EO224
advertisement

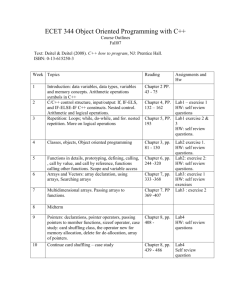
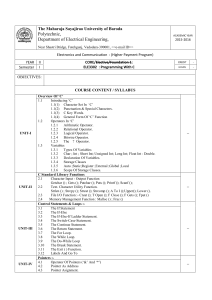
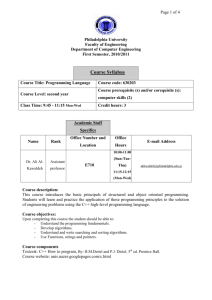
Title Code Level Credit rating Pre-requisites Type of module Aims Learning outcomes/objectives Content Teaching and learning strategies Learning support Allocation of study hours to activities Computer Programming EO224 5 20 EO128 or equivalent Double module, delivered over two semesters To provide the skills and knowledge necessary to develop reliable computer programs using the 'C' high-level language. On successful completion of the module, students will be able to: 1. Demonstrate an understanding of the detailed syntax of the 'C' programming language. 2. Design, write and test reliable and properly-structured 'C' programs for applications in electronic engineering. 3. Recognise the importance of structured-programming techniques in software developmnt. The notion of an algorithm, types of computer language, compilers, syntax errors Integrated Development Environments for editing, compiling, de-bugging and running 'C' programs Data representation, data-types, variables and constants, precision and range of floating-point quantities, casts, the size of operator Expressions, statements, compound statements and assignments Operators: arithmetic, assignment, logical, relational, bit-wise and shift Operator precedence and associativity Input and output functions, such as printf, scanf, getchar, putchar The ‘C’ pre-processor: libraries and constants Control constructs in general: sequence, selection and iteration The control constructs of 'C': if ... else, switch, for, while and do ... while Arrays: declaration, initialisation and multi-dimensional arrays Pointers: data values versus address values, declaration, the indirection operator, incrementing and decrementing pointers, the relationship between arrays and pointers Functions: concept and purpose, prototypes, parameters, local versus global variables, call-by-value, call-by-reference, return statements, passing arrays and strings, recursion, command-line parameters File access: opening files, modes, reading/writing data, fscanf and fprintf, closing files Structures: concept and purpose, declaration, accessing members, manipulation, nesting structures, using pointers with structures, the structure pointer operator, arrays of structures The concept of structured programming, the Unified Modelling Language (U.M.L.) as a design tool for software development, documentation of software, testing A combination of lectures and supervised laboratory sessions McGrath, M., (2009), C Programming in Easy Steps, third edition (Southam, Warwickshire, U.K.: In Easy Steps), ISBN: 978-1-84078-363-6. Kernighan, B.W. and Ritchie, D.M., (1988) The C Programming Language, second edition (Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall), ISBN: 0-13-110362-8. ANSI-compliant C compiler such as Dev-C++ Compiler available from http://www.bloodshed.net/dev/devcpp.html KIS CATEGORY/Activity type Study hours % CATEGORY: SCHEDULED Lecture - 52hr, Lecture - 26%, Type: Lectures, seminars, tutorials, project Practical classes & Practical classes & supervision, demonstrations, practical workshops workshops - 52%. classes and workshops, supervised time in 104hr. workshop/ studio, fieldwork, external visits, work-based learning CATEGORY: GUIDED INDEPENDENT Guided 22% STUDY independent study Type: Independent study including wider reading/ - 44 hr practice, follow-up work, completion of assessment tasks, revision etc.. CATEGORY: PLACEMENT* Type: Learning away from the University that is not a year abroad or work-based learning Assessment tasks KIS CATEGORY/Activity type Type of assessment tasks Summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression (expressed as a %) CATEGORY: WRITTEN Type: Written exam/ test (inc. in-class test) CATEGORY: COURSEWORK Type: Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output Further details Project output (not dissertation) % 100 CATEGORY: PRACTICAL Type: Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment CATEGORY: VARIES Type: Set exercises assessing application of knowledge, analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills Assessment tasks 100% coursework (40% Assignment LOs1-3, 60% Test LOs 1-3) Brief description of module content and/or aims (maximum 80 words) This module reviews the basics of the C language and introduces the student to more advanced features of the language. Area examination board to which module relates Division of Engineering and Product Design Examination Board Module team/authors/coordi nator Semester offered, where appropriate Site where delivered Date of first approval Date of last revision Date of approval of this version Version number Replacement for previous module Dr. D.H. Lawrence (module leader) Field for which module is acceptable and status in that field Course(s) for which module is acceptable and status in that course School home External examiner 1 7/1/2008 7/1/2008 7/1/2012 2 EO112 and EO216 M.Eng./BEng (Hons) Digital Electronics, Computing and Communications – compulsory MEng/BEng (Hons) Electrical and Electronic Engineering – compulsory Foundation Degree Electrical and Electronic Engineering – compulsory Computing, Engineering and Mathematics Dr Khaled Hayatleh (October 2011)