Diffraction grating
advertisement

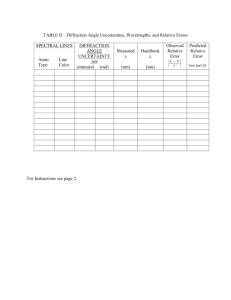
Diffraction grating 2010 Diffraction Grating -1- Areej Al-Jarb Diffraction grating 2010 Table of Contents Section Page Basic Experiments Experiment 1:Diffraction grating -2- ........................................................... 6 Areej Al-Jarb Diffraction grating 2010 Experiment 1: Diffraction grating Diffraction grating : A diffraction grating is an optical instrument consists of a large number of parallel, closely spaced slits, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as the dispersive element. When light of a single wavelength , like the 632.8nm red light from a helium-neon laser strikes a diffraction grating it is diffracted to each side in multiple orders ,The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for the double slit or multiple slits, but with a large number of slits the intensity maximum is very sharp and narrow, providing the high resolution for spectroscopic applications. The peak intensities are also much higher for the grating than for the double slit. On the other hand if light of different wavelengths is incident on a diffraction grating, it is diffracted at different angles (each wavelength of input beam spectrum is sent into a different direction, producing a spectrum), each slit in the grating acts as a point source propagating in all directions. The light in a particular direction θ is made up of the interfering components from each slit, producing sharp intensity maxima. longwave light is deviated more than short-wave light. Generally, the phases of the waves from different slits will vary from one another, and will cancel one another out partially or wholly. However, when the path difference between the light from adjacent slits is equal to the wavelength, λ, the waves will all be in phase. This occurs at angles θm which satisfy the relationship dsinθm/λ=|m| where d is the separation of the slits and m is an integer. Thus, the diffracted light will have maxima at angles θm given by -3- Areej Al-Jarb Diffraction grating 2010 The diffraction grating acts as a "super prism", separating the different colors of light much more than the dispersion effect in a prism. EQUIPMENT –Diffraction grating. –Spectrum tube power supply. –Spectrum tubes such as Mercury, Helium, Cadmium, etc. –magnifier. OBJECTIVE Measure the wavelengths of the used light. PROCEDURE To accurately calculate wavelengths on the basis of diffraction angles, the grating must be perpendicular to the beam of light from the collimator. 1. Align and focus the spectrometer as described earlier (in the prism spectrometer experiment) . The telescope must be directly opposite the collimator with the slit in sharp focus and aligned with the vertical cross-hair. 2. Using the thumbscrews, attach the grating mount so it is perpendicular to the engraved lines. 4. Insert the diffraction grating into the clips of the mount. To check the orientation of the grating, look through the grating at a light source and notice how the grating disperses the light into its various color components. When placed in the grating mount, the grating should spread the colors of the incident light horizontally, so rotation of the telescope will allow you to see the different colored images of the slit. -4- Areej Al-Jarb Diffraction grating 2010 6. Rotate the telescope to find a bright slit image. Align the vertical cross-hair with the fixed edge of the image and carefully measure the angle of diffraction. as shown in fig. 7. The diffraction grating diffracts the incident light into identical spectra on either side of the line of the undiffracted beam. Rotate the telescope back, past the zero diffraction angle, to find the corresponding slit image. Measure the angle of diffraction for this image. 8. If the grating is perfectly aligned, the diffraction angles for corresponding slit images will be identical. -5- Areej Al-Jarb Diffraction grating 2010 ANALYSIS Determine the wavelengths according to the formula: where is the wavelength; d is the distance between lines on the diffraction grating (d =----------------- line/mm grating); is the angle of diffraction; and m is the order of the diffraction spectrum under observation. When Color When Color -6- m=1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) m=2 ( ) Areej Al-Jarb