File
advertisement

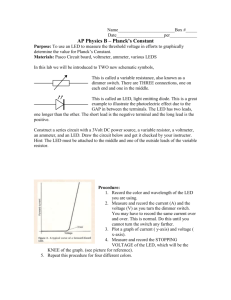
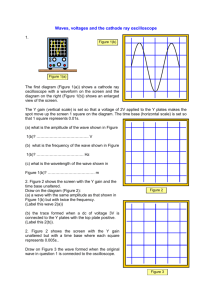
Block: ______________ Date: ___________________Name:______________________________ Introduction to Technology Basic Electricity Alternating Current Waveforms Alternating Current electricity (AC) consists of constantly changing values of voltage and current that follow a wave pattern. The wave can be displayed and measured using an oscilloscope. A typical oscilloscope display is shown. Period Using the oscilloscope, you can measure the peak-to-peak voltage, the peak voltage, and the period of the wave. Using these measurements, you can calculate the RMS voltage and the frequency of the wave. Peak Voltage Peak-to-Peak Voltage EXAMPLE: The VOLTS/DIV knob is set to 0.1 Volts per division. The TIME/DIV is set to 2ms (milliseconds) per division. For the waveform shown, find a. the peak-to-peak voltage (ΔVPK-PK), b. the peak voltage (ΔVoPK), c. the effective voltage (ΔVRMS) d. the period (T) and e. the frequency (f). First, you need to use the settings of the oscilloscope to determine voltages. a. Count the number of divisions from the lowest point of the wave to the highest point. # Divisions = 5.0 Multiply the number of divisions you counted by the VOLTS/DIV knob setting. 5.0 Divisions x 0.1 Volts/Div = 0.5 Volts. This is the peak-to-peak voltage (ΔVPK-PK) b. To find peak voltage, divide ΔVPK-PK by 2. ΔVPK = 0.5 Volts /2 = 0.25 Volts c. To find effective (or RMS) voltage, multiply the peak voltage by 0.707. ΔVRMS = 0.25 Volts x 0.707 = 0.177 Volts 1 Block: ______________ Date: ___________________Name:______________________________ Next, use the oscilloscope settings to find the time for one cycle of the wave (the period). d. Count the number of divisions from left to right for exactly one full cycle of the wave. # Divisions = 6.0 Multiply the number of divisions by the TIME/DIV knob setting. 6.0 Divisions x 2ms/DIV = 12 ms This is the period (T) of the wave. e. To find the frequency (number of cycles per second), divide 1 by the period. First, you have to make sure the period is measured in seconds. You need to know that 1 millisecond is 0.001 second. You can change milliseconds to seconds by dividing by 1000. Just move the decimal point 3 places to the left to change milliseconds to seconds. 12ms / 1000 = 0.012 second f = 1/0.012 seconds = 83.3 cycles per second (hertz) 2 Block: ______________ Date: ___________________Name:______________________________ PROBLEMS. A. Show all steps as in the example problem. Write all answers in the spaces provided. Include the correct units (such as volts, seconds or Hertz). For the waveforms shown, use the oscilloscope settings to find: a. the peak-to-peak voltage (ΔVPK-PK), b. the peak voltage (ΔVPK), c. the effective voltage (ERMS) d. the period (T) and e. the frequency (f). 1. The VOLTS/DIV knob is set to 0.1 Volts per division. The TIME/DIV is set to 2ms (milliseconds) per division. ΔVPK-PK: __________ ΔVPK: ___________ ΔVRMS:_____________ T:____________ f: ____________ 2. The VOLTS/DIV knob is set to 5 Volts per division. The TIME/DIV is set to 0.2s (seconds) per division. ΔVPK-PK: __________ ΔVPK: ___________ ΔVRMS:_____________ T:____________ f: ____________ 3 Block: ______________ Date: ___________________Name:______________________________ B. Draw the waveforms indicated on the oscilloscope screens provided. 1. Draw a triangle wave with a period of 4 divisions and a peakto-peak voltage of 6 divisions. 2. Draw a square wave with a period of 8 divisions and a peakto-peak voltage of 4 divisions. 3. Draw a sine wave with a period of 6 divisions and a peakto-peak voltage of 4 divisions. 4