Brainstorm on Secondary Care MH, AED, Maternal Services
advertisement
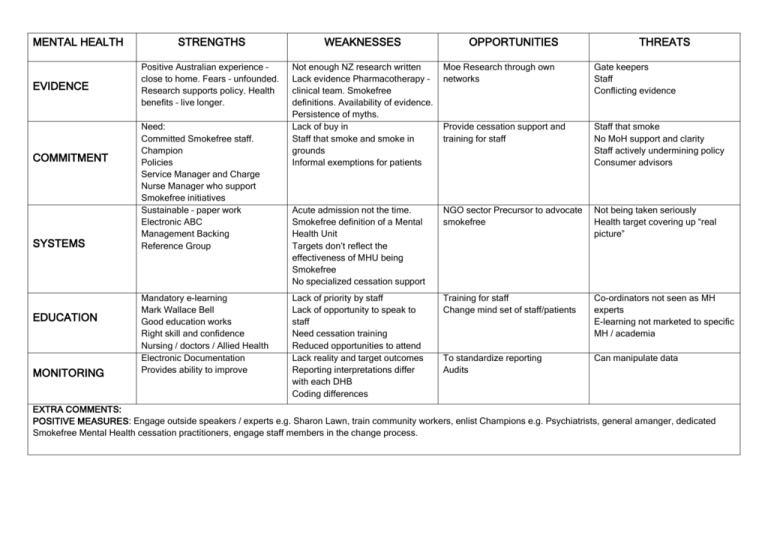
MENTAL HEALTH EVIDENCE COMMITMENT SYSTEMS EDUCATION MONITORING STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES Positive Australian experience – close to home. Fears – unfounded. Research supports policy. Health benefits – live longer. Not enough NZ research written Lack evidence Pharmacotherapy – clinical team. Smokefree definitions. Availability of evidence. Persistence of myths. Lack of buy in Staff that smoke and smoke in grounds Informal exemptions for patients Moe Research through own networks Gate keepers Staff Conflicting evidence Provide cessation support and training for staff Staff that smoke No MoH support and clarity Staff actively undermining policy Consumer advisors Acute admission not the time. Smokefree definition of a Mental Health Unit Targets don’t reflect the effectiveness of MHU being Smokefree No specialized cessation support NGO sector Precursor to advocate smokefree Not being taken seriously Health target covering up “real picture” Lack of priority by staff Lack of opportunity to speak to staff Need cessation training Reduced opportunities to attend Lack reality and target outcomes Reporting interpretations differ with each DHB Coding differences Training for staff Change mind set of staff/patients Co-ordinators not seen as MH experts E-learning not marketed to specific MH / academia To standardize reporting Audits Can manipulate data Need: Committed Smokefree staff. Champion Policies Service Manager and Charge Nurse Manager who support Smokefree initiatives Sustainable – paper work Electronic ABC Management Backing Reference Group Mandatory e-learning Mark Wallace Bell Good education works Right skill and confidence Nursing / doctors / Allied Health Electronic Documentation Provides ability to improve OPPORTUNITIES THREATS EXTRA COMMENTS: POSITIVE MEASURES: Engage outside speakers / experts e.g. Sharon Lawn, train community workers, enlist Champions e.g. Psychiatrists, general amanger, dedicated Smokefree Mental Health cessation practitioners, engage staff members in the change process. MATERNITY EVIDENCE COMMITMENT STRENGTHS MONITORING OPPORTUNITIES THREATS Harm of smoking to foetus, Treatment models are present, “Look at this placenta”, Increased acceptance of ABC. Poor evidence about OK use of drugs, Ethical challenges re trail of drugs. Opportunities for NZ Research, standardization of data collection, is there UK evidence for national frameworks Everybody is measuring things differently, people scared of safety Pregnancy is a catalyst Many relapse after birth, “softly, softly” approach isn’t enough, inconsistent training of midwives Yet to be realized as MoH and all service providers pull together, increased leadership Lack of leadership Smoking status well recorded at enrollment Lack of national leadership, inconsistencies, integration between agencies, no resources specific to hapu women, different forms used by independent agencies vs DHBs Mltiple learning packages, inconsistent messages, still a lack of knowledge Funding for Midwives as Quit Coaches, Icentives, Can we do ABC @ each encounter, free NRT supply for midwives (Partner and mother) MPSO?, Add Smokefree clause to section 88 agreement Midwives as SC coaches, Increase midwifery training, add to undergraduate training AKP providers have a larger % of males, need more female providers. Doubts about outcomes from AKP services Add ABC documentation to M/V reporting to MoH docs SYSTEMS EDUCATION WEAKNESSES ABC on-line, Smokechange – funded, STEPS - coming Monitoring inpatients – is it useful? EXTRA COMMENTS: POSITIVE MEASURES: person to assist with transitioning of clients from maternity to community, build relationship with LMCs, specific pregnancy smoking cessation service. EMERGENCY Dpt EVIDENCE COMMITMENT STRENGTHS WEAKNESSES Population presenting to ED contains a higher prevalence of disadvantaged groups and smokers, nicotine withdrawal needs to be managed, 1 in 40 NNT for brief intervention still applies Lack of evidence to show that there are +ve outcomes from giving brief advice in the acutely unwell population Once protocols are set and clearly explained nurses will apply them, Champions who are recognized in ED will be emulated Difficulty getting buy in because of busy department, large number of staff, lack of cohesion in staff group, smoking cessation is seen as a community issue that should happen outside of hospital Developing systems takes time, can be initially chaotic, requires fiscal support, requires a change in staff attitudes. OPPORTUNITIES Risks to individual going outside to smoke when acutely unwell, fire risks from smokers outside of ED, managing nicotine withdrawal keeps patient calm, ability to share what works well in ED, ability to reach target populations, engage whanau Senior Nurses have kpis to meet, the current health target is putting pressure on them Accessibility, equitability, health promotion THREATS The area is too busy, staff cannot see the relevance, lack of skills in giving brief advice Smokefree is seen as an “add-on”, ensuring sustainability of purpose, the health target becomes the driver rather than the well=being of the individual, lack of ownership by the department Workload increased, Bureaucracy increased. SYSTEMS Ensure: consistency, sustainability, removes barriers, enables auditing EDUCATION Patients are exposed to education, staff acquire skills to improve patient care. Time constraints, non-receptive / challenging patients; inappropriate timing More quit attempts, capitalize on a teachable moment Overestimating knowledge, decreased referrals, decreased follow-up MONITORING Enables feedback and performance management Big brother surveillance, micro managing patient’s lives, just a tick, problems of data integrity Enables improvement in practice Staff resent monitoring, complacency, Focus too narrow.