial plane is parallel to the surface of the Earth is a(n):
(a) asymmetrical fold.
(b) overturned fold.
(c) recumbent fold.
(d) plunging fold.
2. A fold in which the axis intersects the Earth’s surface is known as a(n):
(a) asymmetrical fold.
(b) overturned fold.
(c) recumbent fold.
(d) plunging fold.
3. Vertical displacement occurs in all of the following EXCEPT:
(a) strike-slip faults.
(b) thrust faults.
(c) normal faults.
(d) reverse faults.
4. Normal faults are commonly found near:
(a) transform plate boundaries.
(b) divergent plate boundaries.
(c) subducting plate boundaries.
(d) continental collision plate boundaries.
5. A thrust fault is the result of:
(a) tensional stress, and the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall.
(b) tensional stress, and the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
(c) compressional stress, and the hanging wall moves down relative to the footwall.
(d) compressional stress, and the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
6. The correct fault type/plate boundary association(s) is/are:
(a) normal faults—divergent plate boundaries
(b) reverse and thrust faults— convergent plate boundaries
(c) strike-slip faults—transform plate boundaries.
(d) all of the above
7. Historically, the search for petroleum deposits focused on locating and drilling:
(a) the crests of anticlinal structures.
(b) the flanks of anticlinal structures.
(c) the crests of synclinal structures.
(d) the flanks of synclinal structures.
8. Fold-and-thrust mountains are most likely to occur:
(a) at subducting plate boundaries.
(b) in continental plate collisions.
(c) in the interiors of tectonic plates.
(d) in volcanic regions.
9. The Appalachians represent which mountain type?
(a) Volcanic mountains.
(b) Fold-and-thrust mountains.
(c) Fault-block mountains.
(d) Upwarped mountains.
10. Fault-block mountains such as the mid-ocean ridges are characterized by:
(a) vast upwarped regions.
(b) distinctive reverse or thrust faults.
(c) high-angle normal faults.
(d) thrust-faulted and folded marine sediments.
11. Upwarped mountains are characterized by:
(a) intense folding and faulting.
(b) rugged and extremely high mountain peaks.
(c) numerous series of synclines and anticlines.
(d) almost no rock deformation.
Short Answer (Answer All)
1. What is the difference between a strike-slip fault and a dip-slip fault?
Use a simple diagram showing each.
2.
Explain the miner's method of naming faults. Use a simple diagram showing the shaft, fault line, hanging wall, and footwall for normal and reverse faults. How did the walls get their names?
3. What is the difference between symmetrical, asymmetrical, overturned, and recumbent folds? Use simple diagrams showing each, indicating the axial plane.