Emotion - Monona Grove School District
advertisement
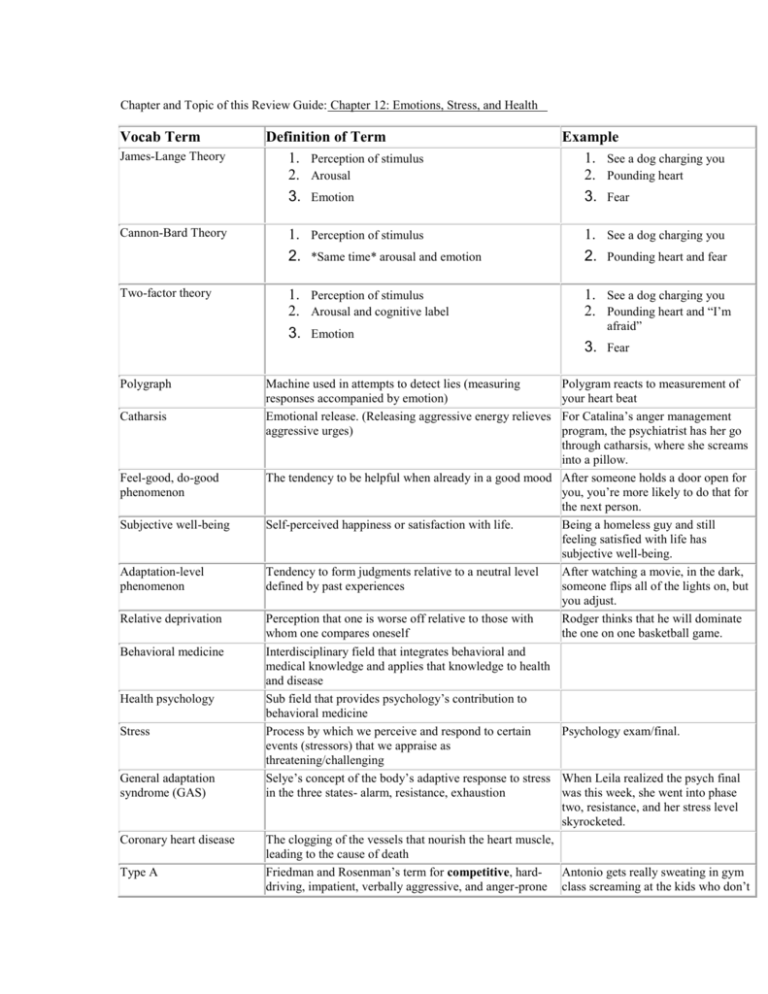
Chapter and Topic of this Review Guide: Chapter 12: Emotions, Stress, and Health Vocab Term James-Lange Theory Definition of Term 1. Perception of stimulus 2. Arousal 3. Emotion Example 1. See a dog charging you 2. Pounding heart 3. Fear Cannon-Bard Theory 1. Perception of stimulus 2. *Same time* arousal and emotion 1. See a dog charging you 2. Pounding heart and fear Two-factor theory 1. Perception of stimulus 2. Arousal and cognitive label 3. Emotion 1. See a dog charging you 2. Pounding heart and “I’m Polygraph Catharsis Feel-good, do-good phenomenon Subjective well-being Adaptation-level phenomenon Relative deprivation Behavioral medicine Health psychology Stress General adaptation syndrome (GAS) Coronary heart disease Type A Machine used in attempts to detect lies (measuring responses accompanied by emotion) Emotional release. (Releasing aggressive energy relieves aggressive urges) afraid” 3. Fear Polygram reacts to measurement of your heart beat For Catalina’s anger management program, the psychiatrist has her go through catharsis, where she screams into a pillow. The tendency to be helpful when already in a good mood After someone holds a door open for you, you’re more likely to do that for the next person. Self-perceived happiness or satisfaction with life. Being a homeless guy and still feeling satisfied with life has subjective well-being. Tendency to form judgments relative to a neutral level After watching a movie, in the dark, defined by past experiences someone flips all of the lights on, but you adjust. Perception that one is worse off relative to those with Rodger thinks that he will dominate whom one compares oneself the one on one basketball game. Interdisciplinary field that integrates behavioral and medical knowledge and applies that knowledge to health and disease Sub field that provides psychology’s contribution to behavioral medicine Process by which we perceive and respond to certain Psychology exam/final. events (stressors) that we appraise as threatening/challenging Selye’s concept of the body’s adaptive response to stress When Leila realized the psych final in the three states- alarm, resistance, exhaustion was this week, she went into phase two, resistance, and her stress level skyrocketed. The clogging of the vessels that nourish the heart muscle, leading to the cause of death Friedman and Rosenman’s term for competitive, hardAntonio gets really sweating in gym driving, impatient, verbally aggressive, and anger-prone class screaming at the kids who don’t Type B people catch the ball and strives for the 4.0. Friedman and Rosenman’s term for easygoing and relaxed people Barbra is the people who is calm in gym and would much rather play croquet. Paula got a headache just thinking about the hard work she needs to put in to get an A on the psych final. Psychophysiological illness “Mind-body” illness, any stress-related physical illness (ex. Hypertension) Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI) Lymphocytes Coping Problem-focused coping Emotion-focused coping Aerobic exercise Biofeedback Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) Study of how psychological, neural, and endocrine processes together affect the immune system and resulting health Two types of white blood cells that are part of the body’s immune system (B form bone marrow and release antibodies; T form in the thymus and attack viruses/cancer/ etc.) Alleviating stress using emotional, cognitive, or behavioral methods Attempting to alleviate stress directly by changing the stressor or the way we interact with the stressor Charlie’s way of coping with stress is taking a jog. Patricia becomes so stressed when her boss calls her into his office. Patricia asked him if rather he could call her on her phone rather than shout across the office. Attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a Patricia completely avoids walking stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one’s by her boss’s office and when he asks stress reaction runs to the bathroom hoping he will forget. Sustained exercise the increases heart and lung fitness Walking, jogging, stair-climbers, etc. (may alleviate depression and anxiety) A system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension Unproven health care treatments intended to supplement or serve as alternatives to conventional medicine, and which typically are not widely taught in medical schools, used in hospitals, or reimbursed by insurance companies. When research shows a therapy to be safe and effective is usually becomes part of accepted medical practice. Name of Important Person What this person is known for Impact on Psychology Hans Selye Stress research General Adaption Syndrome Stage 1: alarm reaction Stage 2: resistance Walter Cannon Stress research Stage 3: exhaustion Stress incidents trigger epinephrine and norepinephrine











