Food Chains and Food Webs
advertisement
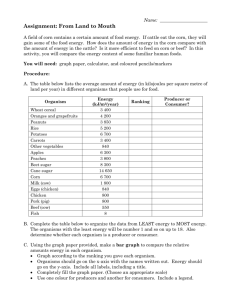
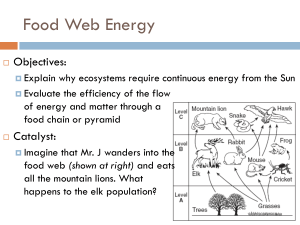
Food Webs: Land and Water Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers Every living organism eats or absorbs nutrients! Plants absorb the sun’s energy and carbon dioxide to make their own food by photosynthesis. An organism that makes its own food is called a producer. All plants and trees are producers. Organisms that cannot make their own food must eat other organisms to obtain energy. An organism that gets its food by eating other organisms is a consumer. Animals, many protists and some bacteria are consumers. A consumer that feeds directly on a producer is a primary consumer (1st). One that feeds on the primary consumer is a secondary consumer (2nd). Then the animal that feeds on the secondary consumer is a tertiary consumer (3rd). Most types of fungus and many bacteria are decomposers. A decomposer is an organism that gets it food energy by breaking down the remains of dead organisms. Decomposers are important because they recycle chemical nutrients back to the environment. Food Chains and Food Webs The feeding levels of the producers and consumers in an environment are called trophic levels (energy pyramid). Organisms take in food and energy from each trophic level. Food chains show the flow of energy from the producers to the consumers and to decomposers. *Arrows are used to connect the organism that is eaten to the animal that eats it. *A food chain is always straight. A food web is used to show how the organisms are connected in the ecosystem. Food webs are used to connect the organism that is eaten to the animal that it eats. *Food webs have arrows going every direction. Land and Water Food Webs A terrestrial, or land based, food web shows the feeding relationships in a land ecosystem and a food web in water, called an aquatic food web. These webs are often interconnected, meaning land animals can eat water animals and water animals can eat land animals. Energy Flow Energy is lost as you go higher in trophic levels because each organism uses energy for its life processes. Only about 10% of the energy is passed up to the next trophic level. Energy pyramids show the decrease in energy. FOLLOW UP QUESTIONS: 1. Give three feeding relationships that might connect a lake and a forest ecosystem. Fish raccoon bear 2. Which of these is a primary consumer? grass hawk mouse wolf 3. If the producers make 150,000 kilocalories of energy, how much energy is available to the third trophic level? a. 15,000 b. 1,500 c. 30 d. 15 4. In this food chain what is the secondary consumer? Grass cricket frog snake a. snake b. frog c. cricket d. grass 5. Put a check under producer or consumer to show each organism’s part in the food chain. Organism Snail Robin Mouse Grass Fox Rose plant Worm Owl Rabbit Corn plant Frog Cat Squirrel Raccoon Deer Food Source Producer Consumer Leaves X Worms, seeds X Seeds, beetles X Photosynthesis X Rabbits X Photosynthesis X Rotting leaves Frogs, mice Plants Photosynthesis X X X X Worms, flies Mice, birds Nuts, snails Berries, fish grass, shrubs X X X X X