Carbon Dioxide and Buffer System
advertisement

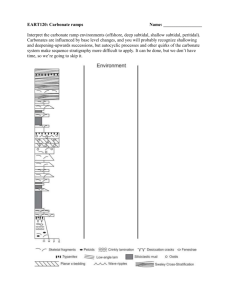
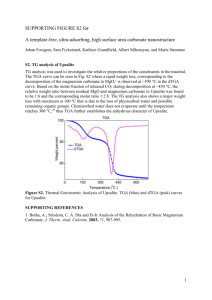
Carbon Dioxide Fundamental ingredient in photosynthesis Highly soluble in water 50X more in ocean than atmosphere most stored as calcium and magnesium carbonates in animal shells or sediments carbonate compounds reservoir in sea concentration relatively constant at 45 – 54 ml/L phytoplankton blooms – decrease CO2 Reacts with water 1st Carbon dioxide reacts with water forming carbonic acid o H2O + CO2 H2CO3 2nd , Carbonic acid dissociates into bicarbonate and then to carbonate ions releasing hydrogen ions H2CO3 H+ + HCO3- CO3-2 carbonic acid Hydrogen icon + Bicarbonate ion Hyrdogen Ion + Carbonate Ion 3rd – Carbonate ions react with calcium and magnesium in seawater to form calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate CO3-2 + Mg+2 + Ca+2 MgCO3 + CaCO3 carbonate ion + magnesium ion + calcium ion magnesium carbonate + calcium carbonate pH values and carbonate buffer system reversible reactions associated with dissolved carbon dioxide regulate the number of hydrogen ions in the ocean concentration of hydrogen ions is pH Carbonate buffer acts as a source of hydrogen ions if too basic and removes hydrogen ions if too acid If seawater becomes too basic: H2CO3 H+ + HCO3- if seawater becomes too acid: H+ + HCO3- H2CO3 Even though carbonic acid is a weak acid, its amount of ionization is so slight that it acts to decrease the number of hydrogen ions in solution Nitrate – nutrient Depth profiles Depth (Z) vs. nitrate Phytoplankton use nitrates so low at surface As depth increases, so does nitrates Levels off Similar to Compensation depth Poop (fecal pellets) sink Remineralized Oxygen minimum zone Compensation – photo and resp are equal Critical – no photo Lot of theories re: why Oxygen has minimum zone About 1000 m N:P in ocean – Redfield Ratio (mole ratio) = C:N:P 106:16:1 16X N than P in ocean Lysocline, CaCO3 compensation depth At some point it goes below a critical Lysocline – dissolution CCD – calcium carbonate compesation depth – no CaCO3 Reservoirs – inventory of various chemicals