Lab12_Population Growth and Diseases - Jocha

STUDY GUIDE
M t .
S A C B i o l l o g y 1
L A B 1 2 : : P o p u l a t i o n G r o w t t h a n d D i s e a s e s
1.
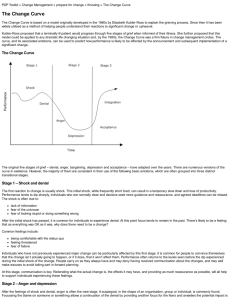
Introduction: Read the introduction and explained the 3 parts for the growth curve (lag, exponential, stable)
2.
Introduction: Define carrying capacity. In which of the previous parts of the growth curve does the population reach its carrying capacity?
3.
Define species’ biotic potential or reproductive capacity
4.
Introduction: Define environmental resistance factors or limiting factors
5.
Introduction: Which one/s of the terms defined before corresponds with natality? Which one corresponds with mortality?
6.
Introduction: Analyze the pyramid for age distribution shown in the introduction for this lab in your lab manual. Understand the three main parts of that pyramid (pre, reproductive, post).
7.
Part I: Population growth: Compare the theoretical growth curve with the human growth curve you drew in your lab manual, what part of the theoretical growth curve is missing in the human curve you obtained? Why is that? (Is it because we increased what you answered in 3 or because we decrease what you answered in 4?)
8.
Part II: Resources use and others. Based on the table we made in class, analyze the following statistics for the five world regions presented in your exercise a) More and less populated regions b) Regions with the highest and lowest birth rate, regions with the highest and lowest death rate c) Regions with the best and worst rate of natural increase d) Life expectancy e) Medical doctors f) Regions of the world that consume the most, regions that consume the least g) Regions’ wealth: Richest and poorest regions in the world
9.
Part III: The apple of our eye. The earth is composed of several layers called core (in the center), mantle (in the middle) and curst (on the surface). Only the crust; and particularly the continental crust (30% of the total surface) are available to humans. Which percent of the planet does this corresponds to according to what you did with the apple?
10.
Part IV: Enough for all? Explain and understand the results obtained with this simple exercise. What happens with the global distribution of wealth and reproduction?
11.
Part V: STD diseases. Are STDs more common now than they were in the past? Explain
12.
Video “World in the balance”: Understand the three different age pyramids presented in the video for India,
Kenya, and Japan and the reasons why they look the way they look.
Instructor: Jose Bava, Ph.D