Word Document
advertisement

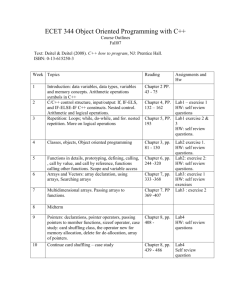
Doğuş University Department of Computer Engineering COME 102 – Summer 2002 COMPUTER APPLICATIONS AND PROGRAMMING Instructor Classroom Class time Office Office Hours E-mail : Assoc. Prof. Dr. Selim Akyokus : : : G-402 : : sakyokus@dogus.edu.tr Course Objectives: The objective of this course is to introduce students to the fundamentals of computer programming and problem solving. The emphasis is on the fundamentals of structured programming, syntax, semantics, testing/debugging, implementation, documentation, and an introduction to objects and classes. The emphasis is on procedural programming languages, and the language that we will focus on is C++. Students will be exposed to development on Microsoft Visual Studio platforms. Required Textbooks: Deitel&Deitel, C++ How To Program 3/e, Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-089571-7; 2001. Additional Textbooks and References: Doğuş University Learning Package (prepared by:Mithat Konar) Web resources given in class Tentative Course Outline: Week 1 Introduction to Computers and C++ Programming (Ch1) Introduction, Computer Organization, Machine Languages, Assembly Languages, and High-level Languages, History of C and C++ , Basics of a Typical C++ Environment, Introduction to C++ Programming, Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators, Thinking About Objects. Week 2 Control Structures I (Ch2) Introduction, Algorithms, Pseudocode, Control Structures, The if Selection Structure, The if/else Selection Structure, The while Repetition Structure, Formulating Algorithms, Assignment Operators, Increment and Decrement Operators, Essentials of Counter-Controlled Repetition, The for Repetition Structure, Examples Using the for Structure Week 3 Control Structures II (Ch2) The switch Multiple-Selection Structure, The do/while Repetition Structure, The break and continue Statements, Logical Operators, Structured-Programming Summary, Thinking About Objects: Identifying the Classes in a Problem Week 4 Functions I (Ch3) Introduction, Program Components in C++, Math Library Functions, Functions, Function Definitions, Function Prototypes, Header Files, Random Number Generation, Example: A Game of Chance and Introducing enum, Storage Classes, Scope Rules Week 5 Functions II (Ch3) Recursion, Example Using Recursion: The Fibonacci Series, Recursion vs. Iteration, Functions with Empty Parameter Lists, Inline Functions, References and Reference Parameters, Default Arguments, Unary Scope Resolution Operator, Function Overloading, Function Templates, Thinking About Objects: Identifying a Class's Attributes Week 6 Arrays I (Ch4) Introduction, Declaring Arrays, Examples Using Arrays, Passing Arrays to Functions, Sorting Arrays, Case Study: Computing Mean, Median and Mode Using Arrays, Week 7 Arrays II (Ch4) Searching Arrays: Linear Search and Binary Search, MultipleSubscripted Arrays, Thinking About Objects: Identifying the Operations of a Class - Midterm Pointers and Strings (Ch5) Introduction, Pointer Variable Declarations and Initialisation, Pointer Operators, Calling Functions by Reference, Using the const Qualifier with Pointers, Bubble Sort Using Call-by-reference, Week 8 Week 9 Pointers and Strings II (Ch5) Pointer Expressions and Pointer Arithmetic, The Relationship Between Pointers and Arrays, Arrays of Pointers, Function Pointers, Introduction to Character and String Processing, Fundamentals of Characters and Strings, String Manipulation Functions of the Stringhandling Library, Thinking About Objects: Collaborations Among Objects Week 10 Classes and Data Abstraction : Part I (Ch6) Introduction, Structure Definitions, Accessing Members of Structures, Implementing a User-Defined Type Time with a struct, Implementing a Time Abstract Data Type with a class, Class Scope and Accessing Class Members, Separating Interface from Implementation, Controlling Access to Members, Access Functions and Utility Functions, Initializing Class Objects: Constructors, Using Default Arguments with Constructors, Using Destructors, When Constructors and Destructors Are Called, Using Data Members and Member Functions, A Subtle Trap: Returning a Reference to a Private Data Member, Assignment by Default Memberwise Copy, Software Reusability, Thinking About Objects: Starting to Program the Classes for the Elevator Simulator Week 11 Classes: Part II (Ch7) Introduction, const (Constant) Objects and const Member Functions, Composition: Objects as Members of Classes, friend Functions and friend Classes, Using the this Pointer, Dynamic Memory Allocation with Operators new and delete, static Class Members, Data Abstraction and Information Hiding, Example: Array Abstract Data Type, Example: String Abstract Data Type, Example: Queue Abstract Data Type, Container Classes and Iterators Proxy Classes, Thinking About Objects: Programming the Classes for the Elevator Simulator C++ Stream Input/Output (Ch 11) Stream Output, Stream Input, Unformatted I/O with read, gcount and Week 12 write, Stream Manipulators, Stream Format States Week 13 File Processing (Ch14) Introduction, The Data Hierarchy, Files and Streams, Creating a Sequential Access File, Reading Data from a Sequential Access File, Updating Sequential Access Files, Random-Access Files, Creating a Random-Access File, Writing Data Randomly to a Random-Access File, Reading Data Sequentially from a Random-Access File, Example: A Transaction Processing Program, Input/Output of Objects Week 14 Revision and review - Final Homeworks and Projects: Students will be assigned to carry out several projects and homeworks during the course. Grading: Midterm Exam Quizes Final Exam Homeworks 20 20 40 20