Experiment P07
advertisement

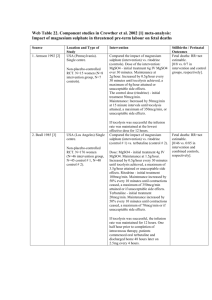
Experiment P07 Application of Hess's Law to determine the ΔH of a reaction indirectly Chemicals: Anhydrous magnesium sulphate (3.01 g), magnesium sulphate-7-water crystals (fine powder, 6.16 g). Apparatus: 50 cm3 Measuring cylinder, expanded polystyrene cup, (1) thermometer (0-100oC, in 0.1o graduations), weighing bottle. (1) Principle: If anhydrous magnesium sulphate is left in the atmosphere, it slowly absorbs water vapour giving the hydrated solid. Water vapour MgSO4(s) MgSO4 7H2O(s) The above enthalpy change cannot be measured directly. (Why?) Consider the following energy cycle: MgSO4(s) + 7H2O(l) ΔH1 ΔH MgSO4 7H2O(s) + nH2O ΔH2 + nH2O 0.5M MgSO4(aq) Can you evaluate ΔH indirectly by measuring ΔH1 and ΔH2 ? P.1 Experiment P07 Application of Hess's Law to determine the ΔH of a reaction indirectly Procedure: A. Determination of heat of solution of anhydrous magnesium sulphate a. Pour 50 cm3 of distilled water from a measuring cylinder into an expanded polystyrene cup and record the temperature. b. Weigh accurately 0.025 mole(3.01 g) of anhydrous magnesium sulphate and add them to the water in the polystyrene cup. Stir to dissolve it as quickly as possible. Record the highest temperature of the solution. c. Calculate the temperature rise and hence the molar heat of solution of anhydrous magnesium sulphate, assuming the specific heat capacity of the solution in the polystyrene cup is 4.18 J g-1 K-1 and that of the polystyrene cup is 1.3 J g-1 K-1. B. Determination of heat of solution of magnesium sulphate-7-water a. Repeat the experiment as described in part A above, but use 0.025 mole (6.16g) of magnesium sulphate-7-water instead of anhydrous salt. b. Calculate the temperature fall and hence the molar heat of solution of magnesiusulphate-7-water, assuming the specific heat capacity of the solution in the polystyrene cup is 4.18 J g-1K-1, and that of the polystyrene cup is 1.3 J g-1K-1. P.2 Experiment P07 Application of Hess's Law to determine the ΔH of a reaction indirectly Name: Seat No.: Date: Data: Grade: 1. Weight of 0.025 mole of anhydrous MgSO4 = 2. Weight of the polystyrene cup = 3. Initial temperature of water Ti1 = 4. Final temperature of the 0.5 M of MgSO4 solution Tf1 = 5. Weight of 0.025 mole of MgSO4 7H2O = 6. Vol. of water used to dissolve 0.025 mole of MgSO4 7H2O to obtain a 0.5 M solution = 7. Initial temperature of water Ti2 = 8. Final temperature of the 0.5 M of MgSO4 solution Tf2 = Questions: 1. Draw an energy cycle to link the corresponding heats of the reactions together. 2. Using Hess' Law, calculate the molar heat of hydration of anhydrous magnesium sulphate to form magnesium sulphate-7-water. 3. The molar heat of hydration of magnesium sulphate cannot be measured directly in the laboratory, Why? P.3