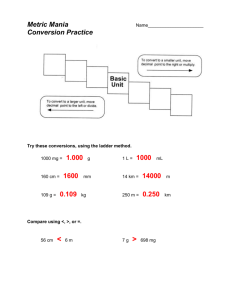
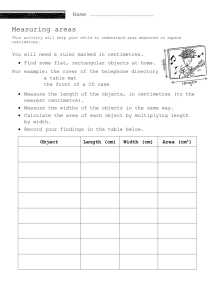
Measurement 1

Measurement Part One
Systems of Measurement
Every day we read or hear numbers that relate to the world around us. These numbers are often descriptions of things. For example, a common object like a car can be described using numbers in many ways:
How far has the car traveled?
How old is the car?
How much is the car worth?
How much does the car weigh?
How hot or cold is the car right now?
124,349 kilometres
6 years
$7,225
4,700 pounds
21ºC
Whenever we describe things using numbers, we are using measurement. Often measurement can be done in more than one way. For example, the age of the car can be measured using years or months.
DESCRIPTION QUALITY BEING
MEASURED
MEASURED
AMOUNT
ALTERNATIVE
AMOUNT
How far has the car traveled?
How old is the car?
Distance
Time
124,349 kilometres 77,718 miles
6 years 72 months
How much is the car worth? Value $7,225
722,500¢
How much does the car weigh?
How hot or cold is the car?
Weight (or mass)
Temperature
4,700 pounds
21º Celsius
2136 kilograms
70º Fahrenheit
Usually, one way of measuring is the most common for a certain situation. The age of person is given in years, unless the person is very young, and then months or days would be used. The weight of a person in this country is usually given in pounds, but in many other countries people use kilograms. We often need to understand the situation in order to know what type of measurement to use.
We sometimes talk about using the Metric System of Measurement and the Imperial System of
Measurement. Canada used the Imperial System until the early 1970’s, but now we use mainly the Metric System. Common exceptions to using metric are the weight of a person (usually measured in pounds) and height of a person (usually measured in feet and inches).
1
Types and Units of Measurement
The chart below shows the units that are typically used for various types of measurement in
Canada and some common instruments used for measuring. This list is not complete.
Units System Measuring instrument Type
Distance kilometers metres centimeters feet and inches metric metric metric
Imperial car odometer carpenter’s measuring tape ruler ruler or tape
Time years, months, days hours, minutes, seconds both both calendar clock, stopwatch
Speed kilometres per hour metres per second litres and millilitres cups metric metric metric
Imperial car speedometer measuring cup measuring cup
Volume
Mass or weight
Value
Temperature kilograms pounds dollars and cents degrees Celsius metric
Imperial both metric grocery store scale bathroom scale usually counted manually thermometer
2
Distance
This ruler has both metric and Imperial scales. The top scale uses the centimetre as the unit of measurement, and the bottom scale uses the inch.
The left arrow above shows a distance of one centimetre from the 0 mark and the other arrow shows a distance of 6 centimetres from 0. One centimetre is about the width of a person’s baby finger.
Each centimetre (cm) is divided into 10 parts called millimetres (mm). There are 10 millimetres in 1 centimetre. One millimetre is about the width of a pencil lead.
The length of the entire pencil shown is 8 centimetres. Since each centimetre contains 10 millimetres, the length of the pencil can also be written as 80 millimetres.
The length of the nail below is 14.7 cm or 147 mm.
Notice that if we multiply the number of centimetres by 10 we get the number of millimetres. If we divide the number of mm by 10 we get the number of cm.
3
Measurement Practice
Measure the length of each of the following objects using a ruler and fill in the blanks with the correct numbers.
_____ cm _____ mm
_____ cm
_____ cm
_____ cm
_____ cm
_____ mm
_____ mm
_____ mm
_____ mm
4
Deca
Hecto
Kilo
Distance Units in the Metric System
Find a metre stick in your classroom and examine it. The stick is one metre long.
How many centimetres are on the stick? (1 cm is about the width of a small finger)
How many millimetres are on the stick? (1 mm is about the width of a pencil lead)
______
______
How many decimetres are on the stick? (1 decimetre has 10 centimetres and is about the width of a person’s hand including the thumb)
You should be able to see that the metre stick has the following lengths:
1 metre = 10 decimetres = 100 centimetres = 1000 millimetres
The units can be written as follows:
______
1 m = 10 dm = 100 cm = 1000 mm
The names of the units in metric are made up of the word “metre” and a prefix. Each prefix means a particular value compared to the metre, which is the base unit.
Prefix Meaning
Milli + metre = millimetre (mm)
1
1000
or 0.001 of a metre
Centi + metre = centimetre (cm)
1
100
or 0.01 of a metre
Deci + metre = decimetre (dm)
1
10
or 0.1 of a metre
+
+
+ metre metre metre
=
=
= metre (m) decametre (dam) hectometre (hm) kilometre (km)
1 metre
10 metres
100 metres
1000 metres
5
Converting Distance Measurements Within the Metric System
To help you change a value from one metric unit of measurement to another, the following
Metric Staircase is useful.
X 10
X 10 kilo (k)
X 10 kilometre hecto (h)
X 10 hectometre deca (da)
X 10 decametre
Base Unit X 10 metre deci (d) decimetre centi (c) centimetre milli (m) millimetre
Kilometre, at the top, is the largest unit on the staircase. Millimetre, at the bottom, is the smallest. Because kilometres are so large compared to millimetres, it takes one million millimetres to equal a single kilometre.
1 km = 1,000,000 mm
Each step down is a multiplication by 10. As you know, multiplying by 10 is simply moving the decimal one space to the right.
1 km = 10 hm = 100 dam = 1000 m = 10,000 dm = 100,000 cm = 1,000,000 mm
Examples:
3 km = 30 hm = 300 dam = 3000 m = 30,000 dm = 300,000 cm = 3,000,000 mm
12 km = 120 hm = 1200 dam = 12,000 m = 120,000 dm = 1,200,000 cm = 12,000,000 mm
0.002 km = 0.02 hm = 0.2 dam = 2 m = 20 dm = 200 cm = 2000 mm
Example: Change 5 hectometres into metres. 5 hm = ??? m
Solution: Starting at hectometres, how many steps do you take to get to metres? Two steps to the right (down the stairs) means to multiply by 10 twice:
5 hm = 50 dam = 500 m
6
Example: Change 0.54 kilometres into decimetres. 0.54 km = ??? dm
Solution: Starting at kilometers, how many steps do you take to get to decimetres? Four steps down means to multiply by 10 four times:
0.54 km = 5.4 hm = 54 dam = 540 m = 5400 dm
Example: How many decimetres are in 3.052 decametres?
Solution: 3.052 dam = ??? dm
Starting at decametres, move two steps to the right. Because you moved two steps to the right, simply move the decimal point two places to the right.
3.052 dam = 305.2 dm
To change a smaller unit into a larger unit, start at the smaller unit and keep dividing by 10 until you reach the larger unit. As you know, the shortcut for dividing by 10 is to move the decimal point one place to the left.
÷ 10
÷ 10 kilo (k)
÷ 10 kilometre hecto (h)
÷ 10 hectometre deca (da)
÷ 10 decametre Base Unit
÷ 10 metre deci (d) decimetre centi (c) centimetre milli (m) millimetre
For example, to change 10 millimetres into metres, begin at mm and move left (up) three steps.
10 mm = 1 cm = 0.1 dm = 0.01 m
Examples: 43 cm = ??? hm
Solution: 43 cm = 4.3 dm = 0.43 m = 0.043 dam = 0.0043 hm
Because hectometres is four steps to the left of centimetres, the shortcut is to move the decimal four places to the left.
7
Practice Converting Metric Distances
Remember: To change from a larger unit to a smaller unit, multiply. To change from a smaller unit to a larger unit, divide.
Moving to the right on the staircase means you need to move the decimal to the right.
Moving to the left on the staircase means you need to move the decimal to the left.
Changing from a smaller unit to larger unit. Changing from a larger unit to a smaller unit.
1.
4.5 km = __________ hm
2.
3.
63.2 dam = __________m
74.02 hm = __________cm
13.
14.
15.
78 cm = __________dm
8579 mm = __________hm
41 hm = __________km
16. 0.5 dam = __________hm
7.
8.
4.
5.
6.
9 km = __________m
0.24 cm = __________mm
0.5 dm = __________cm
4.55 m = __________mm
98 m = __________dm
9.
0904 dm = __________mm
10.
77 dam = __________dm
11.
0.0002 cm = __________mm
12.
0.005 hm = __________ cm
Convert the following.
1.
3855 cm = __________hm
2.
6 dm = __________mm
3.
354 mm = __________m
4.
0.25 km = __________hm
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
5.
6.
7.
8.
0.003 m = __________dam
4889 cm = __________hm
780 dm = __________km
15.2 dam = __________km
5.6 cm = __________m
0.88 mm = __________dm
4899.02 mm = __________km
7 dam = __________km
0.05 dam = __________dm
97.05 m = __________mm
47 km = __________dam
3.2 hm = __________km
8
Complete the following
1. 7cm 4mm = ___________mm
2. 5m 9cm = _____________cm
3. 4m 8dm 2cm = _________cm
4.
5.
3km 2m = ________km
4km 17m 52cm = ______m
9