Care of the Patient Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems
advertisement

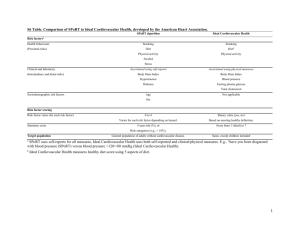
RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems 1. 2. 3. Behavioral Objectives Apply the terms listed in the content column appropriate to the client situations. Compare and contrast the normal anatomy and physiology to the pathophysiology of disease processes in the cardiovascular system across the lifespan. Analyze factors included in the assessment of the client experiencing complex problems of the cardiovascular system, including the developmental and cultural considerations. Clinical Objectives Take a client history using structured and unstructured data collection tools to obtain physical, psychosocial, spiritual, cultural, familial, occupational, environmental information, risk factors, and client resources. Learning Opportunities READ: Lewis (2011) Perform assessment to identify health status and monitor for change in health status. VIDEOS: #0144-12 Lead EKG II. Anatomy & Physiology of the Cardiovascular System. A. Developmental considerations 1. Infant 2. Child 3. Adolescent 4. Adult 5. Older adult B. Pathophysiology of cardiovascular system 1. Alteration in perfusion Validate and report assessment data using assessment tools. #M018-Physical AssessmentThe Heart Identify complex multi-system health care problems of clients. COMPUTER SIMULATIONS: III. Cardiovascular assessment A. Interview 1. Chief complaint 2. History of present illness. 3. Prior medical history 4. Medication history (prescription/nonprescription) 5. Family/social/occupational history 6. Knowledge of health maintenance 7. Identify risk factors for cardiovascular disease. B. Physical exam 1. Level of consciousness 2. Heart sounds (S1, S2, S3, S4, murmurs) 3. Telemetry, heart rate & rhythm Incorporate multiple determinants of health in clinical care when providing care for individuals and families. I. Content Outline Application of terms A. Afterload B. Bruit C. Cardiac output D. Cardiac tamponade E. Gallop rhythm F. Preload G. Stroke volume H. Thalassemia 11 Analyze and interpret health data of clients. Formulate nursing diagnoses based upon analysis of health data. Implement nursing care to promote health and manage acute and chronic health problems and disabilities. Perform therapeutic and preventive nursing measures and administer treatments and medications as authorized by law and determined by the BNE. Identify short and long-term goals/outcomes, select interventions, and establish priorities for care in collaboration with the client. Lehne (2010) McKinney (2009) #5028-Physical Examination of the Cardiovascular System (Laser) #5043-Critical Care NursingCritical Thinking: Cardiovascular Care Review Level II Cardiovascular Medications MEDCOM ONLINE FILMS VIDM109-T Basic Cardiac Monitoring: Understanding Fundamentals VIDM259-T Cardiac Auscultation: the Process of Basic Cardiac Auscultation RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Peripheral pulses/point of maximal impulse (PMI) 5. Color (central & peripheral) 6. Neurovascular assessment of affected extremities a. Pain b. Pallor c. Pulses d. Paresthesia e. Paralysis f. Piokiothermia (coldness) g. Capillary refill 7. Vital signs a. B/P lying, sitting, standing b. HR, Rhythm 8. Activity level 9. Chest pain 10. Peripheral/sacral edema 11. Jugular vein distention 12. Intake/output/daily weights C. Diagnostic tests 1. Laboratory studies a. Cardiac enzymes b. Lipid profile c. Drug levels d. Electrolytes e. Coagulation studies (1) Prothrombin (PT) (2) International normalized ratio (INR) (3) Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) g. Hemoglobin electrophoresis 2. Radiology/Imaging a. Cardiac catheterization b. Nuclear cardiology c. Angiograph 4. 12 Clinical Objectives Serve as model & resource for health education & information. Select and carry out safe and appropriate activities to assist client to meet basic physiologic needs, including: circulation, nutrition, oxygenation, activity, elimination, comfort, rest and sleep. Act as a role model in maintaining client confidentiality. Assume accountability when using independent clinical judgment and established protocols. Evaluate, document, and report responses to medications, treatments, and procedures and communicate the same to other health care professionals clearly and accurately. Apply change strategies to achieve stated outcomes. Use evaluation tools to measure processes and outcomes. Use critical thinking as a basis for decision making in nursing practice. Participate in the evaluation of care administered by the interdisciplinary health care team. Use organizational & management skills when utilizing resources to meet goals/outcomes, & enhance quality of Learning Opportunities VID78584-T Heart Medications: Anatomy Review and Angina VID78587-T Heart Medications: Antiarrhythmic Agents, Part I VID78588-T Heart Medications: Antiarrhythmic Agents, Part II VID78585-T Heart Medications: Blood Pressure Medications and Anticoagulants VID78586-T Heart Medications: Heart Failure Medications and Cholesterol Lowering Agents RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Other a. Electrocardiogram (1) Continuous monitoring; telemetry (2) 12 Lead EKG (3) Holter monitoring b. Echocardiogram c. Stress test d. Electrophysiology studies (EPS) D. Cultural influences 1. Hereditary/genetic influences 2. Environmental 3. Health beliefs/practices E. Developmental 1. Age specific assessment data a. Heart sounds b. Vital signs c. Breathing patterns d. Fluid/electrolytes e. Nutritional 2. Behavioral/emotional response to health care providers 3. 4. Differentiate between the etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations of selected complex cardiovascular problems and associated technology. IV. Complex Cardiovascular Problems A. Angina/myocardial infarction B. Valvular disorders 1. Stenosis 2. Insufficiency 3. Mitral valve prolapse C. Aortic aneurysm D. Peripheral vascular disorder 1. Arterial 2. Venous 13 Clinical Objectives nursing care and level of client satisfaction. Consult with, utilize and make referrals to community agencies and health care resources to provide continuity of care. Advocate on behalf of the client with other members of the interdisciplinary health care team. Learning Opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems Behavioral Objectives 5. Discuss analysis, planning, implementation and evaluation for the nursing management of clients with complex cardiovascular problems. Content Outline E. Dysrhythmia 1. Minor a. Bradycardia b. Tachycardia c. Premature ventricular contractions d. Atrial fibrillation e. Supraventricular tachycardia 2. Major a. Ventricular tachycardia b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Asystole d. Complete heart block F. Hemodynamic monitoring 1. Arterial lines 2. Central venous pressure 3. Pulmonary artery pressure monitoring 4. Intraortic balloon pump a. Venous stasis ulcer b. Venous insufficiency G. Sickle cell disease H. Anemias 1. Iron Deficiency 2. Vitamin B-12 (pernicious) 3. Aplastic 4. Folic Acid deficiency V. Selected nursing diagnoses/nursing implementation/evaluation. A. Alteration in tissue perfusion 1. Independent interventions a. Neurovascular assessment b. Position client c. Maintain body temperature d. Promote factors that improve blood flow e. Exercise 14 Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems Behavioral Objectives Content Outline f. Prevent trauma g. Nutritional support h. Maintain fluid balance 2. Collaborative interventions a. Administer medications and monitor for desired effects/adverse effects/side effects (1) Anticoagulants (2) Antiplatelet aggregator (3) Antidysrthymics (4) Antianginal (5) Antihypertensives b. Oxygen support c. Surgical modalities (1) Abdominal aortic aneurysm repair (2) Femoral-popliteal by-pass (3) Ligation/vein stripping (4) Lumbar sympathectomy (5) Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PCTA) (6) Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) d. Cardioversion e. Defibrillation 3. Recognition of complications a. Thrombus/embolus b. Surgical complications c. Amputation 4. The client will have improved tissue perfusion as evidenced by: a. neurovascular status WNL b. increased activity tolerance c. decreased pain 15 Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems Behavioral Objectives Content Outline B. Pain 1. Independent interventions a. Assess the pain (1) Believe the client (2) Age specific scale (3) Location, type, precipitating factors alleviating factors b. Rule out complications (1) What is the worse thing this pain could be and rule it out? (2) Is the pain expected/unexpected? (3) List specific assessment data to rule out complications c. Take an action (1) Notify the doctor if a complication (2) Administer appropriate medications (see collaborative) d. Independent nursing interventions (1) Imagery (2) Distraction (3) Environment (4) Therapeutic communication (5) Position client e. Safety f. Evaluation 2. Collaborative interventions a. Administer medications and monitor for desired effects/adverse effects/side effects (1) Narcotics (2) Nitrates (3) Thrombolytics (4) Nonopioids (5) NSAIDS 16 Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems Behavioral Objectives Content Outline (6) Around the clock (ATC) analgesics b. Oxygen support c. Respiratory therapy 3. Recognition of complication a. Unrelieved pain 4. The client will state (indicate) that the pain has decreased. C. Altered health maintenance: Knowledge deficit 1. Client teaching a. Assess readiness to learn, ability, knowledge b. Avoid aggravating factors c. Promotion of alleviating factors d. Reportable signs/symptoms e. Medication teaching f. Rest/activity g. Risk factors h. Life style modifications i. Nutrition (1) Low fat (2) Low cholesterol (3) Low salt j. Maintenance of fluid balance k. Health promotion activities l. Genetic counseling 2. Community Resources a. American Heart Association b. Mended Heart Association c. Cardiac rehabilitation d. National Association for Sickle Cell Disease 3. The client will have improved health maintenance as evidenced by: a. Identifying aggravating and alleviating factors. 17 Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities RNSG 2535 – Integrated Client Care Management Unit II - Care of the Client Experiencing Cardiovascular Problems Behavioral Objectives Content Outline Identifying reportable signs and symptoms c. Describing the purpose, correct administration and side effects of prescribed medications. d. Identify risk factors. e. Modification of life style f. No post op complications g. Utilizing community resources. D. Ineffective Individual coping: Anxiety, fear, powerlessness, dependence. See Unit III-Care of the Client Experiencing Respiratory Problems) E. Altered family processes 1. Identify causative and contributing factors a. Family, significant others 2. Provide ongoing information 3. Assist family with appraisal of situation 4. Initiate health teaching and referrals a. Spousal support Groups b. Grief Support Groups c. Parent support groups 5. The family will have improved family processes as evidenced by: a. Participating in planning/care of client b. Verbalizing feelings to nurse and each other c. Verbalizing feelings of grief d. Maintaining functional family unit. e. Facilitating client from sick role to well. Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities b. N:Soph\Fall\RNSG 2535\Unit II Cardiovascular Revised 05/10 18