What is Emotional Intelligence
advertisement

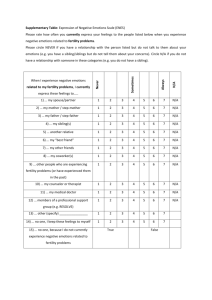
What is Emotional Intelligence? The ability The ability thought The ability The ability growth. to perceive accurately, appraise and express emotion to access and/or generate feelings when they facilitate to understand emotion and emotional knowledge to regulate emotions to promote emotional and intellectual Elements of Emotional Intelligence Personal Competencies 1. SELF-AWARENESS Knowing one's internal states, preferences, resources, and intuitions. 2. MANAGING EMOTIONS Managing one's internal states, impulses, and resources. 3. MOTIVATION Emotional tendencies that guide or facilitate reaching goals. Social Competencies 4. EMPATHY Awareness of others' feelings, needs, and concerns. 5. SOCIAL SKILLS Adeptness at inducing desirable responses in others. Self-Awareness High self-awareness refers to having an accurate understanding of how you behave, how other people perceive you, recognizing how you respond to others, being sensitive to your attitudes, feelings, emotions, intents and general communication style at any given moment and being able to accurately disclose this awareness to others. (page 1 of 5) Skill Indicators Know Know Know Know Know Know Know Know Know when you are thinking negatively when your self-talk is helpful when you are becoming angry how you are interpreting events what senses you are currently using how to communicate accurately what you experience the moments your mood shifts when you are becoming defensive the impact your behavior has on others Skills Assessment Do you recognize your feelings and emotions as they happen? Are you aware of how others perceive you? How do you act when you are defensive? Are you aware of how you speak to yourself? Managing Emotions The capacity to soothe oneself, to shake off rampant anxiety, gloom, despair, or irritability. The ability to be able to keep an emotional perspective. Skill Indicators Able to identify shifts in physiological arousal Be able to relax in pressure situations Act productively in anxiety-arousing situations Calm oneself quickly when angry Associate different physiological cues with different emotional states Use self-talk to affect emotional states Communicate feelings effectively Reflect on negative feelings without being distressed Stay calm when you are the target of anger from others Skills Assessment Do you use anger productively? Can you manage your anxiety in times of change? Can you put yourself in a good mood? (page 2 of 5) Motivation Be able to channel emotions to achieve a goal; to postpone immediate gratification for future gratification; to be productive in low interest, low enjoyment activities; to persist in the face of frustration and generate initiative without external pressure. Skill Indicators Able Able Able Able Able Able Able to to to to to to to "gear up" at will regroup quickly after a setback complete long-term tasks in designated time frames produce high energy in the context of low-enjoyment work change and stop ineffective habits develop new and productive patterns of behavior follow through words with actions Skills Assessment Are you persistent? Do setbacks set you back? Can you psyche yourself up? Empathy The ability to exchange information on a meaningful level. Adept in skills necessary for organizing groups and building teams, negotiating solutions, mediating conflict among others, building consensus, and making personal connections. Skill Indicators Work out conflicts Build consensus Mediate conflict between others Exhibit effective interpersonal communication skills Articulate the thoughts of a group Able to influence others, directly or indirectly Build trust and support teams Sought out by others for advice and support (page 3 of 5) Skills Assessment Is it easy for you to resolve conflict? How well do you give criticism? Are you a good listener Do you frequently praise people? Social Skills Being aware of other people's feelings and emotions; being able to listen to their feelings; being able to help others deal with their feelings and emotions in productive ways and assist them in increasing their awareness about their own impact on others. Skill Indicators Able to accurately reflect back to others the feelings they are experiencing Stay calm in the presence of others' distressful emotions Recognize when others are distressed Able to help others manage their emotions Be perceived by others as being empathic Able to engage in intimate conversations with others Able to manage group emotions Detect incongruence between others' emotions and their behavior Skills Assessment Are you skillful in managing the emotions of others? How do you know when your boss is angry, sad, anxious? Can you manage an angry group? Are you comfortable with your feelings? (page 4 of 5) Emotionally Intelligent Organizations The emotionally intelligent work group or organization has a culture that exhibits: Organizational Self-Awareness of its internal and external needs; Management of Organizational Emotions through leadership, celebration and environment; Organizational Motivation through meaningful work and the delivery of incentives; Organizational Empathy by maintaining effective and meaningful relationships with consumers and employees; Mentoring of Organizational Social Skills through training, productive personnel selection practices, and performance appraisal. Bibliography: Cooper, R.K., & Sawaf, A., 1997. Executive EQ: Emotional intelligence in leadership and organizations. Grosset/Putnam, New York. Gardner, H., 1983. Frames of mind: The theory of multiple intelligences. BasicBooks, New York. Goleman, D., 1998. Working with emotional intelligence. Bantam Books, New York Weisinger, H., 1998. Emotional intelligence at work: The untapped edge for success. Josey-Bass, San Francisco Information revised from the following website: www.tdh.state.tx.us/quality/emotion.htm Careers in Psychology Summer Session 2007 (page 5 of 5)