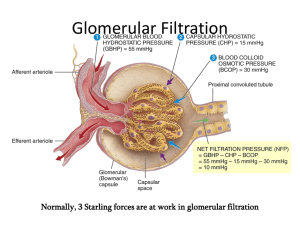
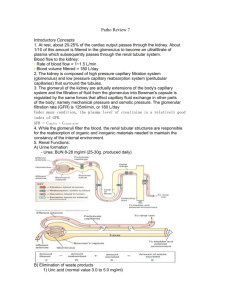
1) Which of the following organs is not a part of the urinary system
advertisement

Exercise, Urinary-Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-base Balance-1 1) Which of the following organs is not a part of the urinary system? A. kidney B ureter C. vagina D. urethra E. bladder 2) Which of the following organs is involved in filtering blood and reabsorbing nutrients from the filtrate? A. kidney B ureter C. vagina D. urethra E. bladder 3) Which of the following hormones is not produced by the kidneys? A. Aldosterone B Renin C. Erythropoietin D. calcitrol 4) The kidneys can not detoxify drugs. A. The above statement is true. B. The above statement is false 5) Which of the following is not excreted primarily by the kidneys? A. carbon dioxide B. urea C. creatinine D. uric acid 6) Nitrogenous waste products are ____. A. safe to human body B. normally accumulated in the blood without generating any adverse effects C. toxic and need to be excreted 7) The functional units of the kidneys are ___. A. nephrons B proximal tubules C. distal tubules 8) A nephron contains all of the following except ____. A. glomerulus B proximal tubule C. distal tubule D. collecting ducts D. loop of Henle E. loop of Henle E. collecting duct 9) Which of the following is the correct route of blood flow in the kidneys? A. renal artery … afferent arteriole glomerulus efferent arteriole peritubular capillary … renal vein B. renal artery … efferent arteriole glomerulus afferent arteriole peritubular capillary … renal vein C. renal artery … glomerulus afferent arteriole efferent arteriole peritubular capillary … renal vein D. renal artery … afferent arteriole peritubular capillary glomerulus efferent arteriole … renal vein 10) At which part of renal blood vessel system does filtration occur? A. renal artery B afferent arterioles C. efferent arterioles D. glomeruli E. peritubular capillaries 11) An increased glomerular blood pressure will cause ___. A. an increase in glomerular filtration rate B. a decrease in glomerular filtration rate C. no change in glomerular filtration rate 12) Glomerular filtration rate refers to _____. A. the blood flow into the two kidneys per minute B. the amount of filtrate formed per minute by the two kidneys combined C. the amount of filtrate formed per minute by a single kidney 13) Glomerular filtration rate ____. A. varies a lot from time to time B. is relatively stable 14) Renal autoregulation aims to ____. A. stabilize glomerular filtration rate B. control reabsorption of filtrate by proximal tubules C. control reabsorption of filtrate by distal tubules D. control reabsorption of filtrate by collecting ducts 15) To which of the following blood components are glomerular filtration membranes least permeable? 1 Exercise, Urinary-Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-base Balance-1 A. urea B uric acid C. electrolytes D. glucose E. proteins 16) The juxtaglomerular apparatus is involved directly in ____. A. maintaining a stable glomerular filtration rate B. maintaining a stable reabsorption of glucose C. maintaining a stable secretion of K+ D. maintaining a stable secretion of H+ 17) The juxtaglomerular apparatus is composed of all of the following except ___. A loop of Henle. B juxtaglomerular cells C macula densa. D. mesangial cell 18) The macula densa is able to detect the salinity of the tubular fluid in ____. A. proximal tubule B the distal tubule C. the collecting duct D. the loop of Henle 19) The juxtaglomerular cells are special ____. A. smooth muscle cells B epithelial cells 20) Renin is secreted by ____. A. macula densa B juxtaglomerular cells C. endothelial cells C. mesangial cellS 21) What percent of nutrients in the filtrate is normally reabsorbed by the entire tubular system? A. 50% B 65% C. 70% D. 80% E. 99% 22) What percent of nutrients in the filtrate is normally reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubules? A. 50% B65% C. 75% D. 85% E 99%. 23) Nutrients in the filtrate is reabsorbed by the proximal convoluted tubules through ____. A. transcellular route only B paracellular route only C. both of the above D. neither of the above 24) Solvent drag, one of the mechanisms for reabsorption, is driven by ___. A. colloid osmotic pressure gradient between tubular fluid and the blood in the peritubular capillaries B. hydrostatic pressure gradient between tubular fluid and the blood in the peritubular capillaries 25) Sodium pumps (Na+-K+ ATPase) are located in _____. A. apical membranes of the proximal convoluted tubular cells B. basolateral membranes of the proximal convoluted tubular cells 26) Sodium pumps (Na+-K+ ATPase) actively transport Na+ from ____. A. intracellular space to extracellular space B. extracellular space to intracellular space 27) Sodium pumps (Na+-K+ ATPase) contribute directly or indirectly to the reabsorption of ____. A. sodium B glucose C. amino acid D. all of the above 28) Electrostatic attraction is a mechanism primarily for the reabsorption of _____ in proximal convoluted tubules. A. glucose. B. the negative ions such as chloride C. amino acids D. proteins 29) The amount of nutrients that the renal tubule can reabsorb is _____. A. unlimited B. limited 30) A. C. D. The unique property of the thick ascending limb of nephron loop (loop of Henle) is that ____. it reabsorbs two thirds of the filtrate B. it is the target of aldosterone and ANF it helps establish a high extracellular osmotic concentration in renal medulla it concentrates urine by reabsorbing water 31) The unique property of the distal convoluted tubule is that ____. 2 Exercise, Urinary-Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-base Balance-1 A. it reabsorbs two thirds of the filtrate B. it is the target of aldosterone and ANF C. it helps establish a high extracellular osmotic concentration in renal medulla D. it concentrates urine by reabsorbing water 32) Aldosterone has the effect of ____ A. increasing reabsorption of sodium only B. increasing secretion of potassium only C. both of the above D. neither of the above 33) A. C. D. The unique property of the collecting duct is that ____. it reabsorbs two thirds of the filtrate B. it is the target of aldosterone and ANF it helps establish a high extracellular osmotic concentration in medulla it concentrates urine by reabsorbing water 34) The collecting duct is ____. A. always permeable to water B. permeable to water depending on ADH C. impermeable to water in the presence of ADH D. very permeable to NaCl 35) A. B. C. D. Reabsorption of water in collecting duct is driven by ____. a high osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid in the medulla a high hydrostatic pressure of extracellular fluid in the medulla a high osmotic pressure of tubular fluid in the collecting duct a low osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid in the medulla 36) ADH ____. A. enhances water reabsorption B. decreases water reabsorption 37) Urine normally contains no ___. A. urea B. sodium C. proteins D. creatinine 38) Diabetes mellitus can be caused by ____. A. deficiency of insulin only B. deficiency of insulin receptors only C. either deficiency of insulin or insulin receptors D. none of the above 39) Patients of diabetes mellitus excrete abnormally high volume of urine because ____. A. the glomerular filtration rate is higher than normal B. the presence of glucose in tubular fluid increases the osmotic pressure of the tubular fluid and hinders the reabsorption of water C. insufficient amount of ADH is present D. water permeability of the collecting duct is increased 40) Patients of diabetes insipidus excrete abnormally high volume of urine because ____. A. the glomerular filtration rate is higher than normal B. the presence of glucose in tubular fluid increases the osmotic pressure of the tubular fluid and hinders the reabsorption of water C. insufficient amount of ADH is present D. water permeability of the collecting duct is increased 41) Some of diuretics increase urine volume by ____. A. decreasing glomerular filtration B. inhibiting sodium reabsorption C. decreasing osmotic pressure of tubular fluid 42) Voiding urine is voluntarily controlled in adults by neurons in _____. A. spinal cord B. medulla oblongata C. pons D. midbrain E. cerebrum 43) Which of the muscles is under voluntary control in adults? A. internal urethral sphincter B. external urethral sphincter C. both of the above D. neither of the above 3 Exercise, Urinary-Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-base Balance-1 44) Which of the following is the most abundant component of human body in terms of weight? A. protein B. lipid C. carbohydrate D. water E. electrolytes 45) Which of the following compartments contains more water? A. intracellular fluid B. tissue fluid C. blood 46) A. B. C. Water movement between tissue fluid and intracellular fluid is determined mainly by ____. osmotic pressure contributed by electrolytes in tissue fluid and intracellular fluid hydrostatic pressure of tissue fluid and intracellular fluid osmotic pressure contributed by proteins in tissue fluid and intracellular fluid 47) Water movement between the blood and tissue fluid is affected by ____. A. capillary blood pressure B. plasma colloid osmotic pressure C interstitium hydrostatic pressure D. interstitium colloid osmotic pressure E all of the above 48) Which of the following routes of water output is under physiological control? A. urine B. feces C. breath D. cutaneous evaporation E. sweat 49) Under which of the following conditions is ADH secretion increased? A. an increase in blood volume B. a decrease in blood volume C. a decrease in blood osmolarity 50) Which of the following ions is primarily located in intracellular fluid? A. K+ B. Na+ C. Ca++ D. Cl51) Which of the following ions is needed for the synthesis of ATP? A. K+ B. Na+ C. Ca++ D. ClE. Phosphate 52) Which of the following ions is the most important contributor to resting membrane potential? A. K+ B. Na+ C. Ca++ D. ClE. Phosphate 53) Which of the following ions is a blood clotting factor? A. K+ B. Na+ C. Ca++ D. Cl- E. Phosphate 54) Calcium is involved in ____. A. initiating muscle contraction B. signal transduction as a second messenger C. initiating the release of neurotransmitters D. all of the above activities 55) Parathyroid hormone (PTH) ____. A. increases blood calcium concentration B. decreases blood calcium concentration C. increases blood phosphate concentration D. decreases blood potassium concentration 56) The primary effect of calcitonin is to ____. A. Cause redistribution of calcium from bones to the blood B. cause redistribution of calcium from the blood to bones C. enhance intestinal absorption of calcium from food 57) The primary effect of calcitrol is to _____. A. cause redistribution of calcium from bones to the blood B. cause redistribution of calcium from the blood to bones C. enhance intestinal absorption of calcium from food 58) Which of the following hormones regulates blood phosphate? A. insulin B. aldosterone C. parathyroid hormone D. ADH 59) The major buffer systems in human body include all of the following except ____. A. bicarbonate buffer B. phosphate buffer C. protein buffer D. Tris buffer 60) Which of the following organs are not directly involved in acid base balance? 4 Exercise, Urinary-Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-base Balance-1 A. kidney B. liver C. lungs 61) Which of the following organs can correct acidosis by directly excreting H+ out of the body? A. kidney B. liver C. lungs 62) A low blood pH of 7.2 caused by an elevated production of organic acids in diabetes is considered as ____. A. respiratory acidosis B. respiratory alkalosis C. metabolic acidosis D. metabolic alkalosis KEY 1C 2A 3A 4B 5A 6C 7A 8E 9A 10D 11A 12B 13B 14A 15E 16A 17A 18B 19A 20B 21E 22B 23C 24A 25B 26A 27D 28B 29B 30C 31B 32C 33D 34B 35A 36A 37C 38C 39B 40C 41B 42C 43B 44D 45A 46A 47E 48A 49B 50A 51E 52A 54D 55A 56B 57C 58C 59D 60B 61A 62C 53C 5