Review Book Topic 4: Genetics - wfs
advertisement

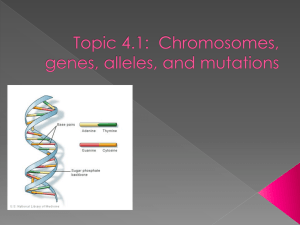
Topic 4.1 Review Book Chromosomes, Genes, Alleles, and Mutations Name ___________________ Review Book Topic 4: Genetics 4.1 Chromosomes, genes, alleles, and mutations Key facts 1. Eukaryotic chromosomes are made of DNA and proteins. 2. Prokaryotic chromosomes only include DNA. 3. A gene is a section of DNA that controls a specific characteristic in an organism. 4. An allele is a specific form of a gene, differing from other alleles by one or more base differences in the DNA sequence. 5. Different alleles for the same gene all occupy the same locus on a chromosome. 6. Genome refers to the whole or complete genetic information of an organism. 7. When genes change in an organism, a mutation is said to have occurred. 8. A mutation involves a base change in a gene, sequence of DNA. 9. Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation in which one base in a gene is replaced by another. 10. An example of a disease caused by a base substitution mutation in humans is sickle cell anemia. 11. Natural selection has maintained the sickle cell allele because when it occurs singly, it results in malaria immunity. It is only when the sickle cell allele occurs with another that the actual disease of sickle cell anemia occurs. Further notes Complete the following. 1. What is the difference between a gene and an allele? 2. Draw and label a chromosome. Annotate by labeling the centromere and indicating a locus. 3. What is the composition of a eukaryotic chromosome? 4. What are the two major parts of a eukaryotic chromosome called after the S phase of the cell cycle? 5. What is the total genetic composition of an organism called? 6. How is the disease known as sickle cell anemia thought to have originated? 7. Why would the allele which is the cause of sickle cell anemia still exist today after thousands of years when it may produce a potentially fatal disease?