6.4 Electrical Power and Potential Difference.
advertisement

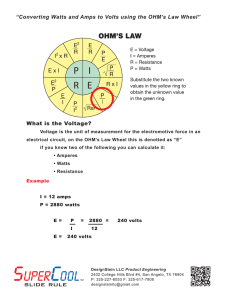
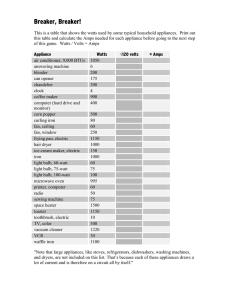
13 April 2015 6.4 Electrical Power and Potential Difference. Can you match these quantities to their units? Current Resistance Power Voltage Charge Ohms Coulombs Amps Watts Volts 13 April 2015 6.4 Electrical Power and Potential Difference. Answers Current Amps Resistance Ohms Power Watts Voltage Volts Charge Coulombs 13 April 2015 6.4 Electrical Power and p.d. Page 190 AQA Physics • The Power of an electrical device is the amount of energy it transfers every second. • The Power depends on the current and potential difference (Voltage) In the USA the Voltage is 110V. What would happen if you plugged a UK device into this Voltage? What might happen if an American plugged their device into the UK mains? Power • Power = Energy transferred (Joules, J) (Watts, W) Time (seconds, s) E.g A light bulb uses 6000J of energy in 1 minute. How powerful is the bulb? Power = ? Energy = 6000J Time = 1 minute = 60s Power = 6000 / 60 Power = 100 Watts Questions 1) An electric heater uses 3600000J in one hour. How much power does it use? 2) A car engine is rated at 100kW. How much energy does it use in 1s, 1min and 1 hour? Page 190 Question a) Electrical Power Power = Watts, W Current x Amperes, A Potential Difference Volts, V E.g. What power is used by a 12V, 5A car bulb? Power = 5A x 12V = 60 Watts Answer Question b) p191. Then Question 2 in the summary questions A pacemaker controls the beat of the heart. These contain explosive materials. If a body is cremated the pacemaker will explode in the incinerator causing quite a bit of damage and a really loud bang – not what you’d want at a funeral!