ESM 214: Principles of Biological Remediation and Mitigation
advertisement
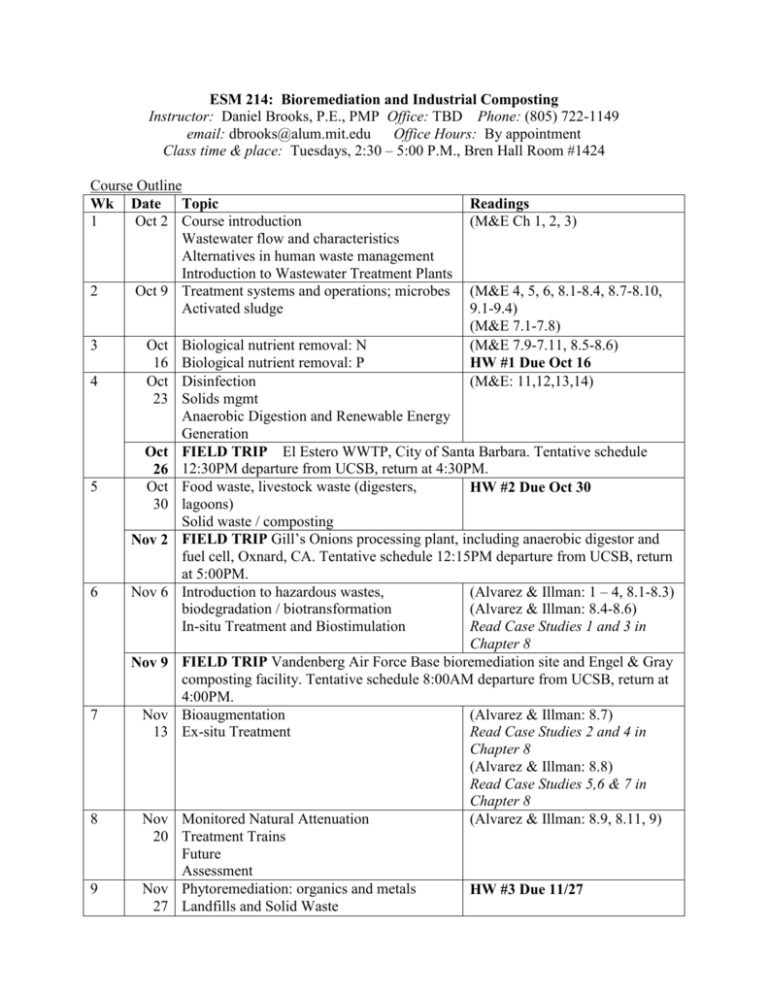
ESM 214: Bioremediation and Industrial Composting Instructor: Daniel Brooks, P.E., PMP Office: TBD Phone: (805) 722-1149 email: dbrooks@alum.mit.edu Office Hours: By appointment Class time & place: Tuesdays, 2:30 – 5:00 P.M., Bren Hall Room #1424 Course Outline Wk Date Topic 1 Oct 2 Course introduction Wastewater flow and characteristics Alternatives in human waste management Introduction to Wastewater Treatment Plants 2 Oct 9 Treatment systems and operations; microbes Activated sludge 3 4 5 Oct 16 Oct 23 Oct 26 Oct 30 Nov 2 6 Nov 6 Nov 9 7 Nov 13 8 Nov 20 9 Nov 27 Readings (M&E Ch 1, 2, 3) (M&E 4, 5, 6, 8.1-8.4, 8.7-8.10, 9.1-9.4) (M&E 7.1-7.8) (M&E 7.9-7.11, 8.5-8.6) HW #1 Due Oct 16 (M&E: 11,12,13,14) Biological nutrient removal: N Biological nutrient removal: P Disinfection Solids mgmt Anaerobic Digestion and Renewable Energy Generation FIELD TRIP El Estero WWTP, City of Santa Barbara. Tentative schedule 12:30PM departure from UCSB, return at 4:30PM. Food waste, livestock waste (digesters, HW #2 Due Oct 30 lagoons) Solid waste / composting FIELD TRIP Gill’s Onions processing plant, including anaerobic digestor and fuel cell, Oxnard, CA. Tentative schedule 12:15PM departure from UCSB, return at 5:00PM. Introduction to hazardous wastes, (Alvarez & Illman: 1 – 4, 8.1-8.3) biodegradation / biotransformation (Alvarez & Illman: 8.4-8.6) In-situ Treatment and Biostimulation Read Case Studies 1 and 3 in Chapter 8 FIELD TRIP Vandenberg Air Force Base bioremediation site and Engel & Gray composting facility. Tentative schedule 8:00AM departure from UCSB, return at 4:00PM. Bioaugmentation (Alvarez & Illman: 8.7) Ex-situ Treatment Read Case Studies 2 and 4 in Chapter 8 (Alvarez & Illman: 8.8) Read Case Studies 5,6 & 7 in Chapter 8 Monitored Natural Attenuation (Alvarez & Illman: 8.9, 8.11, 9) Treatment Trains Future Assessment Phytoremediation: organics and metals HW #3 Due 11/27 Landfills and Solid Waste 10 Dec 4 Trends and Opportunities in Environmental Consulting and Solid Waste Industries REVIEW TBA Final Exam (In class) 8 – 11 am BH 1424 Texts (neither required, but both referred to): M&E: Metcalf & Eddy, Wastewater Engineering: Treatment & Reuse, 4th ed. (2003) Alvarez & Illman. 2006. Bioremediation & Natural Attenuation. John Wiley & Sons. (on course website) ESM 214: Course goals, assignments, and grading Concepts and approaches to alleviate the effects of pollution using biological processes. Biological, chemical, physical, and practical aspects of hazardous and nonhazardous waste remediation, large scale composting, and associated renewable energy generation. Current trends and opportunities in the environmental and solid waste industries. Goals: The course goal is to gain a working understanding of how biological processes can be used to purify waste streams and to clean up pollution. Biological waste treatment is often economical and can generate non-toxic, sometimes useful byproducts. It may be used in combination with physical or chemical treatment processes such as with standard municipal wastewater treatment. The course is in two parts to separately address non-hazardous and hazardous wastes. The principles overlap. This is not a design course. You will learn about the waste, why it is treated, how it is treated (with an emphasis on biological processes), some fundamentals about the design principles, and how the systems should function. You will gain a working vocabulary in bioremediation, composting, and water treatment, you will gain an understanding of treatment objectives and how objectives are being met. The concepts you will learn include: Wastewater characteristics and microbial processes Conventional wastewater treatment processes and new technologies Hazardous wastes in the environment In situ bioremediation of hazardous wastes Biological treatment of hazardous and nonhazardous wastes ex situ Current trends in the environmental and solid waste industries Course Format: Combination of in-class lecture, group activities in class, and field trips. There are homework assignments, and one exam (final). Grading: 40% HW. 30% field trip. 30% final. The field trips are mandatory. Regular attendance and class participation will also be considered in assigning final grades. Homework: 3 assignments. Combination of calculations and writing. Collaboration on homework is permitted. Please list your collaborators. Reading: M&E: Metcalf & Eddy, Wastewater Engineering: Treatment & Reuse, 4th ed. (2003) Alvarez & Illman. 2006. Bioremediation & Natural Attenuation. John Wiley & Sons. (on course website) Brock Biology of Microorganisms, 13th edition. 2010. Madigan, Martinko, Stahl, and Clark. Chapters 19.14 through 19.18. Massachusetts Institute of Technology Open Courseware Waste Containment and Remediation (see readings for Lectures 12 and 13) http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/civil-and-environmental-engineering/1-34-waste-containment-andremediation-technology-spring-2004/calendar/ Water and Wastewater Treatment Engineering http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/civil-and-environmental-engineering/1-85-water-and-wastewatertreatment-engineering-spring-2006/calendar/ Water and Sanitation Infrastructure in Developing Countries http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/urban-studies-and-planning/11-479j-water-and-sanitationinfrastructure-in-developing-countries-spring-2007/calendar/ Some potentially useful Websites and Organizations: US EPA AgSTAR: http://www.epa.gov/agstar/index.html International Water Association: http://www.iwahq.org/templates/ld_templates/layout_632897.aspx?ObjectId=632922 Water Environment Federation: http://www.wef.org/ World Health Organization: http://www.who.int/en/ CA State Water Resources Control Board Water Quality: http://www.swrcb.ca.gov/quality.html US EPA NPDES http://cfpub.epa.gov/npdes/index.cfm NOAA Office of Response and Restoration: http://response.restoration.noaa.gov/index.html US EPA Bioremediation Documents: http://www.clu-in.org/remediation/ US EPA Contaminated Site Information: http://www.epareachit.org/index.html US EPA Remediation Resources: http://www.clu-in.org/remediation/ USGS Bioremediation website: http://water.usgs.gov/wid/html/bioremed.html Bioremediation Discussion Group: http://www.bioremediationgroup.org/ University of Minnesota Biocatalysis/ Biodegradation Database: http://umbbd.msi.umn.edu/ DOE Environmental Remediation Sciences Group: http://esd.lbl.gov/research/projects/ersp/ American Society for Microbiology: http://www.asm.org/ US EPA Microbiology: http://www.epa.gov/microbes/ Microbes Info: http://www.microbes.info/index.html Microbe Zoo: http://commtechlab.msu.edu/sites/dLc-me/zoo/index.html Federal Remediation Technologies Roundtable: http://www.frtr.gov/default.htm