Evolution Essays
advertisement
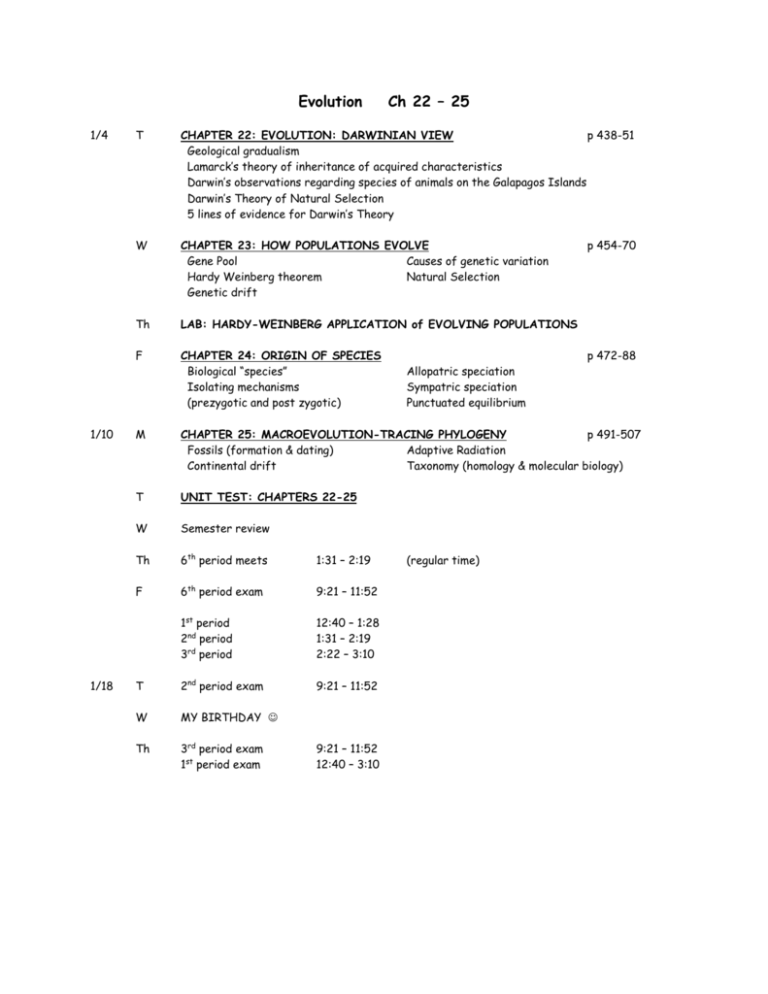
Evolution 1/4 1/10 1/18 Ch 22 – 25 T CHAPTER 22: EVOLUTION: DARWINIAN VIEW p 438-51 Geological gradualism Lamarck’s theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics Darwin’s observations regarding species of animals on the Galapagos Islands Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection 5 lines of evidence for Darwin’s Theory W CHAPTER 23: HOW POPULATIONS EVOLVE Gene Pool Causes of genetic variation Hardy Weinberg theorem Natural Selection Genetic drift Th LAB: HARDY-WEINBERG APPLICATION of EVOLVING POPULATIONS F CHAPTER 24: ORIGIN OF SPECIES Biological “species” Isolating mechanisms (prezygotic and post zygotic) p 454-70 p 472-88 Allopatric speciation Sympatric speciation Punctuated equilibrium M CHAPTER 25: MACROEVOLUTION-TRACING PHYLOGENY p 491-507 Fossils (formation & dating) Adaptive Radiation Continental drift Taxonomy (homology & molecular biology) T UNIT TEST: CHAPTERS 22-25 W Semester review Th 6th period meets 1:31 – 2:19 F 6th period exam 9:21 – 11:52 1st period 2nd period 3rd period 12:40 – 1:28 1:31 – 2:19 2:22 – 3:10 T 2nd period exam 9:21 – 11:52 W MY BIRTHDAY Th 3rd period exam 1st period exam 9:21 – 11:52 12:40 – 3:10 (regular time) Evolution Essays 1989: Do the following with reference to the Hardy-Weinberg model. a. Indicate the conditions under which allele frequencies (p and q) remain constant from one generation to the next. b. Calculate, showing all work, the frequencies of the alleles and frequencies of the genotypes in a population of 100,000 rabbits of which 25,000 are white and 75,000 are agouti. (In rabbits the white color is due to a recessive allele, w, and agouti is due to a dominant allele, W.) c. If the homozygous dominant condition were to become lethal, what would happen to the allelic and genotypic frequencies in the rabbit population after two generations? 1992: Evolution is one of the unifying concepts of modern biology. a. Explain the mechanisms that lead to evolutionary change. b. Describe how scientists use each of the following as evidence for evolution: 1) Bacterial resistance to antibiotics 2) Comparative biochemistry 3) The fossil record 1994: Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2004: Darwin is considered the “father of evolutionary biology.” Four of his contributions to the field of evolutionary biology are listed below. o o o o The nonconstancy of species Branching evolution, which implies the common descent of all species Occurrence of gradual changes in species Natural selection as the mechanism for evolution a. For EACH of the four contributions listed above, discuss one example of supporting evidence. b. Darwin’s ideas have been enhanced and modified as new knowledge and technologies have become available. Discuss how TWO of the following have modified biologists’ interpretation of Darwin’s original contributions. o Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium o Punctuated equilibrium o Genetic engineering











