GEOGRAPHY – PAPER 1 MAKING SCHEME Section A: Conditions
advertisement
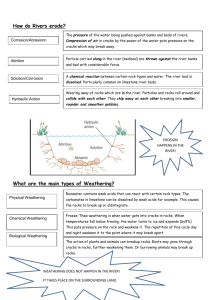
GEOGRAPHY – PAPER 1 MAKING SCHEME Section A: 1. Conditions considered in choosing a suitable site for a weather station It should be an open space away from tall objects/buildings/tree The ground should be level/gently sloping The area should be free from flooding The area should have a wide view 3x1=3marks 2. (a)Why air cools as it rises As air rises, it expands thus spreading out its molecules over a wider area and hence becoming cooler 2marks (b)Importance of weather forecasting It enables farmers to plan for farming activities It helps people to plan on suitable clothing for the day It influences the design of houses it helps in guiding the landing and taking off of aircraft/ship It helps in timing and planning of sporting activities It helps in guiding tourists activities It helps in planning military activities Accept other relevant reason (max 3 marks) 3. (a)formation of oasis A pre-existing depression/localised fault is deepened by eddy action/deflation Gradually the depression excavated through the removal of the unconsolidated material/wind abrasion The surface is lowered until it reaches the water bearing rock/aquifer Water oozes out of the ground and collects in the depression to form an oasis Must be mentioned to score. max 3. Otherwise 2 (b) Characteristics of hot desert climate Low annual rainfall (less than 250mm) – dry climate Occasional flash floods /sporadic rains Clear skies/clear sunny day/high torrential radiation - High temperatures during the day/relatively low temperatures during the night Strong winds Low pressure in summer/high pressure in winter High mean annual temp/hot climate (27oC) and above Large mean annual range of temp Intensive solar insolation Rainfall is unreliable/erratic Low humidity throughout the year High evaporation rate throughout the year Max 4 4. (a)- Weathering by solution in limestone areas - Deposition by water/ice - Erosion by wind/ice - Meteorite falling - Human activities/damming - Mass movements Max 3 (b)- Are reservoirs in the water cycle - Support bio-diversity/support flora and fauna - Enable self purification of water and air - Modify local weather and climate - Regulation of river flow/controlling flooding 5. (a) - Pressure exerted by overlying rock mass - Radio-active decay - Heat retained during formation of the earth Max 3 (b) - Temp of the water i.e. high temp leads to higher concentration of salts due to evaporation - Supply of fresh water by rivers , rainfall and melting of ice decreases salinity - Degree of mixing of surface and sub-surface water caused ocean currents Section B: 6. a) (i) 194155 (ii) - Settlement/hut - Dam - Other track/footpath (iii) 288 o (+or-1 o) (iv) 7.5km2 (+or-0.5)=7 – 8km2 (v) 8.0km (+or-0.2km)= 7.8 – 8.2km (1mk) (1mk) (2mks) (2mks) (b) L. Victoria 1 (i) Accurate rectangle – 1 mark (ii) Lake Victoria – 1 mark (iii) Ridge –1 mark (iv) Road – 1 mark (v) Seasonal swamp – 1 mark Total = 5marks (c) (i) - Economic activity Agriculture Transportation Trade/commerce evidence Agricultural department and cotton shed Jetty/ferry/roads/tracks Mkts/shops Max 2 (ii) - Relief – the hilly areas have no settlements because the slopes are steep. Gentler slopes havedense settlements Drainage – southern parts of the area have scarce settlement due to poor drainage/swamps. River Nzoia valley is densely settled due to rich river deposits as evidenced by presence of ox-bow lakes. Well drained areas have dense settlements Vegetation – areas covered with thickets have scarce settlements because the vegetation is thick. (d)- Ox-bow lakes - Islands/braided channels - Sand deposits - Pronounced meanders - Rock outcrops - River confluences/tributaries Seasonal swamp River valley A pond 7. a) - is a zone of low atmospheric pressure - is a zone within the tropics/between 23 ½o N and 23 ½o S - is a zone where the South-East and North East trade winds converge - migrates to the north and south of the equator with the apparent movement of the overhead sun - is associated with convectional rainfall rain and thunderstorms - is characterised by high temps Max 3 b) Diagram 2 marks - a water body/sea/lake is heated causing evaporation of water moist air from the sea is forced to ascend up a hill/mountains side forced ascent leads to cooling of air the moisture in the air condenses forming clouds rainfall mainly on the windward side of the hill/mountain descending air warms up the leeward side of the mountain (c) - frequent outbreak of bush fires - human activities due to the increasing population encroachment on grasslands is a common feature replacing them with farms and settlement - frequent droughts destroys grass degenerating vegetation to arid semi-arid type - domestic and wild animals overgraze causing stunted growth of grass while clearing some of it - pests such as army worms and locusts destroy grass 3 x 2=6 2 (d) (i) - To show extend of the district - To show the routes to be followed during the field study - To show the distribution of vegetation in the district - To show the variation of the elements of climate within the district within the district - To help estimate the distances to be covered during the study Accept any other relevant answer Max 3. (ii) - random systematic stratified (iii) - it would save on time - it would focus on the relevant areas - it would be less expensive - allows for detailed study - reduces bias - a district is too large to be covered in totality (iv) - drawing sketch maps - taking photographs - note taking labelling samples tabulating tape recording tallying - 8. (a) i) Aridity is the state of land being deficient of moisture leading to scanty vegetation while desertification is the steady encroachment of barren land into formerly productive agricultural land ii) Sandy/erg Stony/reg Rocky/hamanda (b) - Presence of loose/dry sand which is easily carried by wind - Strong storm/winds erode and carry away a lot of materials - Absence of vegetation cover to break wind force - Flat terrain/absence of obstacles to break wind force/speed (c) - Deflation – the loose dry materials are lifted to the air by wind force and are carried away - Abrasion – the materials carried by wind are used to grind scrap and polish the desert rock surface - Attrition – materials carried by wind hit and rub against each other and break into smaller pieces (d) i) Barchans Seif dunes/longitudinal dunes Transverse dunes/lateral dunes - 3mks ii) - Desert wind carry loess unconsolidated materials in suspension On reaching the wetter areas the suspended materials are deposited in large quantities as they are washed down from the air by the rain Over a long period of time thick layers of fine dust are compacted forming sedimentary rocks - The rocks are then weathered giving rise to deep fertile soils Max 4 mks (e) (i) - Inselbergs - Messas and buttes - Gorges - Wadis - Pediments/ pediplains (ii) - Scotching heat/sun burn - Attack from wild animals e.g. snake bites - Fatigue/sickness 2mks 9. (a) - Normal fault - Reverse fault - Shear/tear fault - Anticlinal faults 4mks (b) - Vertical faulting across a river may cause waterfall/river rejuvenation - Rift Mfaulting in an enclosed area may lead to formation of a lake if rivers drain into the basin - Some rivers flow along fault lines/fault-guided drainages - Uplifting of landscape which lead to faulting may cause rivers to reverse their direction of flow - Rivers may disappear into the ground through a fault line k 3 x 2=6 (c)(i) s - Steep escarpment discourage the construction of transport lines - The distribution of transport facilities is greater on the gentle slopes on the floor of the rift valley - Faults disrupt transport lines (ii) - The rain shadow effect causes low rainfall – discourages agriculture - SomeM rift valley lakes provide water for irrigation a - Faulting causes thin soil on the steep slopes thus discouraging agriculture - There is an accumulation of deep fertile soil down the slope (d) (i) - Relief rainfall is experienced in the direction of rain – bearing winds/windward side - A rainshadow effect is experienced on the opposite side of the mountain/leeward side which lead to aridity - A microclimate comes about as a result of the raised relief thus lowering the temperatures compared to the temps of the surrounding lowlands (ii) - Causes disjointing of land which leads to the disruption of communication lines, water sewerage or pipelines - ‘block mountains may cause the reverse of drainage - Faulting may lead to destruction of life and property due to sinking of land - Faulting features attract tourists who bring in foreign exchange - Hot springs and geysers can be harnessed for geothermal power 3 (e) - Symmetrical folds are folds formed by compression forces of equal magnitude which are weak to moderate in the strength causing rocks to bend evenly - Asymmetrical folds are folds that result from unequal compressional forces acting on the crustal rocks. One of the forces is stronger than the other resulting in a limb steeper than the other 10. (a) – weathering is the breaking disintegration and decomposition of rocks on or below the earth’s surface in situ while mass wasting is the movement of weathered material down the slope under the influence of gravity 2mks (b) (i) - Exfoliation - Granular disintegration - Slaking - Frost action/frost shattering - Pressure release/unloading - Crystal growth 2x1=2mks ii) - Carbonation - Hydration - Oxidation - Hydrolysis - Solution 2x1=2mks (c) (i) - Climate (d) - During the day , the rock surface is heated up rapidly and expands and at night it cools and contracts - This causes strain between the inner and outer layers of the rocks - With time the outer shell the outer shell develops cracks and peels off - This leaves the smooth rounded mass of 2 srock called an exfoliation dome (e) Three effects of mass wasting on the environment - It leads to formation of derelict land - Materials from landslides may create a barrier across a river valley leading to formation of a lake - Landslides may cause rivers to change their causes reducing the volume of water downstream - Landslides cause damage to property when materials cover homes/farms - Mass wasting e.g. rock fall lead to loss of life when people or animals are buried under large quantities of rock wastes - Mass wasting may create tourist attraction sceneries - Mass wasting accelerates soil erosion due to loosening of top soil - Mass wasting may lead to deposition of fertile soils down slope which promote agriculture - Relief/topography - Nature of rocks - Animals 4x1=4mks (ii) - Plant roots grow deep into the ground and open up joints - Plants decay releasing organic acids that accelerate rate of weathering - Plants like algae and lichens cover the surface of the rocks keeping them moist thereby facilitating chemical weathering 2 4