Plankton Basics
advertisement

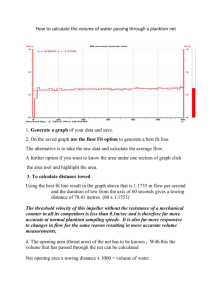
Simple Marine Organisms – PLANKTON Plankton Basics What is plankton? Any organism that floats/drifts with ocean currents. Being plankton is a behavior, not a size-based or feeding classification. What is nekton? Organisms that can swim against currents and control their position in the water- the opposite of plankton. Most plankton are Plankton tiny , but some- like jellyfish can be large. comes from a Greek term meaning “drifter”. How do plankton remain floating for days or years? cilia or flagella (used by the smallest plankton), tentacles (jellyfish), oil (being lighter than water), and long spikes to distribute their body weight. Phytoplankton Phytoplankton are primary producers that use the sun’s energy to convert CO2 and H2O into sugars. In doing so, they form the base of the ocean’s food chain , and provide more than 50% of our world’s O2. Because of these two roles, phytoplankton are arguably important organisms on Earth! the most The growth of phytoplankton depends on temperature , light , and nutrient availability. Because of their light requirements, the growth of phytoplankton is limited to the photic zone Examples of Zooplankton phytoplankton include: diatoms : unicellular algae with skeletons of silica dinoflagellates : unicellular algae with flagella cyanobacteria : called blue-green algae- actually bacteria green algae : unicellular green protists coccolithophores : unicellular algae with CaCO3 plates Zooplankton are passively drifting animals. Can range from micro to macro in size. Example of zooplankton include: radiolarians : unicellular protozoans with silica tests foraminifera : unicellular protozoans with CaCO3 tests larvae : newly hatched young of fish/invertebrates crustaceans : including tiny copepods, cladocerans and ostracods, and larval krill and shrimp jellies : multicellular stinging organisms including true jellyfish, comb jellies, and their relatives Planktonic organisms can be either: Meroplankton : organisms that spend only part of their lives as plankton (for example: fish and invertebrate larvae) Holoplankton : organisms that spend their entire lives as plankton (for example: diatoms, jellyfish, copepods)