Literacy Audit
advertisement
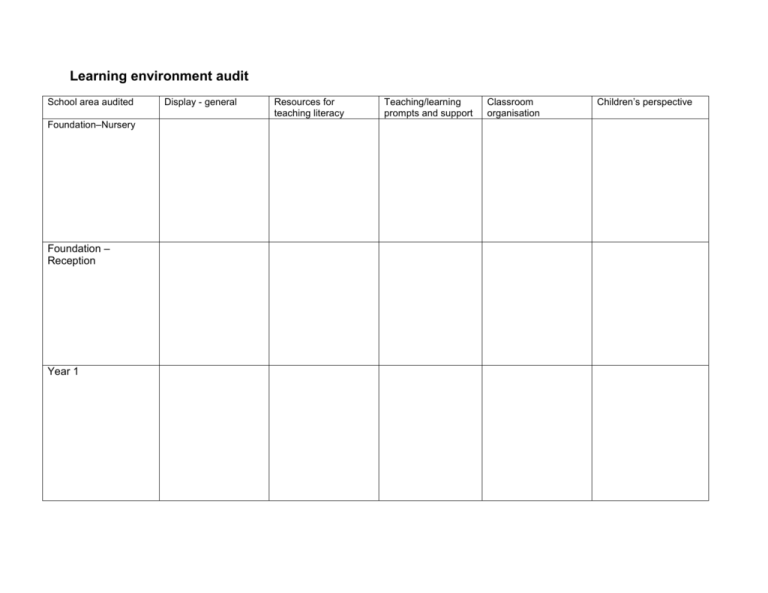
Learning environment audit School area audited Foundation–Nursery Foundation – Reception Year 1 Display - general Resources for teaching literacy Teaching/learning prompts and support Classroom organisation Children’s perspective School area audited Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Display - general Resources for teaching literacy Teaching/learning prompts and support Classroom organisation Children’s perspective School area audited Year 5 Year 6 ‘Public’ areas Display - general Resources for teaching literacy Teaching/learning prompts and support Classroom organisation Children’s perspective Creating an effective learning environment School literacy audit Class ……………. Year group …………………. Date of audit ………………………. Carried out by …………………. Key question: How does this classroom environment support the teaching and learning of literacy? N.B these prompts are generic. They will need to be adapted to be more precise and specific, according to year group/phase and according to school context and priorities. Area of focus The role play area provides stimulating and worthwhile literacy tasks, with relevant prompts and support to enable children to access the planned reading and writing opportunities. There is an attractive and inviting book area, which includes interactive displays, with named ‘book/author of the week’; book reviews, group and class anthologies; puppets and story sacks; a listening centre and tapes. There is a wide and relevant collection of reading materials, which is well cared for and accessible and includes fiction and non-fiction, poetry and plays, dual language texts and tapes. The book area includes prompt and reminders on how to access texts and how to use a range of reading strategies. An informal display/folder invites children to write brief responses to texts they have read, advise others on choice of author, and so on. There are good models of a range of writing around the room in English and other languages. Notice boards and other informal communication areas invite children to read and write for specific and relevant purposes. Yes/No Comments A writing table offers opportunities for children to use a range of writing implements and materials for a variety of purposes. Dual language use is encouraged. Notes, diagrams, labels and other prompts remind children of the writing process: oral rehearsal, planning, drafting, re-reading, etc. There are accessible prompts and check-lists to support the organisation and structure of writing –f or example, table-top laminated story openings; bland storyboards and writing frames to aid planning and drafting; connectives and conjunctions used for specific effects in report writing or explanations. Cross-curricular displays reinforce particular structures for writing –for specific purposes and for specific text types. Vocabulary is enhanced and developed through display, labelling, key words, cross-curricular topic vocabulary and a bank of favourite words and phrases. This bank may be computer-based, a wall display a scrap-book or a group or individual collection. Displays encourage children to think about the history of words and how words in other languages relate to English. Spelling is supported in a number of ways around the classroom: ‘family’ spelling patterns are displayed, a magnetic board and letters for ‘have a go’ attempts at spelling, phoneme frames, word walls and topic vocabulary for example. There are explicit and accessible reminders of different spelling strategies children can use to improve their spelling. Interactive displays inviting children to experiment with trying out spelling strategies; using different spellings for the same sound, use of prefixes and suffixes, syllabification. There is a range of suitable dictionaries, glossaries, thesaurus, alphabet strips in the classroom. Children are aware of the teaching and learning prompts around the room and know how to access them appropriately and independently. Children have a real sense of reading and writing as essential means of communication. Children further their learning by actively engaging with the prompts and displays, adding to them and developing them as progressive and cumulative support systems.