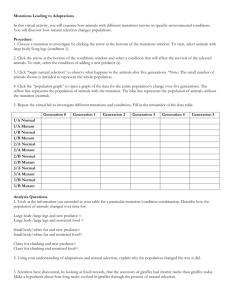
Flow chart for fruit fly genetics exercise
advertisement

Fruit fly genetics simulation: An assignment worth 50 points plus an extra credit 5pts. ------------SEE FLOW CHART HANDOUT TO HELP YOU WITH THIS. 1. Go to http://biologylab.awlonline.com 2. Click on “Fly lab” 3. Log in using username "lima101" (ending in one zero one) and the password "hypothesis2" 4. Select fruit fly mutant types and, by experimental matings, determine the nature of each mutation. Here are the five possible types of mutations: - dominant and not sex linked - recessive and not sex linked - dominant and sex linked - recessive and sex linked - lethal when homozygous Number your paper 1-10. After each number put the name of a mutation and what type that mutation is from the above 5 possible types. You will, thus, select 10 fruit fly mutations. Then show the appropriate genetic notation and final punnett square from your experimental matings that fully demonstrate why the mutation is what you say it is. Clearly indicate the phenotype of flies represented by each box of your punnett square. Only use X and Y chromosomes in your genetic notation and punnett squares if you are trying to show that the mutation is sex linked. Otherwise ignore sex and don’t use X and Y chromosomes. 2.5 points for each correct answer. 2.5 additional points for the correct genetic notation and punnett squares supporting your correct answer. A bonus of five points will be awarded if you can completely correctly identify one each of all of the above five types of mutations. Do not use the mutations White Eyes or Dumpy Wings because there were done for you in class today. If F1 are 1/2 mutant & 1/2 normal with no sex bias, then homozygous lethal mutant is possible To verify this cross two mutants. Mutant X Mutant If offspring are 2/3 mutant and 1/3 normal with no sex bias then mutant is homozygous lethal If F1 are 1/2 normal females and 1/2 mutant males then mutant is sex linked and recessive Start Here Normal male X Mutant female If F1 offspring are all normal with no sex bias, then mutant may be recessive. To verify this cross two F1. F1 normal X F1 normal If F2 are 3/4 normal & 1/4 mutant with no sex bias, then mutant is recessive and not sex linked If F1 are all mutant, then mutant may be dominant. To verify, cross two F1. F1 mutant X F1 mutant If F2 are 3/4 mutant and 1/4 normal with no sex bias, then mutant is dominant and not sex linked. If F2 are 3/4 mutant, including both males and females, and 1/4 normal males with no normal females then mutant is sex linked and dominant.